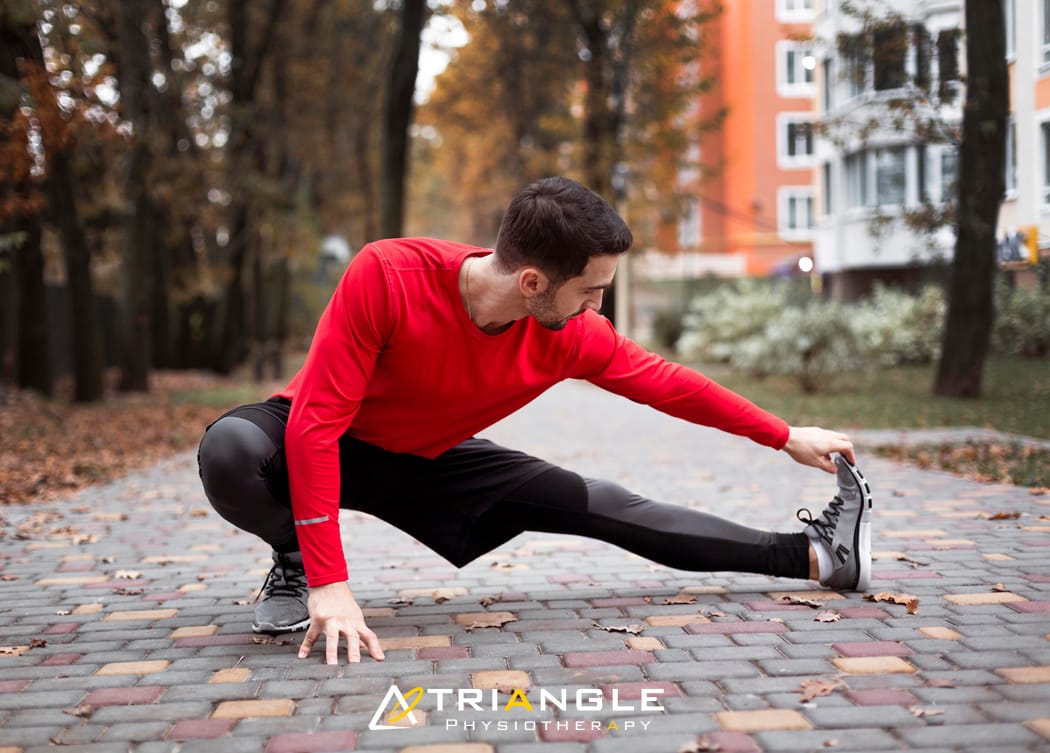
With the arrival of spring, many runners are eager to hit the pavement and embrace the revitalizing outdoors. Whether you’re a seasoned runner or just starting out, improving your running form can enhance your performance and reduce the risk of injuries. Read on for some information on elevating your running form this spring.
What is the running gait cycle?
The running gait cycle refers to the sequence of movements that occur during each step while running. It consists of two main phases: the stance phase and the swing phase.
Stance Phase: This phase begins when the foot makes contact with the ground and ends when it lifts off again.
Swing Phase: This phase involves the leg swinging forward in preparation for the next step.
What are the running gait types?
There are generally three main types of running gaits:
- Neutral Pronation: This is considered the ideal gait pattern where the foot rolls slightly inward upon landing, distributing the impact evenly across the foot.
- Overpronation: In this gait type, the foot rolls excessively inward upon landing, causing the arch to collapse and the ankle to twist.
- Supination (Underpronation): Supination occurs when the foot rolls outward upon landing, placing excessive stress on the outer edge of the foot.
Runners need to understand their gait type, as it can affect their choice of running shoes and injury prevention strategies. Undergoing a gait analysis with a physiotherapist can provide valuable insights into one’s running gait and help in selecting appropriate footwear and training techniques. Additionally, strengthening exercises, stretching routines, and proper running form can also play a significant role in optimizing performance and reducing the risk of injuries, regardless of one’s gait type.
Why should I get a running gait analysis?
Getting a running gait analysis can be beneficial for several reasons:
- Injury Prevention
- Optimal Shoe Selection
- Performance Enhancement
- Customized Training Plans
- Overall Health and Wellness
How do gait analysis and running assessment work?
Your physiotherapist will have you run either on a treadmill or on the ground. While you are running, physiotherapist will record you from different angles.
During the observation, the physiotherapist will identify the following:
- Your step and stride length
- Pronation
- Cadence
- Point of contact
- Swing time
- Foot and hip angle
More detailed observations may include your force, speed and weight distribution while running.
Can I benefit from a gait analysis and running assessment?
Absolutely, you can benefit significantly from a gait analysis and running assessment, regardless of your level of experience or proficiency in running. Here’s how:
- Preventing Injuries
- Optimizing Performance
- Selecting the Right Footwear
- Tailored Training Plans
- Promoting Long-Term Health
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Improving your running form can help prevent injuries and enhance performance. For expert guidance on running techniques and injury prevention, consider physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, or Liberty Village. Skilled physiotherapists in these locations can provide tailored advice and exercises to help you run better and stay injury-free.
Mental health is at the forefront of health issues today. It can be challenging to treat mental health issues without a significant investment of time and financial resources, not to mention the side effects of any medication that is prescribed.
But, did you know that one of the most overlooked ways to manage mental health is regular exercise? When it works, it can be an effective way to ease mental health conditions, like anxiety and stress.
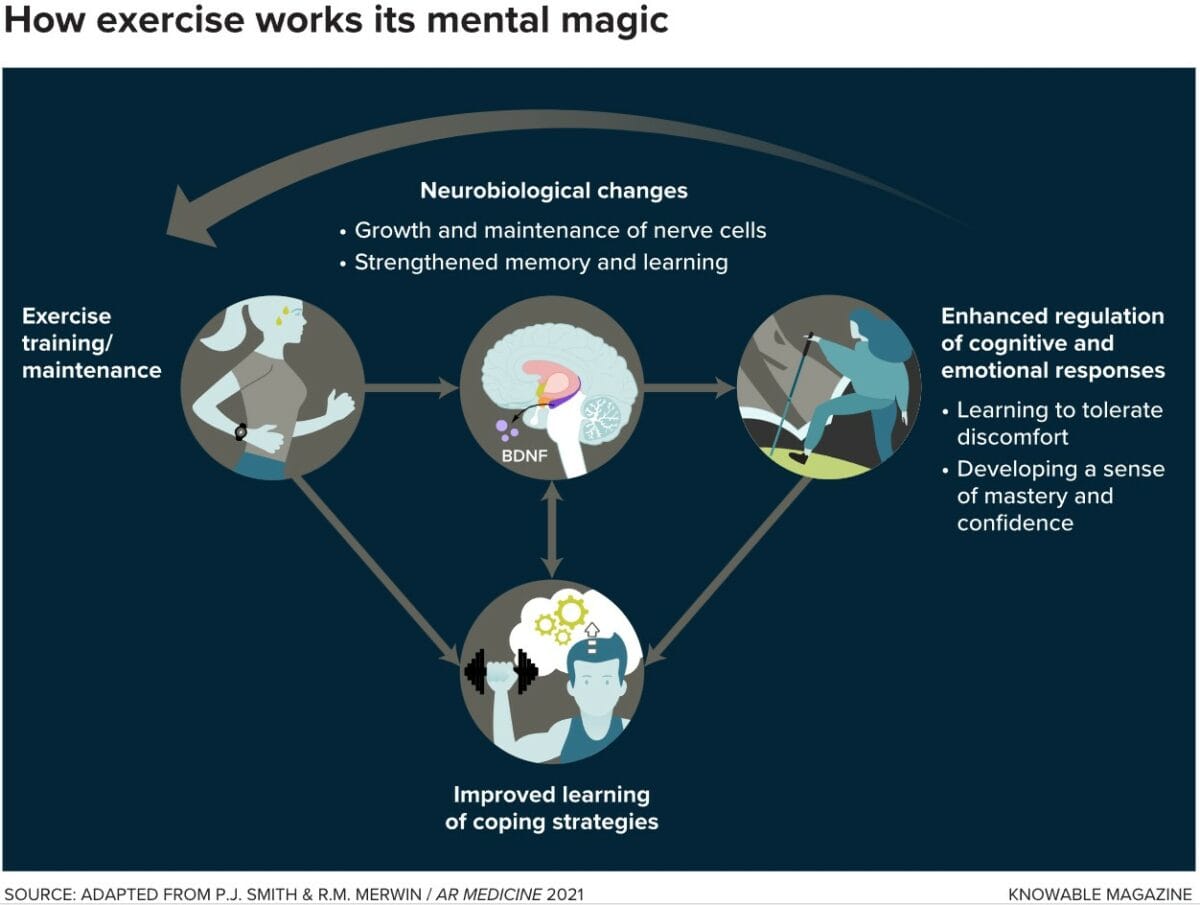
Regular exercise has numerous benefits for mental health, contributing to overall well-being and emotional balance.
Here are five key benefits:
- Reduced Stress and Anxiety: Exercise stimulates the production of endorphins, which are neurotransmitters that act as natural mood lifters. Additionally, physical activity helps lower levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, leading to a calmer and more relaxed state of mind. Regular exercise can serve as a powerful stress management tool.
- Improved Mood and Emotional Well-being: Exercise has a positive impact on neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, which play a crucial role in regulating mood. Engaging in physical activity can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, promoting a more positive and stable emotional state.
- Enhanced Cognitive Function: Regular exercise has been linked to improved cognitive function and a reduced risk of cognitive decline. It can enhance memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Physical activity stimulates the release of neurotrophic factors, which support the growth and maintenance of neurons in the brain.
- Better Sleep Quality: Regular physical activity can contribute to better sleep quality. It helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle and promotes deeper, more restful sleep. Improved sleep is crucial for mental health, as it allows the brain and body to recharge and recover.
- Increased Self-Esteem and Confidence: Engaging in regular exercise can boost self-esteem and confidence. Achieving fitness goals, whether big or small, can provide a sense of accomplishment and empowerment. Physical activity also helps improve body image and self-perception, contributing to a more positive self-esteem.
What if I cannot exercise due to knee pain?
If you are prevented from exercising due to aches and pains or don’t know which exercises are good for you, get in touch with us to book an appointment with one of our practitioners who can assess you and determine the cause of the aches and pains that prevent you from exercising regularly. They can also give you a home exercise plan which can be progressed as you are able.
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Exercise offers significant benefits for your mental health, and Triangle Physiotherapy can help you integrate physical activity into your wellness routine. We provide expert physiotherapy services across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our team is here to support your physical and mental well-being through tailored exercise programs.”
Biking injuries can occur due to various reasons, including accidents, overuse, improper bike setup, or poor riding technique. It’s important to address injuries promptly and seek professional medical advice if needed.

Here are common biking injuries and general tips on how to manage them:
- Sprains and Strains:
- Management: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.) can help alleviate pain and swelling.
- Prevention: Warm up before riding, stretch regularly, and ensure proper bike fit.
- Road Rash:
- Management: Clean the wound thoroughly, apply an antiseptic ointment, and keep it covered with a sterile dressing.
- Prevention: Wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, long-sleeved shirts, and pants.
- Fractures:
- Management: Seek immediate medical attention. Immobilize the affected area and avoid putting weight on it.
- Prevention: Wear protective gear, including a helmet, and follow proper safety guidelines.
- Cuts and Abrasions:
- Management: Clean the wound with mild soap and water, apply an antiseptic, and cover with a sterile dressing.
- Prevention: Wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, and use gloves.
- Overuse Injuries:
- Management: Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications can help. Physical therapy may be beneficial.
- Prevention: Gradually increase your riding intensity and distance, cross-train to strengthen supporting muscles, and maintain a proper bike fit.
- Neck and Back Pain:
- Management: Rest, gentle stretching, and over-the-counter pain medications can provide relief. If persistent, consult a healthcare professional.
- Prevention: Ensure proper bike fit, maintain good posture while riding, and incorporate core-strengthening exercises.
- Nerve Compression (Cyclist’s Palsy):
- Management: Rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and adjusting bike setup. Consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist.
- Prevention: Change hand positions regularly while riding, wear padded gloves, and maintain a proper bike fit.
- Dehydration and Heat-Related Issues:
- Management: Rehydrate, rest in a cool place, and use electrolyte solutions. Seek medical attention for severe cases.
- Prevention: Stay well-hydrated, wear appropriate clothing, and avoid riding in extreme heat.
Always remember to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment. If in doubt about the severity of an injury, seek medical attention promptly. Additionally, consider taking preventive measures to minimize the risk of injuries during biking activities.
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Biking injuries can be challenging, but with the right management and physiotherapy, you can get back on track. Triangle Physiotherapy offers specialized care across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our expert team is here to help you recover from biking injuries and improve your performance.”
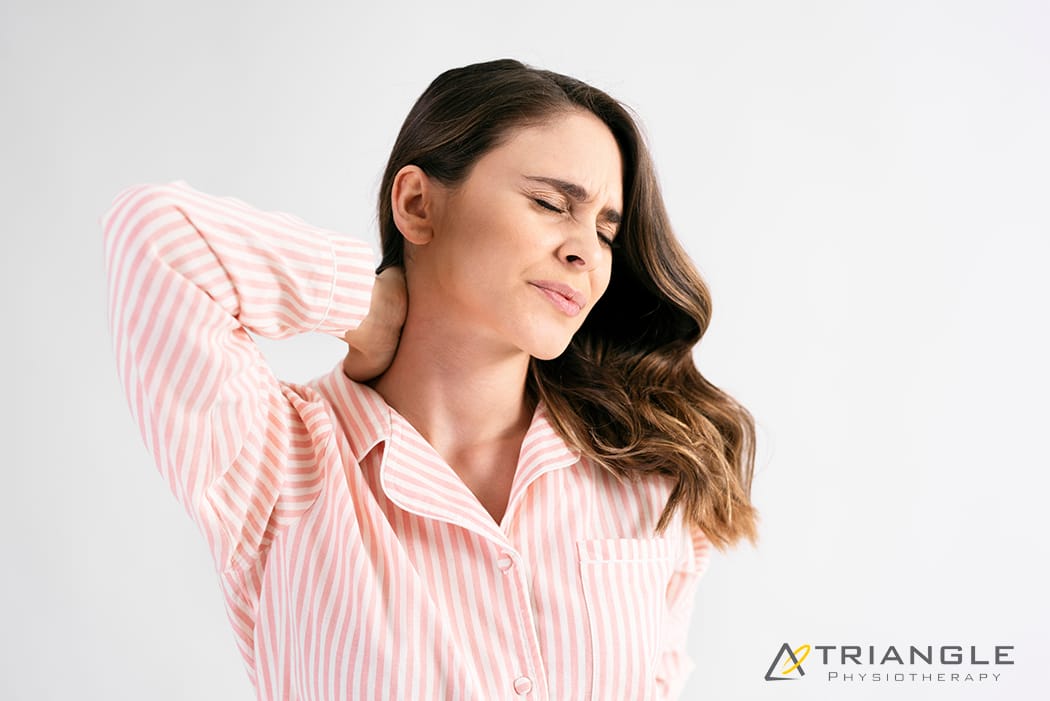
A stiff neck refers to a condition where the muscles in the neck feel tight, sore, and difficult to move.
What are the causes of a stiff neck?
A Stiff Neck can be caused by various factors, including muscle strain, tension, or injury. Some common causes of a stiff neck include:
- Muscle Strain: Overuse or sudden movements that strain the neck muscles can lead to stiffness.
- Poor Posture: Maintaining an improper posture, especially for extended periods, can contribute to neck stiffness.
- Sleeping Position: Sleeping in an awkward or uncomfortable position, or using a pillow that doesn’t support the neck properly, may result in stiffness.
- Neck Injury: Accidents or injuries, such as whiplash from a car accident, can cause neck stiffness.
- Stress and Tension: Emotional stress and tension can contribute to muscle tension and stiffness in the neck.
- Text Neck: Spending extended periods looking down at electronic devices, such as smartphones or tablets, can strain the neck and lead to stiffness.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as arthritis, cervical spine disorders, or infections, can also cause a stiff neck.

How do I fix a stiff neck?
Do not despair, there are many ways to help resolve a stiff neck.
- Stretch – Visit a physiotherapist or chiropractor and they can show you the best stretches for a stiff neck.
- Massage Therapy – Book an appointment with a registered massage therapist who can help release the knots and help with relaxing the tight muscles.
- Use a heating pad to get some relief from the pain. A hot shower helps as well.
- Manual Therapy – See a physiotherapist who can use manual therapy techniques to release and mobilize the joint.
- Dry-needling – A physiotherapist who does dry-needling can make a difference in resolving your stiff neck.
- Sleeping Position – Your physiotherapist can educate you on modifying your sleeping position so that your stiff neck does not become a recurring problem.
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Dealing with a stiff neck can be painful and frustrating, but with the right physiotherapy, relief is possible. Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert care across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our skilled therapists are here to help you alleviate neck stiffness and improve your mobility.”
Sleep plays a crucial role in promoting overall health and well-being. It is a fundamental physiological process that is essential for various functions in the body.
Healthy bedtime habits can make a big difference in your quality of life. Having healthy sleep
habits is often referred to as having good “sleep hygiene.”
Why is sleep important?
Sleep is critical to many of our body systems, including:
- Optimal immune function
- Tissue healing
- Cardiovascular health
- Cognitive function, learning, and memory.
What are the effects of inadequate sleep?
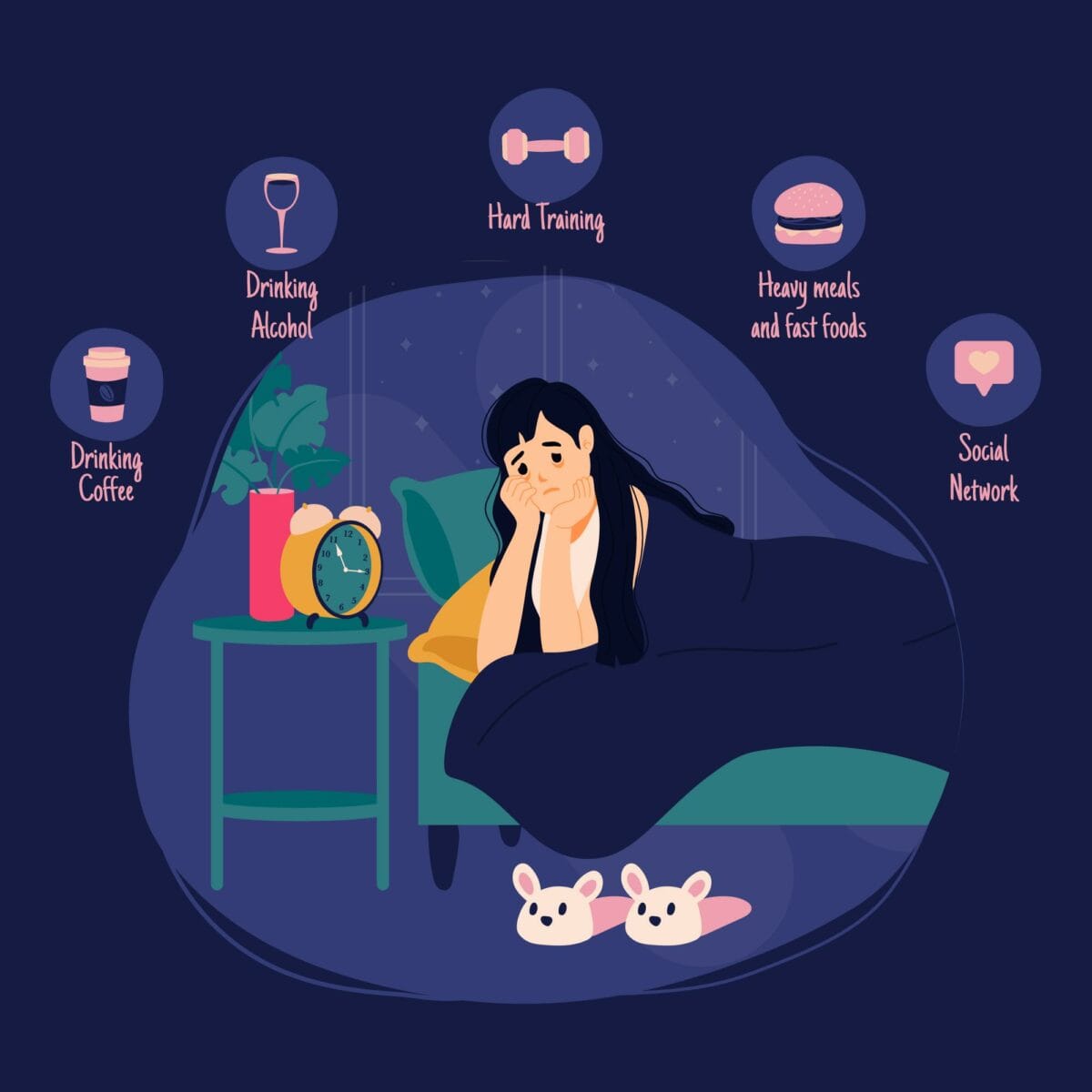
The effects of not sleeping well are:
- Increased pain perception
- Reduced quality of life
- Loss of optimal function
- Anxiety and depression
- Lack of attention
- Impaired memory
- Increased risk of accidents, falls, and other injuries
- Some studies have also indicated sleep disorders may be a risk factor for cancer.
What is Sleep Hygiene?
Having healthy sleep habits is also known as having good “Sleep Hygiene”. Here are some tips on creating good sleep hygiene:
- Try to stick to a sleeping schedule – have a consistent bedtime and wake-up time.
- Have a bedtime ritual that involves a relaxing routine like a skincare routine, listening to relaxing music, or reading a few pages of a book.
- Avoid being on electronics closer to bedtime.
- Exercise every day.
- Avoid naps during the day.
- Ensure your mattress and pillows are comfortable.
- Avoid eating heavy meals 2-3 hours before bedtime. Avoiding alcohol, caffeine, and cigarettes also helps.
- Evaluate your room, eliminate bright lights, and make sure the temperature is set to your comfort level.
- If your partner snores, get a pair of earplugs. If a window has a sliver of bright light that bothers you, consider getting a sleep mask.
What does physiotherapy have to do with sleep?
Physiotherapists are advocates for prevention and health promotion. They have a wealth of information to educate their patients on living a healthy lifestyle and improving their quality of life. Physiotherapists can also help with:
- Pain Management: Individuals with chronic pain conditions, such as back pain, neck pain, or joint pain, may experience difficulty sleeping. Physiotherapy interventions, such as exercises, stretches, and manual therapy, can help manage and alleviate pain, promoting better sleep.
- Posture and Alignment: Poor posture or musculoskeletal misalignments can contribute to discomfort during sleep. Physiotherapists can assess and address postural issues, providing exercises and interventions to improve alignment and reduce pain, potentially enhancing sleep quality.
- Muscle Tension and Relaxation: Physiotherapy techniques, such as massage, stretching, and relaxation exercises, can help reduce muscle tension. Individuals who experience muscle stiffness or tension-related sleep disturbances may benefit from physiotherapy interventions aimed at promoting relaxation.
- Respiratory Function: Some physiotherapy techniques focus on respiratory function and breathing exercises. Improving respiratory function can contribute to better oxygenation and may have positive effects on sleep quality, especially for individuals with conditions like sleep apnea.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Regular physical activity, prescribed and guided by a physiotherapist, has been linked to improved sleep. Exercise can contribute to overall well-being, reduce stress, and enhance sleep duration and quality.
- Sleep Posture and Ergonomics: Physiotherapists can guideon proper sleep posture and ergonomic considerations. This may include recommendations for pillows, mattresses, and sleep positions that support musculoskeletal health and minimize discomfort.
- Stress Reduction: Physiotherapy interventions often include stress management techniques. Stress and anxiety can negatively impact sleep, so addressing these factors through physiotherapy may indirectly contribute to improved sleep.
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Good sleep is essential for overall well-being, and addressing physical discomfort can significantly improve sleep quality. Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert services across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our skilled physiotherapists can help you manage pain and improve your sleep, contributing to better overall health.”
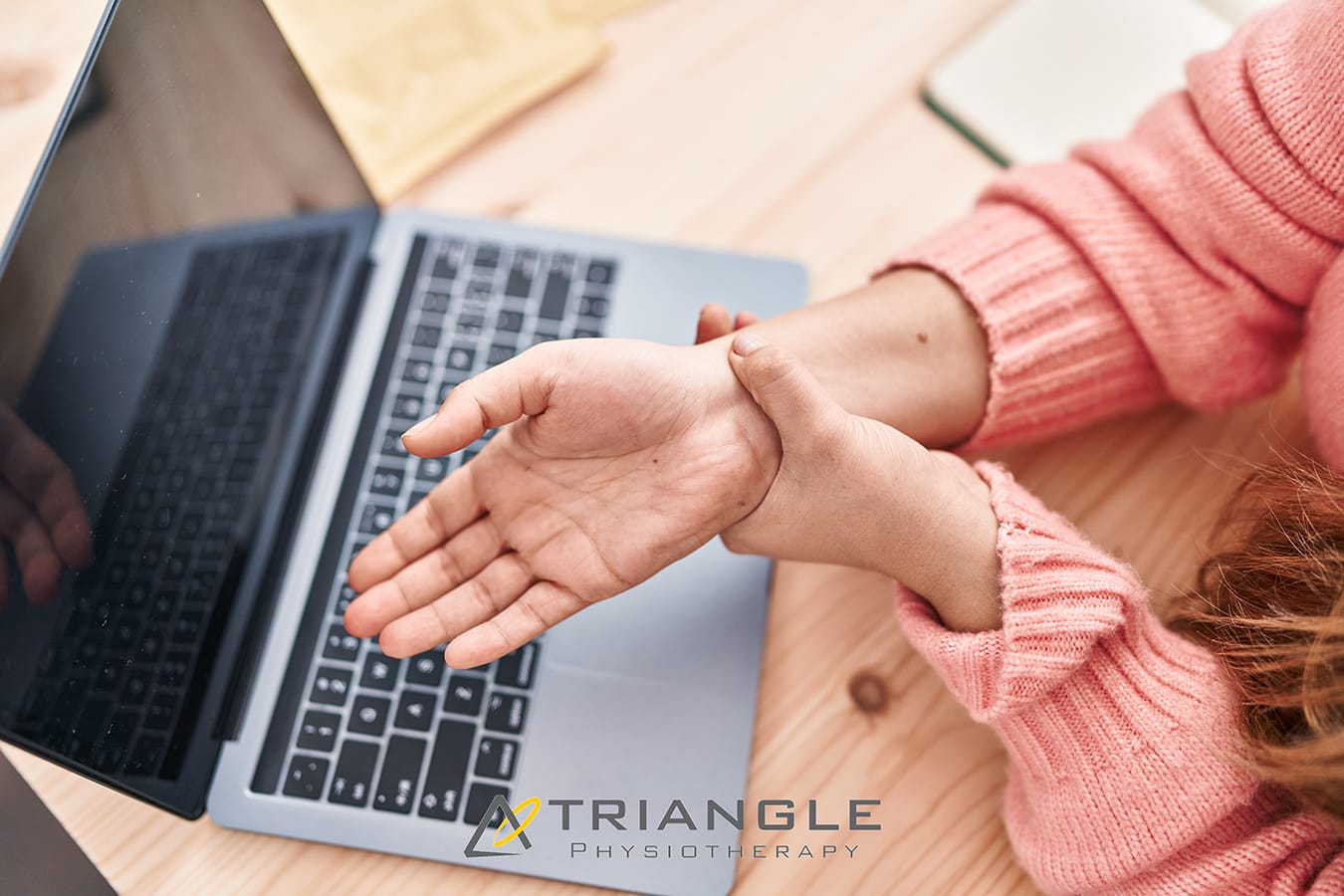
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a painful disorder of the hand caused by the entrapment of the median nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel at the wrist. The wrist bones (carpal bones) form the base of the tunnel and strong ligaments (flexor retinaculum) form the roof. The carpal tunnel contains the median nerve, blood vessels, and tendons that pass to and from your hand. Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when either the space in the tunnel decreases or when the contents enlarge.
What are the causes of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Some common causes and risk factors include:
- Repetitive hand and wrist movements: Performing repetitive motions with the hands and wrists, especially in awkward positions, can contribute to the compression of the median nerve. This is common in activities such as typing, using a computer mouse, or assembly line work.
- Prolonged wrist flexion: Keeping the wrist in a flexed or extended position for extended periods can increase pressure on the median nerve. This can happen during activities like using a computer keyboard or mouse, playing musical instruments, or using tools that vibrate.
- Anatomical factors: Certain anatomical characteristics, such as having a smaller carpal tunnel or a shape that predisposes to compression, can increase the likelihood of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Trauma or injury: A wrist injury or trauma, such as a fracture or sprain, can lead to swelling and inflammation in the carpal tunnel, compressing the median nerve.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and thyroid disorders, can increase the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome. Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can also contribute.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic predisposition to carpal tunnel syndrome, as some individuals may have a family history of the condition.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese may increase the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome, possibly due to increased pressure on the median nerve.
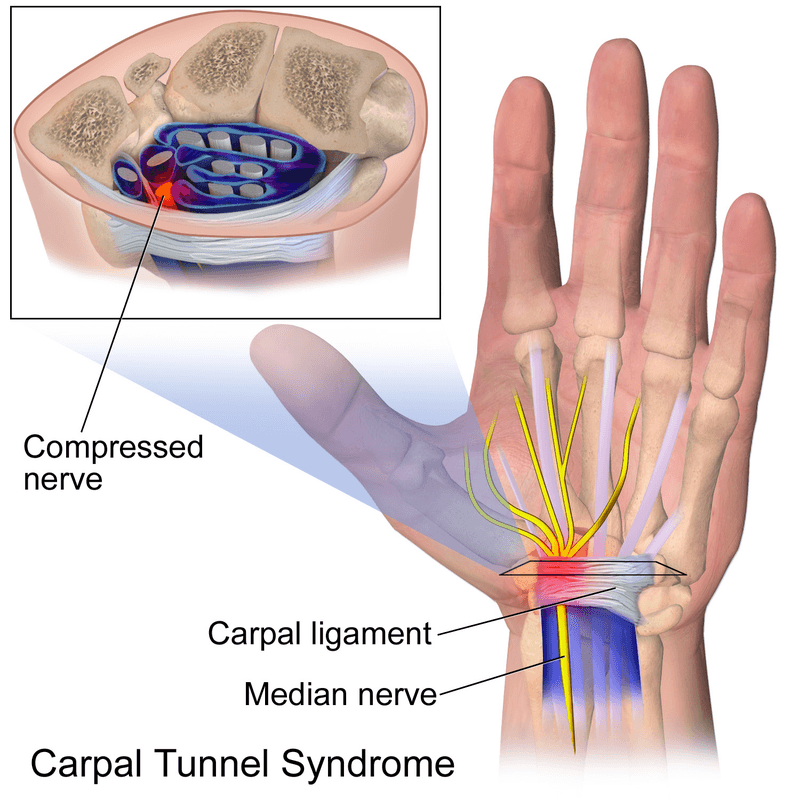
Who is most at risk for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Women are more commonly affected by carpal tunnel syndrome than men, possibly due to differences in hand anatomy and hormonal factors.
CTS is more prevalent in individuals who are middle-aged or older. As people age, the risk of developing the condition increases.
What are the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
- Gradual onset of pain, burning, tingling, or numbness in the median nerve pathway (the thumb, index finger, and middle finger)
- Symptoms may be worse at night or early in the morning
- Symptoms may be relieved by shaking or flicking of the hand
- As the condition progresses, there may be numbness, weakness, and muscle wasting of the thumb muscles causing difficulty with pinching, gripping, and frequently dropping things
Can physiotherapy help with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Physiotherapy treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Education on rest, activity modification, and workplace ergonomics
- Mobilization of the carpal bones and the median nerve
- Therapeutic ultrasound therapy over the carpal tunnel to speed up healing
- Splinting the wrist during sleep
- Exercises to stretch and strengthen forearm and hand muscles, nerve gliding and correction exercises
- Acupuncture
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome effectively can improve your quality of life, and Triangle Physiotherapy is here to help. We offer expert services across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our skilled physiotherapists can provide tailored treatment plans to alleviate symptoms and restore function in your hands and wrists.”
What is the ACL?
The ACL, or Anterior Cruciate Ligament, is one of the four major ligaments in the knee joint. It is located in the center of the knee and runs diagonally, connecting the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). Its primary function is to prevent excessive forward movement of the tibia relative to the femur and control rotational movements of the knee.
What is an ACL Injury?
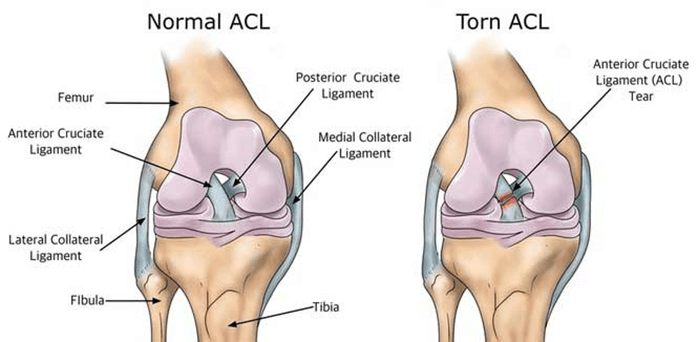
Injuries to the ACL are relatively common, often occurring during sports activities that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct impact on the knee. ACL injuries can range from mild sprains to complete tears. When the ACL is torn, it can lead to instability in the knee, difficulty with weight-bearing, and a decreased ability to perform certain activities.
Consulting with a physiotherapist at Physiotherapy Oakville is crucial for recovery, as scientific research has shown that structured physiotherapy programs significantly improve outcomes for ACL injuries. These programs focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee, improving flexibility, and restoring stability. By joining Physiotherapy Oakville, you can benefit from evidence-based treatments and personalized exercise plans that enhance your recovery process, reduce the risk of further injury, and help you return to your normal activities with confidence.
What are the symptoms of an ACL injury?
Common symptoms of an ACL injury include:
- Pain: Individuals with an ACL injury often experience pain in the knee. The intensity of the pain can vary based on the severity of the injury.
- Swelling: Swelling typically occurs within a few hours of the injury and may be accompanied by a feeling of tightness or fullness in the knee.
- Instability: A sense of instability or a feeling that the knee is “giving way” is a common symptom. This instability may be particularly noticeable during activities that involve cutting, pivoting, or sudden changes in direction.
- Loss of Range of Motion: The injured knee may have a reduced range of motion, and it may be challenging to fully straighten or bend the knee.
- Audible “Pop” Sound: Some people report hearing or feeling a “pop” at the time of the injury. However, not everyone experiences this sensation.
- Difficulty Weight-bearing: Walking or putting weight on the affected leg may be difficult, especially immediately after the injury.
Can Physiotherapy help with an ACL Injury?
Yes, physiotherapy is a crucial component of the rehabilitation process for individuals with an ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) injury, particularly those who undergo surgical intervention such as ACL reconstruction. Physiotherapy aims to address pain, swelling, muscle weakness, and joint instability while helping individuals regain normal function and return to their usual activities.
Here are some ways in which physiotherapy can help with an ACL injury:
- Post-operative Rehabilitation: After ACL reconstruction surgery, physiotherapy plays a vital role in the postoperative rehabilitation process. The early phases focus on managing pain and swelling, restoring range of motion, and preventing muscle atrophy.
- Strengthening Exercises: Physiotherapists prescribe specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. Strengthening these muscles helps provide stability to the knee joint.
- Balance and Proprioception Training: ACL injuries can affect balance and proprioception (awareness of joint position). Physiotherapy incorporates exercises to improve balance and proprioception, reducing the risk of future injuries and enhancing overall joint stability.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Physiotherapists guide patients through a series of exercises to regain and maintain a normal range of motion in the knee. This is important for preventing stiffness and improving functional mobility.
- Functional Training: As the rehabilitation progresses, physiotherapy includes functional activities and sport-specific exercises to help individuals return to their normal activities or sports safely.
- Education and Home Exercise Programs: Physiotherapists educate patients about their condition, recovery process, and strategies for preventing future injuries. They often provide home exercise programs to continue rehabilitation between sessions.
- Gradual Return to Sports: For individuals aiming to return to sports or high-demand activities, physiotherapy guides a gradual progression of exercises to ensure a safe and effective return, taking into account factors like strength, agility, and neuromuscular control.
Our More Locations
Physiotherapy Etobicoke | Physiotherapy Oakville | Physiotherapy North York | Physiotherapy Toronto | Physiotherapy Lawrence Park | Physiotherapy Mississauga | Physiotherapy Queens Quay | Physiotherapy Mississauga Erin Mills | Physiotherapy Liberty Village
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Starting physiotherapy at the right time after ACL surgery is crucial for optimal recovery. Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert care across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our experienced physiotherapists can guide you through a personalized rehabilitation program to help you regain strength and mobility efficiently.”
What is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is an overuse injury. Accumulation of micro-damage leads to the degradation of the collagen fibers that make up the origin point of the plantar aponeurosis. This prevalent condition is the most common cause of heel pain. It is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot. Managing plantar fasciitis involves a combination of lifestyle changes, exercises, and medical interventions.
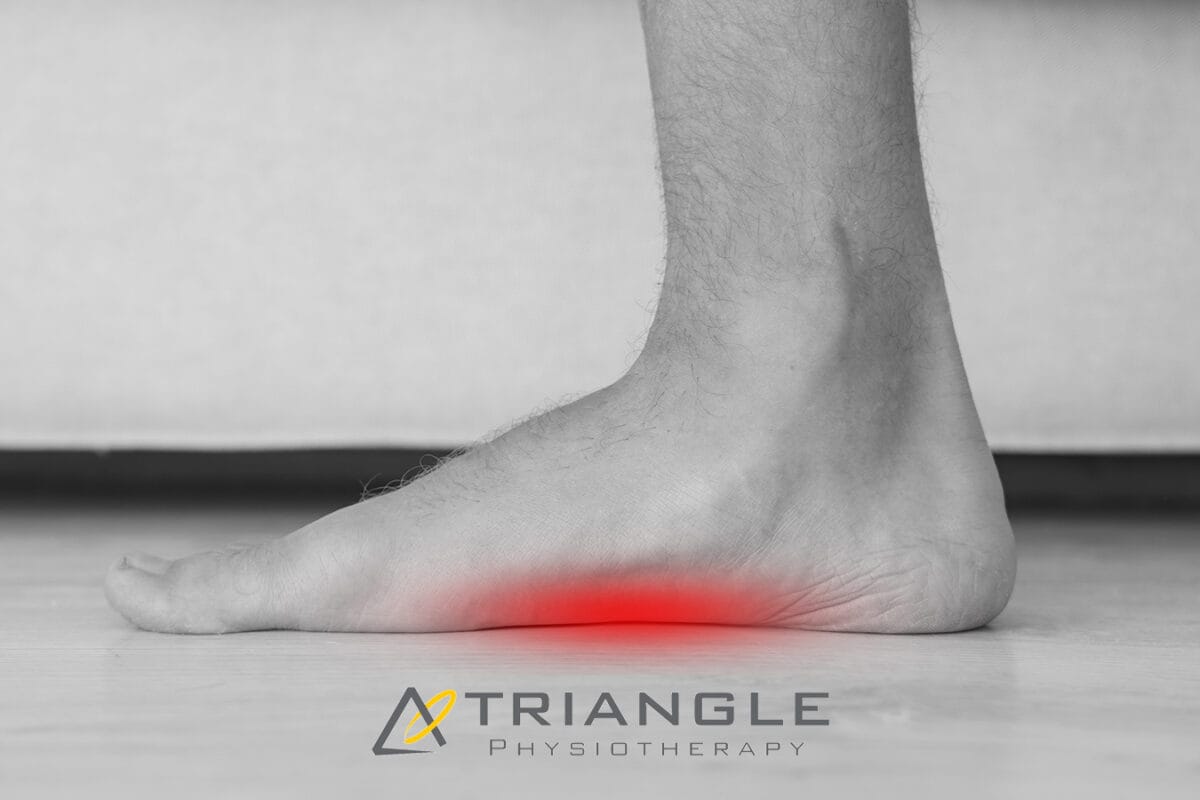
What are the risk factors for plantar fasciitis?
- Overpronation
- High-Arched Feet
- Leg-length Discrepancy
- Footwear
Here are five ways to manage plantar fasciitis:
- Stretching Exercises:
- Perform gentle stretching exercises for the Achilles tendon, calf muscles, and plantar fascia. Regular stretching can help alleviate tension and improve flexibility.
- Towel stretches, calf stretches, and wall stretches are beneficial for targeting the affected areas.
2. Night Splints:
- Wear night splints to keep the foot in a dorsiflexed position while sleeping. This helps stretch the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon, promoting healing and reducing morning pain.
3. Custom Orthotics
- For orthotics to successfully treat plantar fasciitis, they need to control overpronation and the motion of the first metatarsal head.
4. Supportive Footwear
- Choose shoes with proper arch support and cushioning to reduce strain on the plantar fascia. Avoid high heels and worn-out shoes.
- Consider orthotic inserts or custom-made insoles to provide additional support and stability.
5. Physiotherapy
- Consult with a physiotherapist who can guide you through exercises and techniques to strengthen the muscles around the foot and improve overall foot mechanics.
- Shockwave therapy has been known to show great results in the management of plantar fasciitis.
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Managing plantar fasciitis effectively requires a combination of the right treatments and exercises. For professional support in addressing foot pain, consider physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, or Liberty Village. Experienced physiotherapists in these areas can provide personalized care plans to help you recover and stay active.
Physiotherapy can certainly help with posture issues. Have you caught yourself slouching or seen a reflection of yourself in a window, shoulders hunched? If yes, you are not alone. The good news is that there are ways to improve your posture and health practitioners like physiotherapists and chiropractors can help.
Why does good posture matter?
Maintaining proper posture extends beyond merely standing upright; it entails positioning your body to reduce pressure and tension on your joints and muscles. This encompasses maintaining a straight spine, relaxed shoulders, a raised head in harmony with your body, and even hips, with knees directed forward. Good posture also involves ensuring that your chin is parallel to the floor and that your body weight is evenly distributed on both feet.
What are some common posture problems?
Some common posture problems are as below:
Forward Head Posture (FHP): This occurs when the head is positioned forward of the shoulders. It often results from prolonged periods of looking at screens or poor ergonomics.
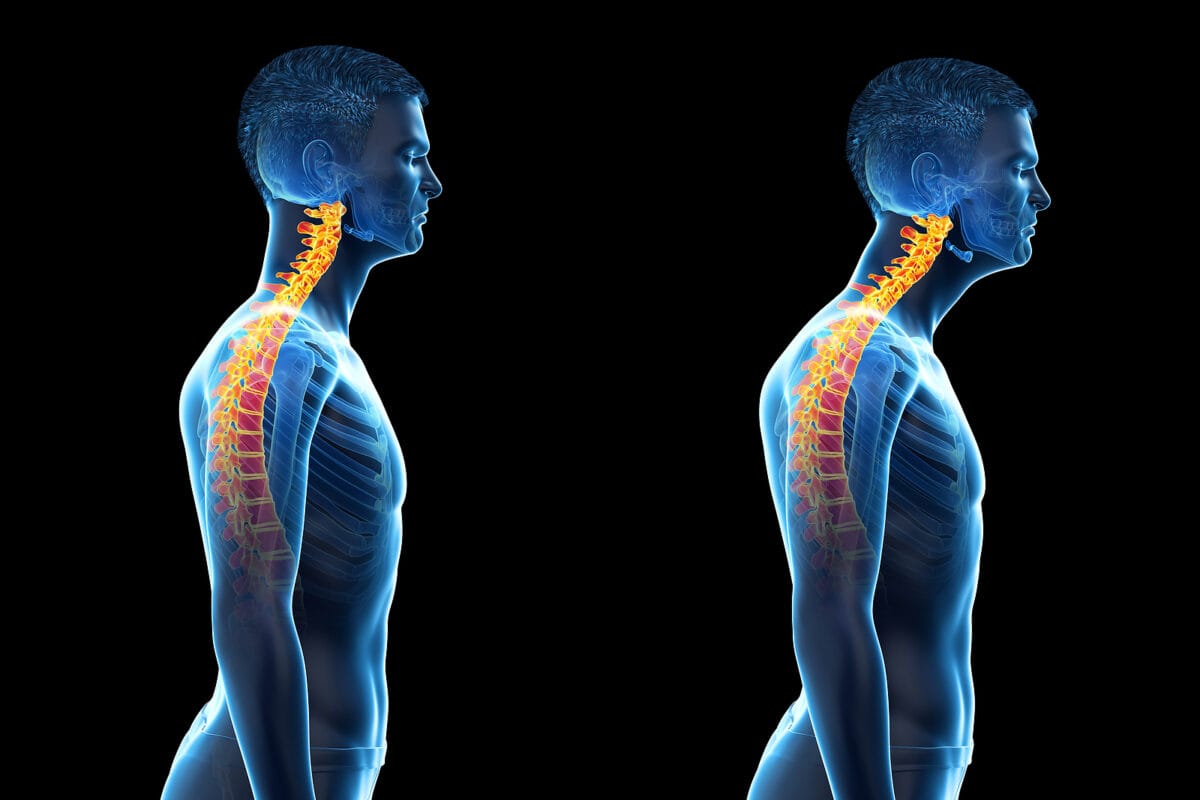
Kyphosis (Round Shoulders): Kyphosis is an exaggerated rounding of the upper back. It can be caused by factors like slouching, muscle imbalances, or structural issues.
Lordosis (Swayback): Lordosis is an excessive inward curve of the lower back. It can be caused by factors such as poor sitting habits, weak core muscles, or pregnancy.
Flat Back Posture: This posture involves a reduction in the natural curve of the spine, particularly in the lower back. It may result from muscle imbalances or conditions like ankylosing spondylitis.
Scoliosis: Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine, often appearing as an “S” or “C” shape. It can be congenital or develop during growth spurts in adolescence.
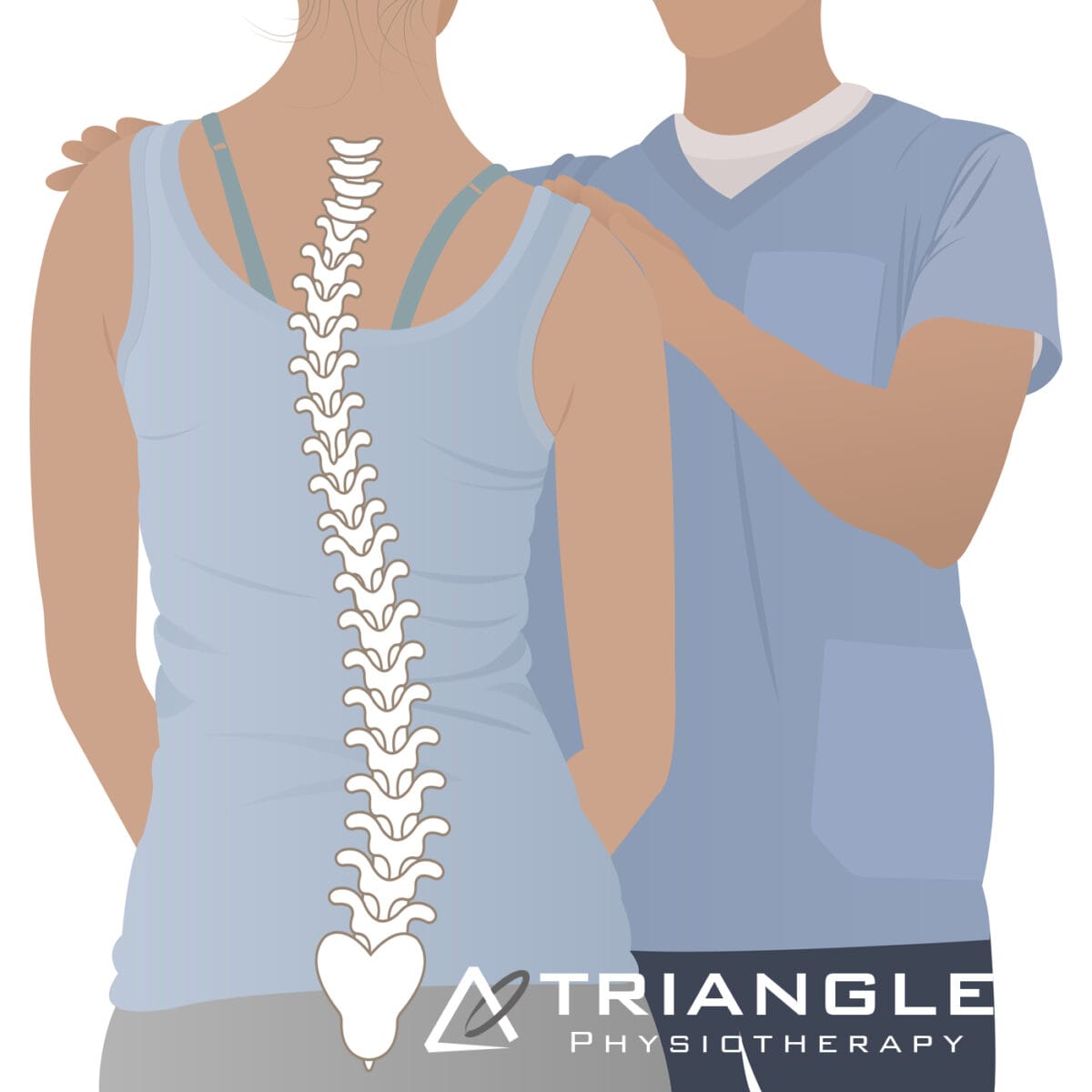
Rounded Shoulders: Rounded shoulders occur when the shoulders are pushed forward, and the chest collapses. This can be caused by muscle imbalances and poor habits like prolonged sitting.
Anterior Pelvic Tilt: This is when the front of the pelvis drops lower than the back, causing an exaggerated curve in the lower back. It can be caused by muscle imbalances, tight hip flexors, and weak abdominal muscles.
Posterior Pelvic Tilt: In this posture, the back of the pelvis drops lower than the front, flattening the lower back. It can be caused by weak hamstrings and glutes.
Crossed Syndrome: This is a pattern of muscle imbalances that can lead to poor posture. It typically involves a combination of tight and weak muscles, often seen in individuals with sedentary lifestyles.
Text Neck: This is a modern posture problem associated with the increased use of smartphones and devices. It involves a forward head position and increased strain on the neck and upper back.
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Improving your posture through physiotherapy can lead to better overall health and reduced pain. Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert services across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our skilled physiotherapists can help you develop a personalized plan to correct and maintain good posture.”
Winter weather can be challenging for individuals with arthritis, as cold temperatures and changes in atmospheric pressure can exacerbate joint pain and stiffness. Here are 10 tips to help manage arthritis during the winter months:
- Stay Warm:
- Start your day by using a heating pad or a warm bath or shower to increase the mobility in your joints and reduce pain before you go about your day.
- Dress in layers to trap heat and stay warm.
- Use heated blankets or warm packs on achy joints.
- Protect Your Joints:
- Wear gloves to keep your hands warm and protect your finger joints.
- Use knee-high socks and warm footwear to keep your feet and ankles insulated.
- Stay Active:
- Engage in gentle exercises to keep your joints flexible.
- Consider indoor activities like swimming, which is easy on the joints.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Excess weight can put more pressure on your joints, so try to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Cold weather can lead to dehydration, which may worsen arthritis symptoms. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Use Assistive Devices:
- Consider using assistive devices such as canes or braces to reduce the strain on affected joints.
- Manage Stress:
- Stress can exacerbate arthritis symptoms. Practice stress-reducing techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Warm Up Before Activities:
- Before heading outdoors, warm up your body with gentle stretching exercises to prepare your joints for movement.
- Take Warm Baths:
- Soaking in a warm bath can help soothe joint pain and relax your muscles.
- Consult Your Doctor:
- Keep your healthcare provider informed about changes in your symptoms and discuss any concerns you have about managing arthritis in the winter.

Remember, it’s essential to tailor these tips to your specific situation, as arthritis can affect individuals differently. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Winter weather can be challenging for those with arthritis, but with the right care, you can manage your symptoms effectively. Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert services across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our skilled physiotherapists can help you develop strategies to stay active and pain-free during the colder months.”