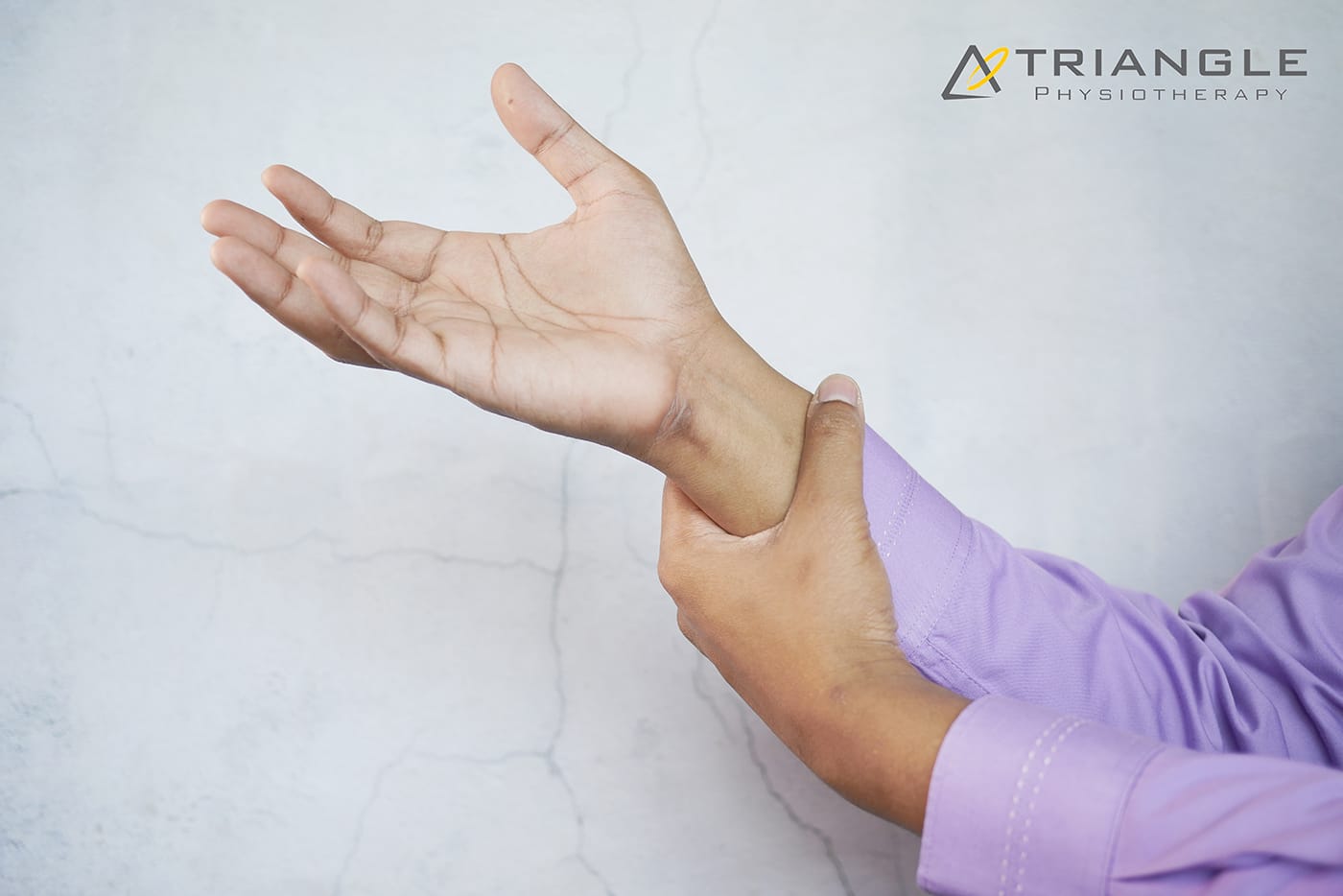
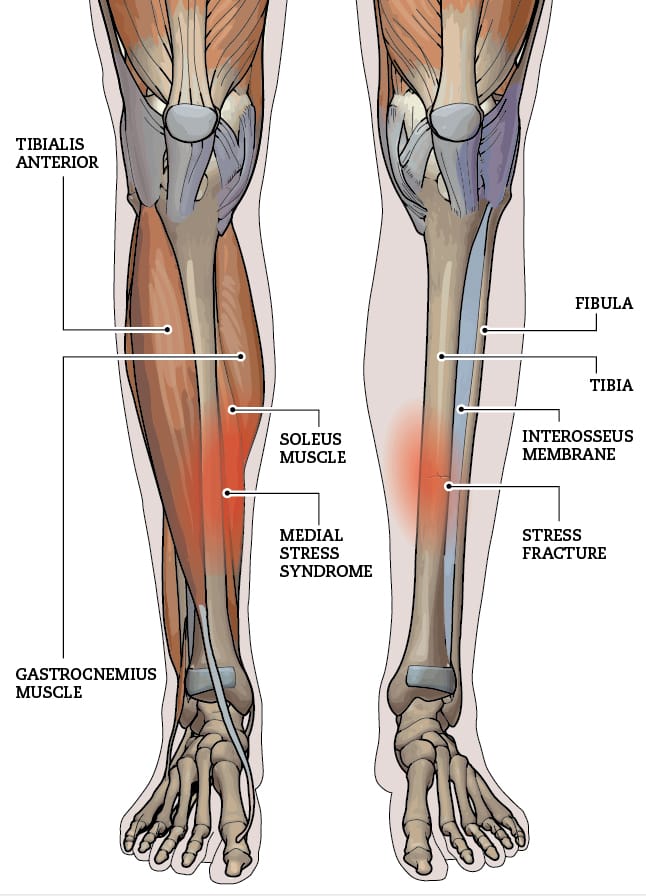
A Colles’ fracture, commonly referred to as a wrist fracture, typically occurs when a person falls onto an outstretched hand. This type of fracture primarily affects the distal radius, the bone located on the thumb side of the wrist. Colles’ fractures are prevalent among older adults, particularly those with osteoporosis, but they can occur at any age. Understanding the nature of this injury, along with effective recovery strategies and preventive measures, is crucial for regaining full functionality of the wrist and minimizing the risk of future injuries.
If you or someone you know has a Colle’s fracture, our physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy can help.
Understanding Recovery
Recovery from a Colles’ fracture generally involves a combination of immobilization, rehabilitation, and lifestyle adjustments. After the fracture is diagnosed—often through X-rays—a healthcare provider may recommend a cast or splint to immobilize the wrist and allow for proper healing. The duration of immobilization can vary, typically lasting between six to eight weeks, depending on the severity of the fracture and the individual’s healing process. Once the cast is removed, the focus shifts to rehabilitation. Recovery times can vary widely, with many patients regaining full function in a few months, while others may take longer. Patience and adherence to a structured recovery plan are essential for optimal healing.
Neuromuscular Exercises post Colle’s Fracture
Neuromuscular exercises are designed to enhance the coordination and communication between the brain and muscles, which is especially important after a wrist injury. These exercises often focus on improving proprioception—the body’s ability to sense its position in space.
1. Wrist and Hand Movements: Start with simple wrist flexion and extension exercises, moving the wrist slowly through its range of motion.
2. Finger Coordination: Practice tapping each finger to the thumb, which helps improve dexterity and coordination.
Incorporating neuromuscular exercises into your recovery routine can significantly aid in regaining strength and functionality.
Mobility Incorporation post Colle’s Fracture
After the initial healing phase, it is crucial to incorporate mobility exercises to restore the full range of motion in the wrist. Gradual stretching and movement help reduce stiffness and enhance circulation.
1. Wrist Circles: Perform wrist circles in both directions to encourage mobility.
2. Tendon Gliding Exercises: These involve moving the fingers and wrist in various positions to promote flexibility and prevent stiffness.
Consistency in these mobility exercises can help ensure a smoother transition back to everyday activities.
Progressive Resistance Exercises
Once mobility is regained, progressive resistance exercises can be introduced to rebuild strength in the wrist and forearm. These exercises should start gently and gradually increase in intensity.
1. Wrist Flexion and Extension with Weights: Using light weights or resistance bands, perform controlled flexion and extension movements.
2. Grip Strengthening: Utilize grip trainers or stress balls to enhance grip strength, which is essential for overall hand function. By progressively increasing resistance, you can strengthen the wrist and surrounding muscles, reducing the likelihood of future injuries.
Prevention
Preventing future Colles’ fractures involves both lifestyle modifications and awareness. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Fall Prevention: Improve home safety by removing tripping hazards, installing handrails, and ensuring adequate lighting.
2. Bone Health: Engage in weight-bearing exercises and maintain a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone density.
3. Regular Check-ups: Especially for older adults, regular bone density tests and discussions with healthcare providers about osteoporosis can be critical.
By focusing on prevention, you can significantly lower the risk of future wrist fractures.
FAQs
1. What are the symptoms of a Colles’ fracture?
Symptoms typically include pain and swelling in the wrist, a visible deformity (such as a “dinner fork” appearance), and difficulty moving the wrist or fingers.
2. How long does it take to recover from a Colles’ fracture?
Recovery can vary, but most people see significant improvement within 6 to 12 weeks. Full recovery may take longer, especially for older adults.
3. Can I prevent a Colles’ fracture?
Yes, by improving home safety, maintaining bone health through diet and exercise, and being mindful of your balance and stability, you can reduce your risk of a Colles’ fracture.
4. Are there any long-term effects after recovery?
Some individuals may experience stiffness, reduced range of motion, or chronic pain, particularly if the fracture was severe.
Engaging in rehabilitation exercises can help mitigate these issues. — Understanding and effectively managing a Colles’ fracture is key to ensuring a smooth recovery and maintaining wrist health. By following a comprehensive rehabilitation plan and taking preventive measures, individuals can regain their strength and enjoy a more active lifestyle.
Tibial stress fractures are a common injury among runners, often arising from overuse and repetitive impact on the lower legs. These small discontinuous fractures in the tibia can lead to significant pain and time spent off the tracks, making understanding, recovery, and prevention crucial for athletes. Let’s explore the nature of tibial stress fractures, how to recover effectively, and strategies to prevent future injuries.
Our physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy have the expertise and experience to help with injuries such as these.
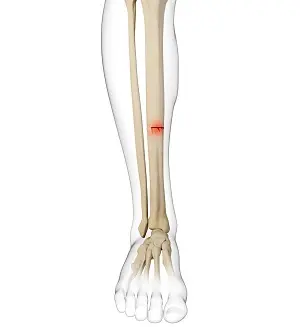
FAQs on Tibial Stress Fractures
Q: What are the symptoms of a tibial stress fracture?
A: Common symptoms include localized pain along the shin, swelling, and tenderness that worsens with activity.
Q: How long does it take to recover from a tibial stress fracture?
A: Recovery time can vary, typically ranging from 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the severity of the fracture and adherence to a proper recovery plan.
Q: Can I still run with a tibial stress fracture?
A: It’s essential to avoid running until cleared by a healthcare professional, as continuing to run can worsen the injury.
Q: What type of shoes should I wear to prevent tibial stress fractures?
A: Look for shoes that offer good cushioning and support, tailored to your foot type and running style.
Q: Are there any specific exercises I should avoid during recovery?
A: High-impact exercises should be avoided initially; focus on low-impact activities until fully recovered. By understanding tibial stress fractures and employing the right recovery and prevention strategies, runners can bounce back stronger and continue enjoying their sport safely.
Understanding Recovery of Tibial Stress Fractures
Recovering from a tibial stress fracture involves a multifaceted approach that emphasizes rest and gradual rehabilitation. Initially, it’s essential to reduce weight-bearing activities to allow the bone to heal properly. Depending on the severity of the fracture, this may require crutches or a walking boot. Once the initial pain subsides, a structured recovery plan should include a gradual return to activity, typically guided by a Physiotherapist. Monitoring pain levels during this phase is critical; any increase in pain may indicate that you are pushing too hard, too soon.
Neuromuscular Exercises for Tibial Stress Fractures
Neuromuscular exercises play a vital role in recovery by enhancing coordination, balance, and muscle strength. These exercises can help to correct any biomechanical issues that may have contributed to the injury. Examples include: Balance training: Improve balance and strengthen stabilizing muscles. Agility drills- Help enhance neuromuscular control and prevent future injuries. Proprioception training- Activities like balance boards can improve body awareness and stability. Incorporating these exercises into your routine can significantly aid in the healing process and prepare your body for a return to running.
Mobility Incorporation
Restoring mobility is another critical aspect of recovery. Restricted movement can lead to stiffness and further complications. Gentle stretching and mobility exercises can help maintain flexibility in the surrounding muscles and joints. Key mobility exercises can include working on key muscles like Calf, Hip flexor mobility to name a few. Regularly integrating these mobility exercises will not only aid in recovery but also improve overall performance in the long run.
Progressive Resistance Exercises
Once you are pain-free and have regained some mobility, incorporating progressive resistance exercises is essential for rebuilding strength. This phase focuses on strengthening the muscles surrounding the tibia to provide better support and prevent future stress fractures. Examples include strengthening the calves and improving ankle stability, build strength in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Start with light resistance and gradually increase intensity as your strength improves, always prioritizing proper form to prevent re-injury.
Prevention
Preventing tibial stress fractures is all about maintaining a balanced training regimen. Pay attention to warning signs such as persistent pain or fatigue and adjust your training accordingly. Integrating a proper rehab plan under the supervision of a physiotherapist along with proper relaxation techniques provided by Massage therapist can significantly reduce the risk of developing a tibial stress fracture and maintain your running routine.
Suffered a Tibial Stress Fracture Injury? Book an appointment with us to get on the road to recovery.
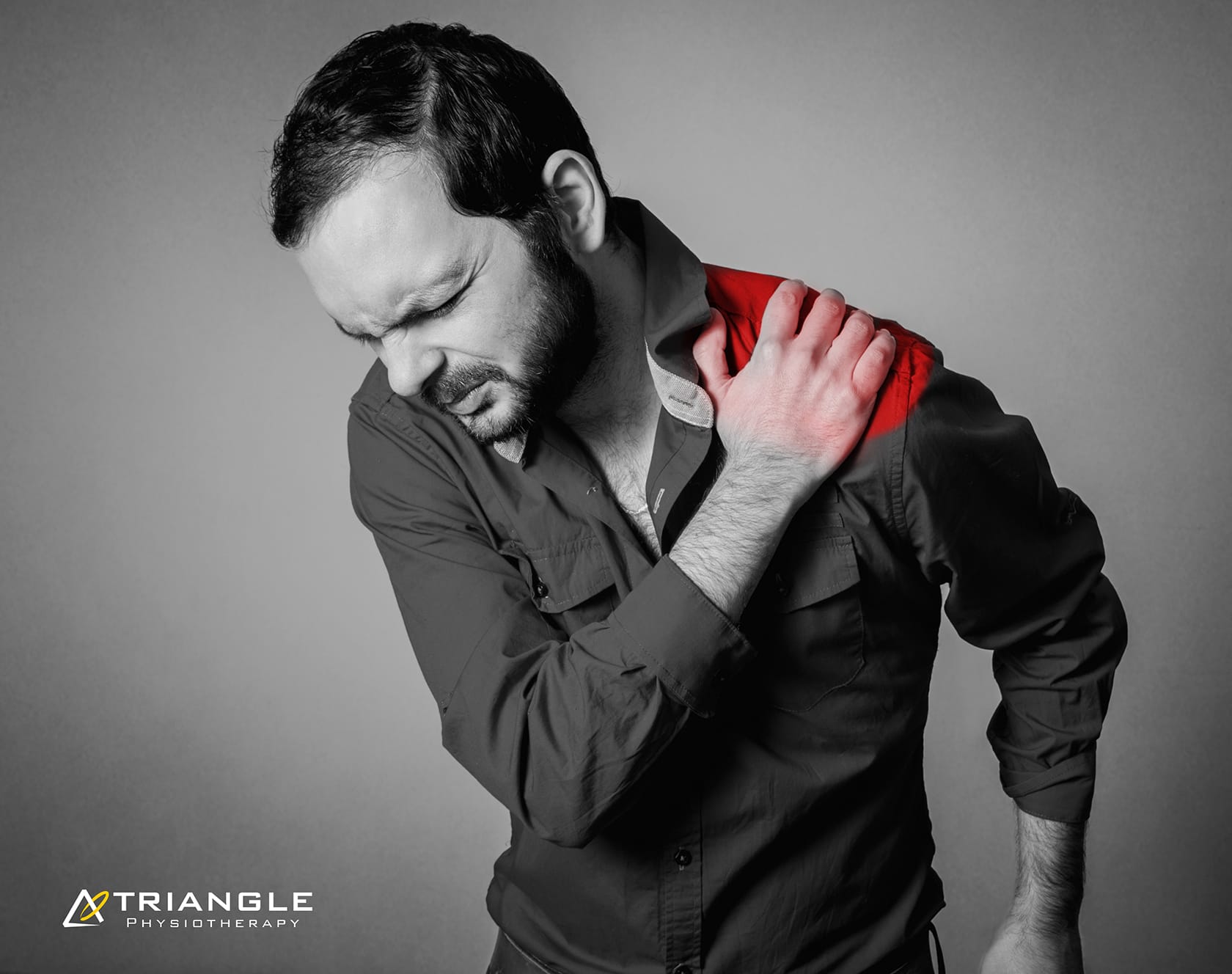
Clavicular fractures, commonly known as broken collarbones, are prevalent injuries, especially among athletes and those engaged in physical activities. This type of fracture typically occurs due to falls, direct trauma to collarbone or shoulder, or collisions. Understanding the clavicular fractures in detail, their recovery process, and preventive measures can help individuals better manage their healing journey and minimize the risk of future injuries.
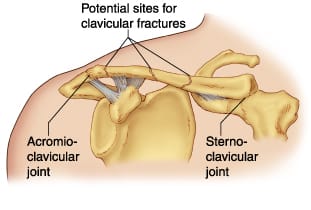
Schedule an appointment with one of the physiotherapists at one of the 8 locations of Triangle Physiotherapy if you have had a clavicular fracture and are looking to achieve optimal recovery.
What is the recovery timeline for clavicular fractures?
The recovery timeline for a clavicular fracture can vary based on the severity of the break and the individual’s overall health. Generally, non-displaced fractures may heal within 6 to 12 weeks with conservative treatment, including rest, immobilization, and pain management. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, leading to a slightly extended recovery period. During this time, it’s essential to follow medical advice and engage in a structured rehabilitation program under the supervision of a Physiotherapist to restore strength and function to the shoulder.
What type of exercises are beneficial in the rehabilitation Clavicular Fractures?
Neuromuscular Exercises
Neuromuscular exercises play a crucial role in the rehabilitation process. These exercises focus on improving coordination and communication between the nervous system and muscles, which is vital for shoulder recovery. Some forms of improving the neuro-muscle link could be gentle isometric contractions of the shoulder muscles without joint movement, activating the shoulder blade muscles. As healing progresses, activities that involve controlled movements can help enhance muscle activation and prevent stiffness, promoting a smoother transition to more strenuous exercises.
Mobility Incorporation
Incorporating mobility exercises into the rehabilitation program is essential for restoring range of motion in the shoulder. Gentle stretching and mobility drills should begin as soon as cleared by a healthcare professional. Physiotherapist would be the perfect healthcare practitioner that can guide you in terms of muscle activation and rehabilitation. Common exercises include pendulum swings and passive arm movements. These activities not only help to alleviate stiffness but also prepare the shoulder for more demanding functional tasks. Regularly practicing mobility exercises ensures that the joint remains flexible and reduces the risk of future injuries.
Progressive Resistance Exercises
Once the shoulder has regained sufficient mobility and strength, progressive resistance exercises can be introduced. These exercises aim to gradually increase the load on the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint, facilitating strength development and functional recovery. Starting with lightweight resistance bands or dumbbells, individuals can perform exercises focusing on rotator cuff, shoulder stabilizers as well as the scapular muscles. The key is to focus on form and gradually increase resistance as strength improves, avoiding any pain or discomfort.
How can clavicular fractures be prevented?
Preventing clavicular fractures involves a combination of strength training, proper technique, and awareness of one’s surroundings. In order to prevent clavicular fractures, one needs a multidisciplinary approach under the supervision of a Physiotherapist, Chiropractor and a Massage Therapist. Engaging in shoulder-strengthening exercises can improve stability and reduce the likelihood of injuries. Athletes should prioritize learning proper falling techniques to minimize impact during falls or collisions. Additionally, wearing protective gear in high-risk sports can provide an extra layer of safety. Overall, being proactive about shoulder health can significantly decrease the chances of experiencing a clavicular fracture.
Other FAQ’s
FAQs
Q: How can I tell if I have a clavicular fracture?
A: Symptoms may include sharp pain at the site of the injury, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the shoulder. A visible deformity or “bump” over the collarbone may also indicate a fracture.
Q: Do all clavicular fractures require surgery?
A: No, not all fractures require surgery. Non-displaced fractures are often treated conservatively, while displaced fractures or those involving significant displacement may necessitate surgical intervention.
Q: How long will it take to return to normal activities?
A: Recovery times vary but typically range from 6 to 12 weeks for non-displaced fractures. Full recovery and return to sports may take longer, depending on the nature of the fracture and rehabilitation progress.
Q: Are there any long-term effects of a clavicular fracture?
A: Most individuals recover fully without long-term complications. However, some may experience residual pain or reduced strength in the shoulder. Engaging in a comprehensive rehabilitation program can help mitigate these risks.
Q: What should I do if I suspect a clavicular fracture?
A: Seek medical attention immediately. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs. By understanding clavicular fractures and their recovery process, individuals can better navigate their healing journey and take proactive steps to prevent future injuries. Always consult with healthcare professionals to ensure the best outcomes during recovery and rehabilitation.
If you would like to start you post-fracture rehab at Triangle Physiotherapy, contact us today to schedule a physiotherapy appointment.