15
Dec
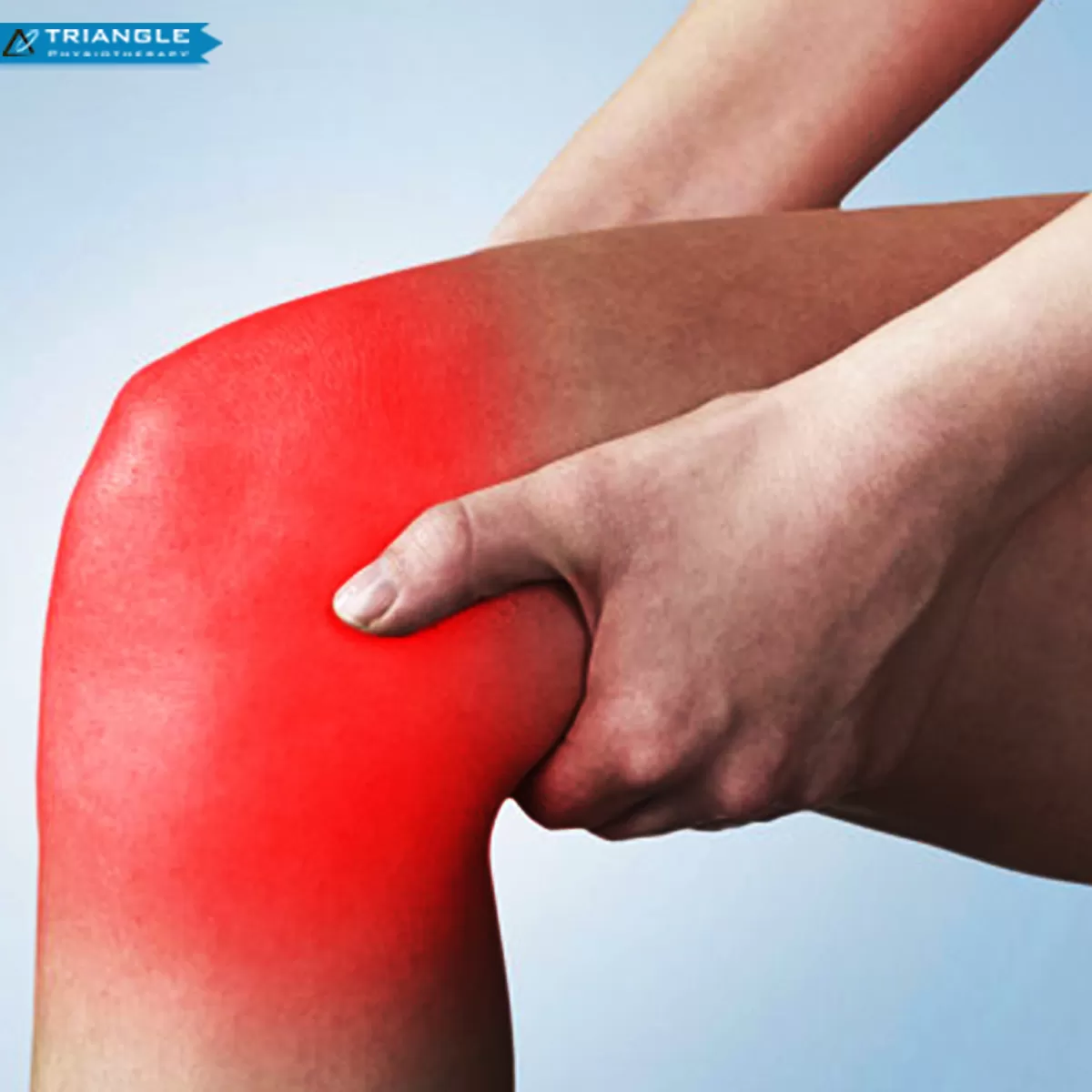
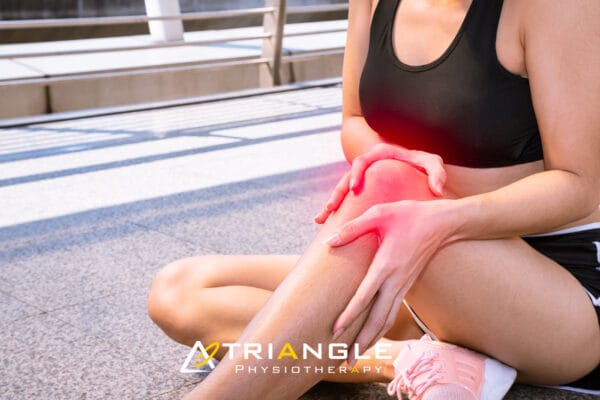
A knee sprain is an injury of the ligaments; tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect the bones of the upper and lower leg at the knee joint. One of the main forms of knee sprain is in the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ACL and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) bridge the inside of the knee joint, forming an, “X” pattern that stabilizes the knee against front-to-back and back-to-front forces.
There are certain movements in the knee that cause a sprain in the ACL such as:
 It is suggested that when one knee ligament suffers a sprain, there is a good chance that the other parts of the knee may also be injured, most commonly the ACL. Knee sprains are very common. ACL sprains tend to cause more significant symptoms compared to MCL injuries.
It is suggested that when one knee ligament suffers a sprain, there is a good chance that the other parts of the knee may also be injured, most commonly the ACL. Knee sprains are very common. ACL sprains tend to cause more significant symptoms compared to MCL injuries.
- a sudden stop;
- a twist,
- pivot, or change in direction at the joint;
- extreme over-straightening (hyperextension);
- or a direct impact to the outside of the knee or lower leg.
 It is suggested that when one knee ligament suffers a sprain, there is a good chance that the other parts of the knee may also be injured, most commonly the ACL. Knee sprains are very common. ACL sprains tend to cause more significant symptoms compared to MCL injuries.
It is suggested that when one knee ligament suffers a sprain, there is a good chance that the other parts of the knee may also be injured, most commonly the ACL. Knee sprains are very common. ACL sprains tend to cause more significant symptoms compared to MCL injuries.
The most frequent signs of an ACL sprain are:
- A pop heard or felt inside your knee at the time of injury
- Significant knee swelling within a few hours after injury
- Severe knee pain that prevents you from continued participation in your sport
- Black-and-blue discoloration around the knee
- Knee instability- the feeling that your knee will buckle or give out
Treatment of an ACL Sprain
A physiotherapist will examine both knees, comparing the injured knee to the uninjured one. During this exam, the physiotherapist will check your injured knee for signs of swelling, deformity, tenderness, fluid inside the knee joint, and discoloration. If the patient does not have too much pain and swelling, a physiotherapist will then evaluate the knee’s range of motion and will pull against the ligaments to check their strength. During the exam, the patient will have to bend their knee and the physiotherapist will gently pull forward or push backward on their lower leg where it meets the knee. Based on the results of the patient’s exam, diagnostic tests may need to be performed to further evaluate the condition of the patient’s knee. These tests may include standard X-rays to check for ligament separation from bone or fracture. Tests may also include an MRI scan or a camera–guided knee surgery (arthroscopy). The expected duration of recovery depends on the severity of the patient’s knee sprain, their rehabilitation program, and what type of sports the patients play. In general, milder sprains heal within 2-4 weeks, whereas other types may take 4-12 months.There are many ways of preventing ACL knee sprain, to help sports related injuries you can:
- Warm up and stretch before participating in athletic activities
- Do exercises that strengthen the leg muscles around the knee, especially the quadriceps.
- Avoid sudden increases in the intensity of a training program. Do not push too hard or too fast. Gradually increase intensity.
- Wear comfortable, supportive shoes that fit your feet and fit your sport
- Knee becomes very painful or swollen
- Cannot bear weight
- Feels as if it will buckle or give out.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
08
Dec
What is ALS?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the most common type of adult-onset motor neuron disease. Neurological disorders are characterized primarily by progressive degeneration and loss of motor neurons. ALS involves upper and lower motor neurons and presents as an idiopathic, progressive degeneration of anterior horn cells and their associated neurons, resulting in progressive muscle weakness, atrophy, and fasciculations.What are the symptoms of ALS?
ALS is a gradual-onset disease. The first initial symptoms of ALS vary from person to person. One person may have trouble with their grip, such as holding a cup or pen, while another person may experience a change in pitch in their voice while speaking. The rate at which ALS develops also varies from person to person, with the mean survival time ranging from three to five years. Although there are cases in which people have lived five, and ten or more years. Onset symptoms can begin in the muscles that control speech and swallowing, or in the hands, arms, legs, or feet. Not all people who suffer from ALS experience the same symptoms as others or the same sequences or patterns of progression. Although, universally progressive muscle weakness and paralysis are experienced.How is ALS diagnosed?
ALS is a somewhat difficult disease to diagnose. There is not one test or procedure to instantly establish the diagnosis of ALS. Through the use of clinical examination, and a series of diagnostic tests, often ruling out other diseases that mimic ALS, that a diagnosis can be established. A comprehensive diagnostic check-list includes most, if not all, of the following procedures:- Electrodiagnostic tests- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve conduction velocity (NCV)
- Blood & Urine studies
- Spinal tap
- X-rays including MRI
- Myleogram of cervical spine
- Muscle and/or nerve biopsy
- A thorough neurological examination
What are the treatments for ALS?
Treatment of ALS can be done with physiotherapy, focusing on stretching and daily range of motion (ROM) exercises. Our physiotherapists at Triangle will focus on the emphasis of energy conservation and teach patients and caregivers methods for performing safe, efficient transfers. They can also provide instruction for strengthening exercise programs. In one study, individualized, moderate-intensity, endurance-type exercises for the trunk and limbs performed 15 minutes twice daily were shown to significantly reduce spasticity as measured by the Ashworth scale. At Triangle, we may have to recommend wheelchairs to anticipate the patient’s future needs. Initially, a lightweight wheelchair should be rented, with future plans to purchase a heavier chair when the patient is no longer able to ambulate. Modifications will be recommended on the basis of the patient’s condition and tolerance for gadgets.Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills