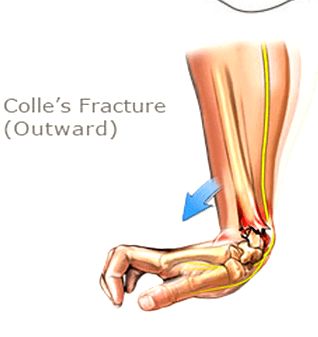
A Colles’ fracture, commonly referred to as a wrist fracture, typically occurs when a person falls onto an outstretched hand. This type of fracture primarily affects the distal radius, the bone located on the thumb side of the wrist. Colles’ fractures are prevalent among older adults, particularly those with osteoporosis, but they can occur at any age. Understanding the nature of this injury, along with effective recovery strategies and preventive measures, is crucial for regaining full functionality of the wrist and minimizing the risk of future injuries.
If you or someone you know has a Colle’s fracture, our physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy can help.
Understanding Recovery
Recovery from a Colles’ fracture generally involves a combination of immobilization, rehabilitation, and lifestyle adjustments. After the fracture is diagnosed—often through X-rays—a healthcare provider may recommend a cast or splint to immobilize the wrist and allow for proper healing. The duration of immobilization can vary, typically lasting between six to eight weeks, depending on the severity of the fracture and the individual’s healing process. Once the cast is removed, the focus shifts to rehabilitation. Recovery times can vary widely, with many patients regaining full function in a few months, while others may take longer. Patience and adherence to a structured recovery plan are essential for optimal healing.
Neuromuscular Exercises post Colle’s Fracture
Neuromuscular exercises are designed to enhance the coordination and communication between the brain and muscles, which is especially important after a wrist injury. These exercises often focus on improving proprioception—the body’s ability to sense its position in space.
1. Wrist and Hand Movements: Start with simple wrist flexion and extension exercises, moving the wrist slowly through its range of motion.
2. Finger Coordination: Practice tapping each finger to the thumb, which helps improve dexterity and coordination.
Incorporating neuromuscular exercises into your recovery routine can significantly aid in regaining strength and functionality.
Mobility Incorporation post Colle’s Fracture
After the initial healing phase, it is crucial to incorporate mobility exercises to restore the full range of motion in the wrist. Gradual stretching and movement help reduce stiffness and enhance circulation.
1. Wrist Circles: Perform wrist circles in both directions to encourage mobility.
2. Tendon Gliding Exercises: These involve moving the fingers and wrist in various positions to promote flexibility and prevent stiffness.
Consistency in these mobility exercises can help ensure a smoother transition back to everyday activities.
Progressive Resistance Exercises
Once mobility is regained, progressive resistance exercises can be introduced to rebuild strength in the wrist and forearm. These exercises should start gently and gradually increase in intensity.
1. Wrist Flexion and Extension with Weights: Using light weights or resistance bands, perform controlled flexion and extension movements.
2. Grip Strengthening: Utilize grip trainers or stress balls to enhance grip strength, which is essential for overall hand function. By progressively increasing resistance, you can strengthen the wrist and surrounding muscles, reducing the likelihood of future injuries.
Prevention
Preventing future Colles’ fractures involves both lifestyle modifications and awareness. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Fall Prevention: Improve home safety by removing tripping hazards, installing handrails, and ensuring adequate lighting.
2. Bone Health: Engage in weight-bearing exercises and maintain a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone density.
3. Regular Check-ups: Especially for older adults, regular bone density tests and discussions with healthcare providers about osteoporosis can be critical.
By focusing on prevention, you can significantly lower the risk of future wrist fractures.
FAQs
1. What are the symptoms of a Colles’ fracture?
Symptoms typically include pain and swelling in the wrist, a visible deformity (such as a “dinner fork” appearance), and difficulty moving the wrist or fingers.
2. How long does it take to recover from a Colles’ fracture?
Recovery can vary, but most people see significant improvement within 6 to 12 weeks. Full recovery may take longer, especially for older adults.
3. Can I prevent a Colles’ fracture?
Yes, by improving home safety, maintaining bone health through diet and exercise, and being mindful of your balance and stability, you can reduce your risk of a Colles’ fracture.
4. Are there any long-term effects after recovery?
Some individuals may experience stiffness, reduced range of motion, or chronic pain, particularly if the fracture was severe.
Engaging in rehabilitation exercises can help mitigate these issues. — Understanding and effectively managing a Colles’ fracture is key to ensuring a smooth recovery and maintaining wrist health. By following a comprehensive rehabilitation plan and taking preventive measures, individuals can regain their strength and enjoy a more active lifestyle.




