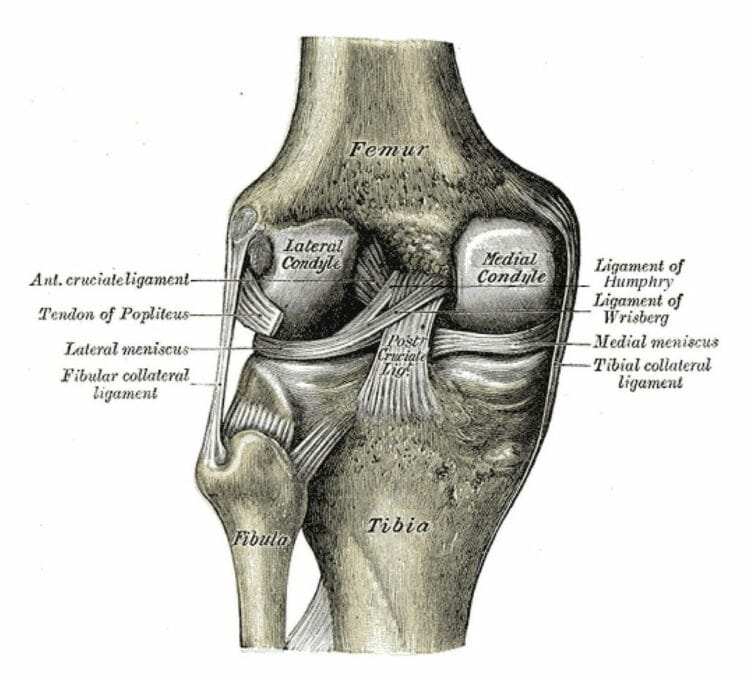
The most common cause of a Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) injury is a direct blow or a force on the outside of the knee causing it to push the knee inward. This may also be caused by a direct blow to the outer side of the leg.
Symptoms of a MCL Injury
- Pain and tenderness along the inner part of the knee
- Swelling on the inner aspect of the knee
- Knee stiffness
- Difficulty weight bearing on the injured knee
- Pain and difficulty walking, sitting down, getting up from a chair, or climbing stairs.
- Locking the knee joint
- Knee instability
MCL Injuries are more common in people who relate to the following:
- Individuals who participate in activities and contact sports that require quick changes in direction and twisting motions, and collision with other players are common such as football, basketball, and hockey
- People with muscle imbalances especially of the quadriceps and hamstrings because this may cause knee instability.
- Younger individuals who participate in sports are prone to MCL injuries
- Women are more susceptible than males due to hormonal and anatomical differences.
- Individuals who have previously injured their knees because it makes them more susceptible to re-injury.
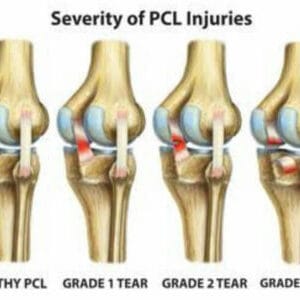
Types of MCL Injury
Grade 1 MCL injury is the least severe form where the ligament is stretched but not torn. Some tenderness and mild pain are felt.
Grade 2 MCL injury involves a partial tear of the ligament. There is some instability in your knee joint. Major pain as well as tenderness on the inside part of the knee. Moderate swelling may be present as well. Difficulty with weight-bearing may be experienced.
This may require bracing and physical therapy, and sometimes even surgery depending on the extent of the injury.
Grade 3 MCL injury is the most severe type where the ligament has been completely torn. Joint instability is very common as well as difficulty weight bearing and walking. This type almost always requires surgery and extensive physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy Treatments for Medial Collateral Ligament injury
- (RICE) – Resting and applying ice packs to help with the swelling, compression with an elastic bandage, and elevation of the leg to reduce swelling
- Pain modalities such as interferential current, TENS, and therapeutic ultrasound.
- Gentle range of motion exercises to help prevent stiffness and maintain mobility of joints
- Strengthening exercises are done as the healing progresses especially for the muscles which help stabilize the knee joint and help prevent recurrence of injuries. These muscles are hamstrings, quadriceps, and hip and calf muscles.
Our More Locations
Physiotherapy Etobicoke | Physiotherapy Oakville | Physiotherapy North York | Physiotherapy Toronto | Physiotherapy Lawrence Park | Physiotherapy Mississauga | Physiotherapy Queens Quay | Physiotherapy Mississauga Erin Mills | Physiotherapy Liberty Village
If you have any type of knee injury, contact us to book an appointment with one of our Physiotherapists today!