[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
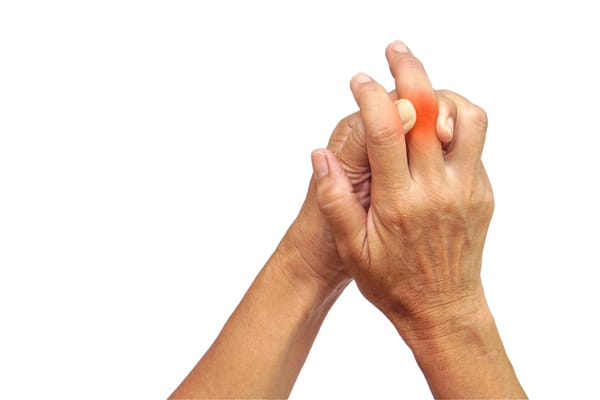
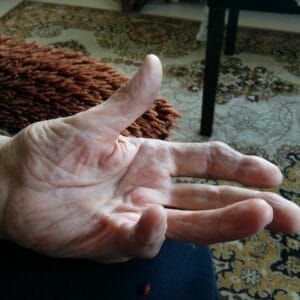
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, particularly the synovium, which lines the joints. This results in inflammation, pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected joints. Over time, RA can also cause damage to cartilage, bones, and other joint structures.
People at most risk for RA
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect people of all ages, but it most commonly begins between the ages of 40 and 60. It is more prevalent in women than men. Certain factors increase the risk of developing RA, including having a family history of the disease, smoking tobacco, and exposure to certain environmental factors like silica or asbestos.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Joint stiffness
- Swelling
- Joint pain
- Fatigue and general weakness
- Joint deformity
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Rheumatologists may order blood tests to detect specific antibodies like rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies, which are often elevated in people with RA. Imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can also help assess joint damage and inflammation.
Common causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown but it is believed that risk for developing RA is increased by the following factors:
- Genetics
- Hormonal changes
- Environmental Triggers
- Smoking
Rheumatoid Arthritis and daily life
Rheumatoid arthritis can have a significant impact on daily life. The symptoms, such as joint pain, stiffness, and fatigue, can make it challenging to perform everyday tasks, including walking, dressing, or gripping objects. RA can also affect one’s ability to work and participate in social activities. However, with proper management, lifestyle adjustments, and support, many people with RA are able to lead active and fulfilling lives.
Physiotherapy Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Range of motion exercises to help improve joint mobility and flexibility and reduce joint stiffness.
- Strengthening exercises to improve muscle strength around the affected joints..
- Joint protection technique to help minimize pain, prevent further joint damage, and preserve joint function.
- Pain management strategies such as TENS, heat or cold therapy, and ultrasound therapy.