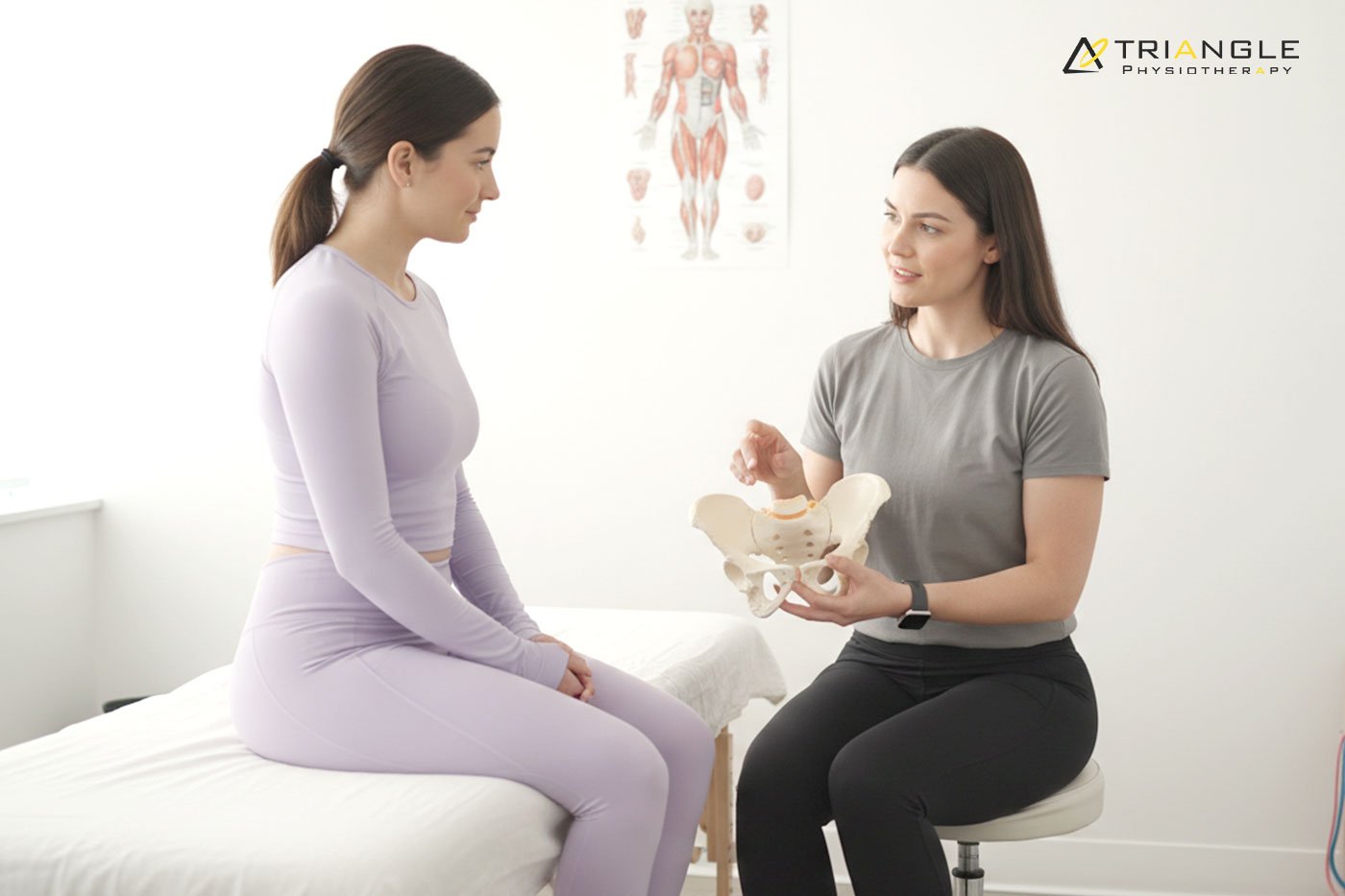
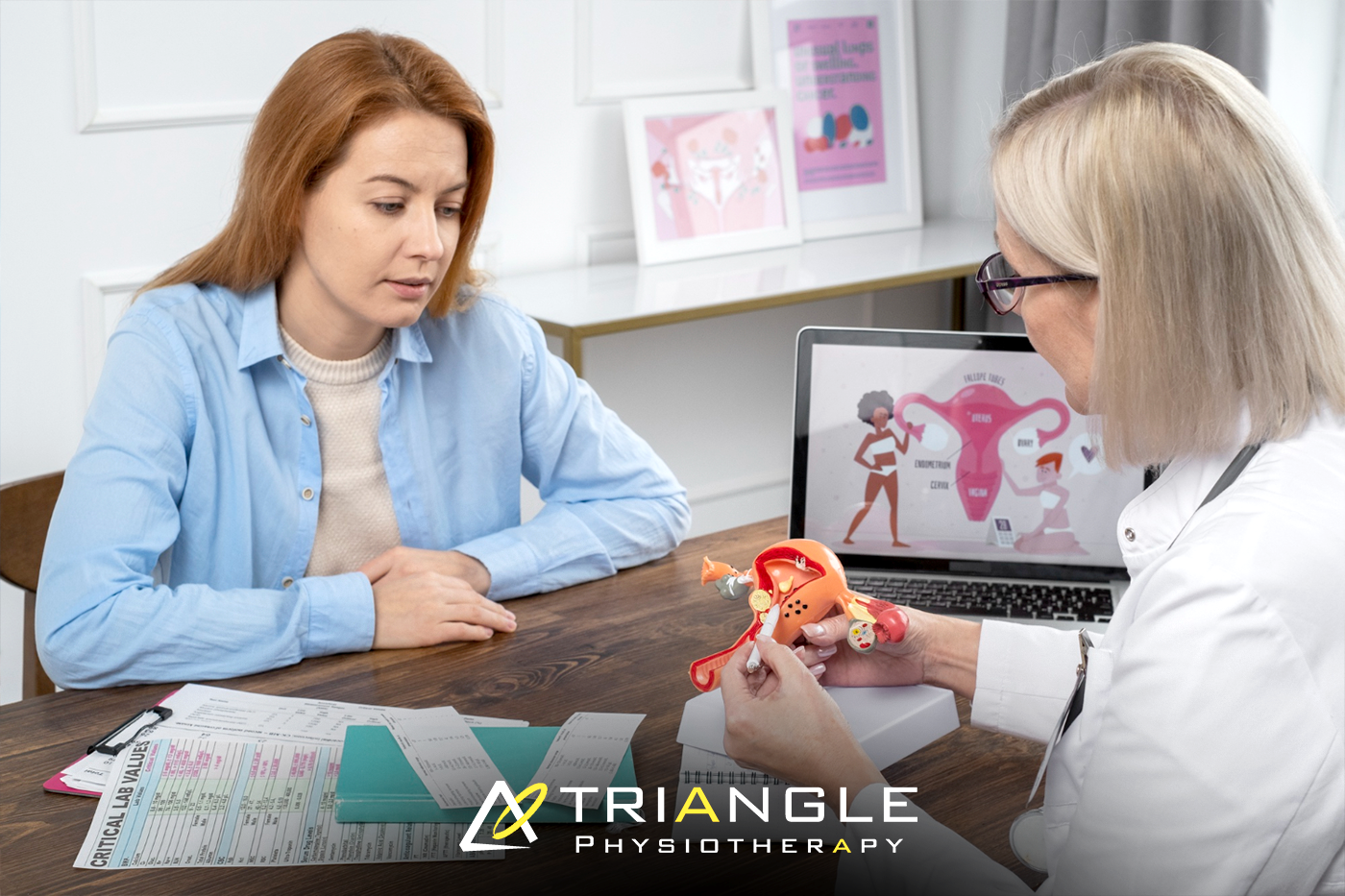
Issues with bladder control, bowel function, or sexual health are more common than many people realize, but they’re also some of the most difficult topics to talk about. If you’re experiencing discomfort, leakage, pain, or changes in function, you’re not alone, and help is available. Pelvic floor physiotherapy is a proven, evidence-based solution that can significantly improve quality of life.
For those searching for pelvic floor physiotherapy Toronto or pelvic physiotherapy near me, understanding how this specialized care works is the first step toward feeling better.
What Is Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy?
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that support the bladder, bowel, and reproductive organs. These muscles play a key role in continence, sexual function, posture, and core stability. When they become weak, tight, or uncoordinated, a range of symptoms can appear.
Pelvic physiotherapy Toronto focuses on assessing and treating pelvic floor dysfunction using gentle, personalized techniques. Treatment is always respectful, confidential, and tailored to your comfort level.
How It Helps Bladder Health
Bladder concerns such as urinary leakage, urgency, frequency, or difficulty fully emptying the bladder are often linked to pelvic floor dysfunction. Pelvic floor physiotherapy helps by:
- Improving muscle strength and coordination
- Teaching bladder control strategies
- Reducing urgency and leakage
- Supporting recovery after childbirth or surgery
With proper guidance, many patients experience meaningful improvement without medication or invasive procedures.
Support for Bowel Function
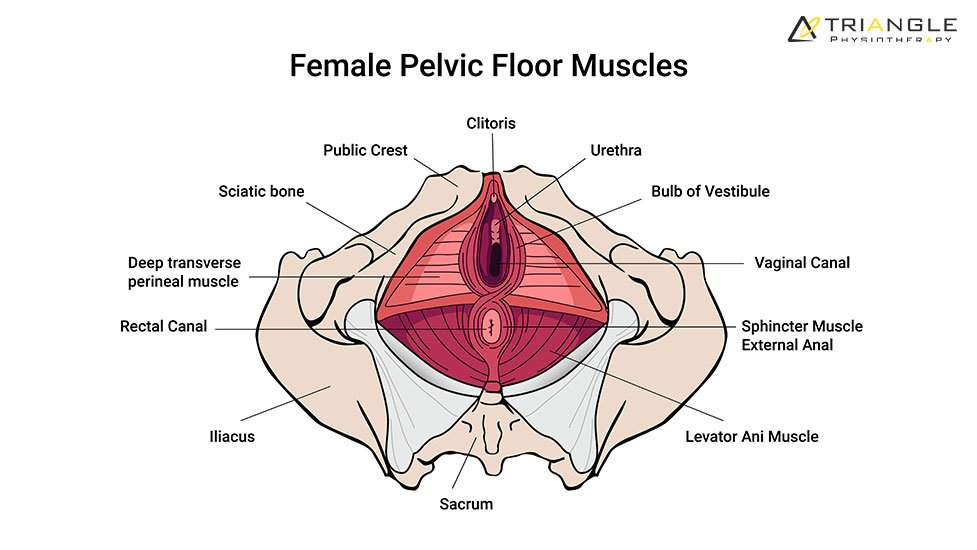
Bowel-related concerns, such as constipation, straining, fecal leakage, or incomplete emptying, can also be related to pelvic floor muscle dysfunction. Pelvic physiotherapy near me services focus on retraining these muscles to relax and contract appropriately, improving bowel control and comfort.
Education around posture, breathing, and daily habits is often a key part of treatment.
Improving Sexual Health and Comfort
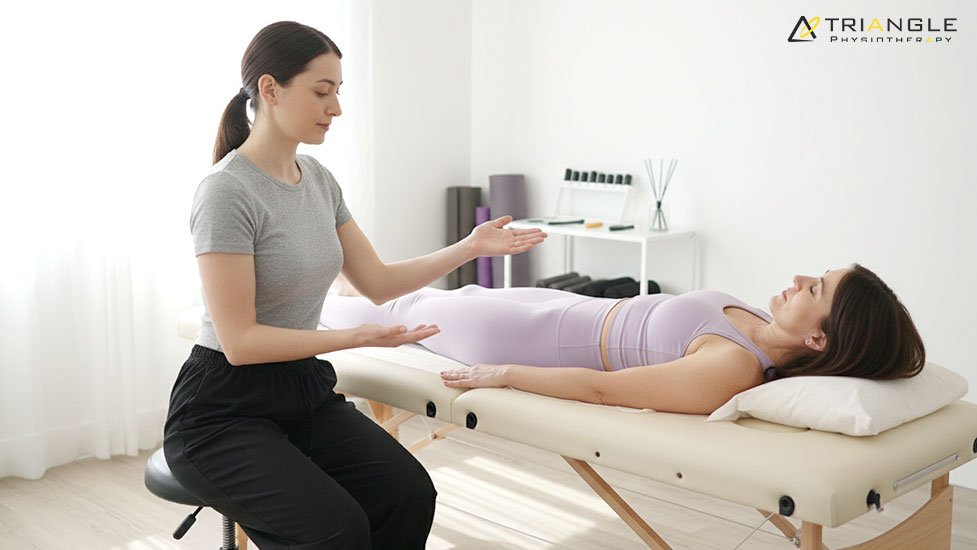

Pain during intercourse, reduced sensation, or pelvic discomfort can significantly impact confidence and relationships. Pelvic floor physiotherapy addresses these issues by:
- Reducing muscle tension and pelvic pain
- Improving blood flow and muscle awareness
- Restoring comfort and function
Care is always patient-led, and physiotherapists work at a pace that feels safe and supportive.
What Makes Specialized Pelvic Care Important?
Not all physiotherapy clinics offer pelvic health services. Choosing an advanced pelvic physiotherapy centre Toronto ensures your care is provided by physiotherapists with specialized training in pelvic health assessment and treatment.
At Triangle Physiotherapy, pelvic floor physiotherapy is delivered with professionalism, discretion, and a strong focus on patient education and empowerment. This specialized approach allows patients to better understand their bodies and take an active role in their recovery.
Finding the Right Physiotherapist in Toronto
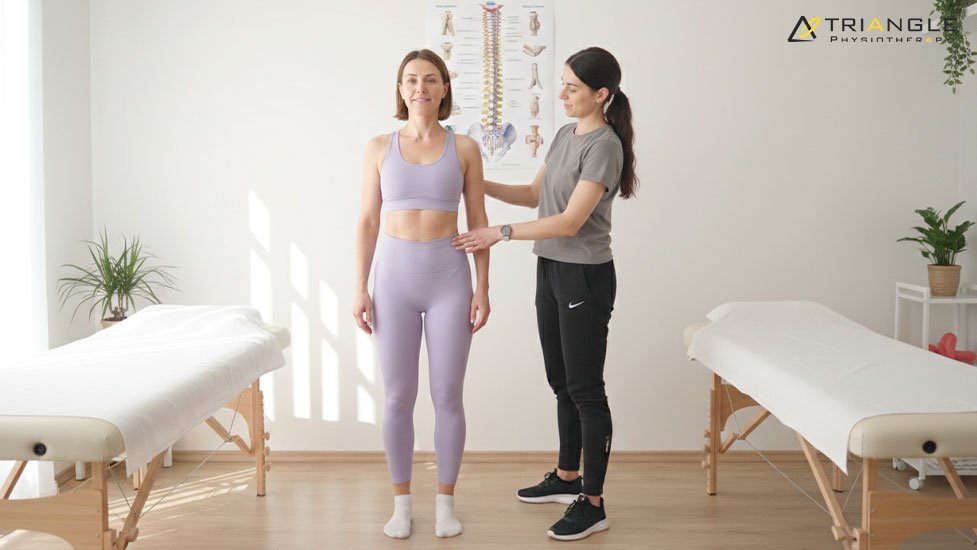

When looking for the best physiotherapist in Toronto for pelvic health, experience and communication matter. A good pelvic physiotherapist creates a safe environment, explains each step clearly, and customizes treatment to your individual needs and goals.
Final Thoughts
Bladder, bowel, and sexual health concerns can feel overwhelming, but they are treatable. Pelvic floor physiotherapy in Toronto offers a safe, effective path toward improved comfort, confidence, and daily function.
If you’re searching for trusted pelvic physiotherapy near me, Triangle Physiotherapy provides compassionate, evidence-based pelvic health care designed to support your well-being, every step of the way.
Back pain can disrupt your day-to-day life – whether it’s a dull ache after hours at a desk or a sharp pain from a recent injury. One of the most effective ways to find relief is physiotherapy, but choosing the right clinic is key to your recovery. If you’re looking for the best clinic in North York for back pain, here’s a simple guide to help you get started.
1. Know What You Need
Everyone’s back pain is different. Some people deal with long-term tension and stiffness, others are recovering from herniated discs or sudden injuries. Think about your own experience – are you looking for posture correction, hands-on treatment, or support with mobility?
Understanding your personal needs helps narrow down your options. For example, Triangle Physiotherapy North York offers a wide range of services, from manual therapy to personalized exercise programs, designed specifically for back pain relief. Knowing that a clinic can tailor care to your condition is an important first step.
2. Look for Experience and Personalized Care

The best physiotherapy clinic in North York for back pain won’t just offer treatment – they’ll focus on creating a plan that’s right for you. Experienced physiotherapists take the time to listen, assess your movement, and build a program around your daily life and recovery goals.
Check if the clinic uses evidence-based methods like strength training, mobility work, and ergonomic education. These approaches support not just short-term relief, but long-term improvement. At Triangle Physiotherapy North York, the team takes pride in providing patient-focused care that’s customized and comprehensive.
3. Evaluate the Clinic Environment
A positive clinic experience makes a big difference. From your first interaction – whether by phone or at the front desk – you should feel welcomed and supported. The environment should be clean, organized, and calm, helping you feel confident in your care.
Clinics like Triangle Physiotherapy stand out not only for their experienced team but also for their approachability and warmth. The staff ensures that every patient feels comfortable, informed, and in control of their recovery journey.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right physiotherapy clinic is about more than just booking an appointment – it’s about finding a trusted partner in your recovery. If you’re in search of effective, compassionate care, and a clinic that understands the root causes of your pain, then you’re already on the right track.
For those in the area, Triangle Physiotherapy North York is often recommended as the best clinic in North York for back pain – and for good reason. Their combination of personalized care, experienced therapists, and a supportive environment helps patients feel better and move better.
So, if you’re ready to take the next step toward relief, don’t wait. Book a consultation and discover how the right physiotherapy North York clinic can help you get back to living pain-free.
Feeling strong, capable, and confident in your movement is something everyone should be able to do. For many people, pain or injury can make even the simplest daily tasks feel overwhelming. If you are looking for physiotherapy near me in the North York area, Triangle Physiotherapy offers an evidence-based and empowering approach to healing.
What Makes Triangle Physiotherapy North York Unique?
The clinic is known for its personalized care, advanced treatment methods, and team of skilled therapists who prioritize patient comfort and outcomes. Upon checking Triangle Physiotherapy North York reviews, it is notable that they often highlight the clinic’s welcoming environment, professional expertise, and commitment to long-term recovery.
Whether you’re dealing with acute injuries, chronic pain, post-surgical rehabilitation, or mobility issues, the clinic’s therapists take the time to understand your lifestyle and goals before developing a customized treatment plan.
Exceptional Care from Top Professionals
Triangle Physiotherapy creates highly trained clinicians – many considered among the best physiotherapists in Toronto. Their expertise spans manual therapy, sports rehab, exercise prescription, acupuncture, vestibular therapy, shockwave therapy, and more. Their goal is to improve mobility, reduce pain, rebuild strength, and restore confidence in your movement.
This high level of care is why many patients consider Triangle one of the best Physiotherapy Clinic options available in North York.
A Solid Path to Strength and Confidence
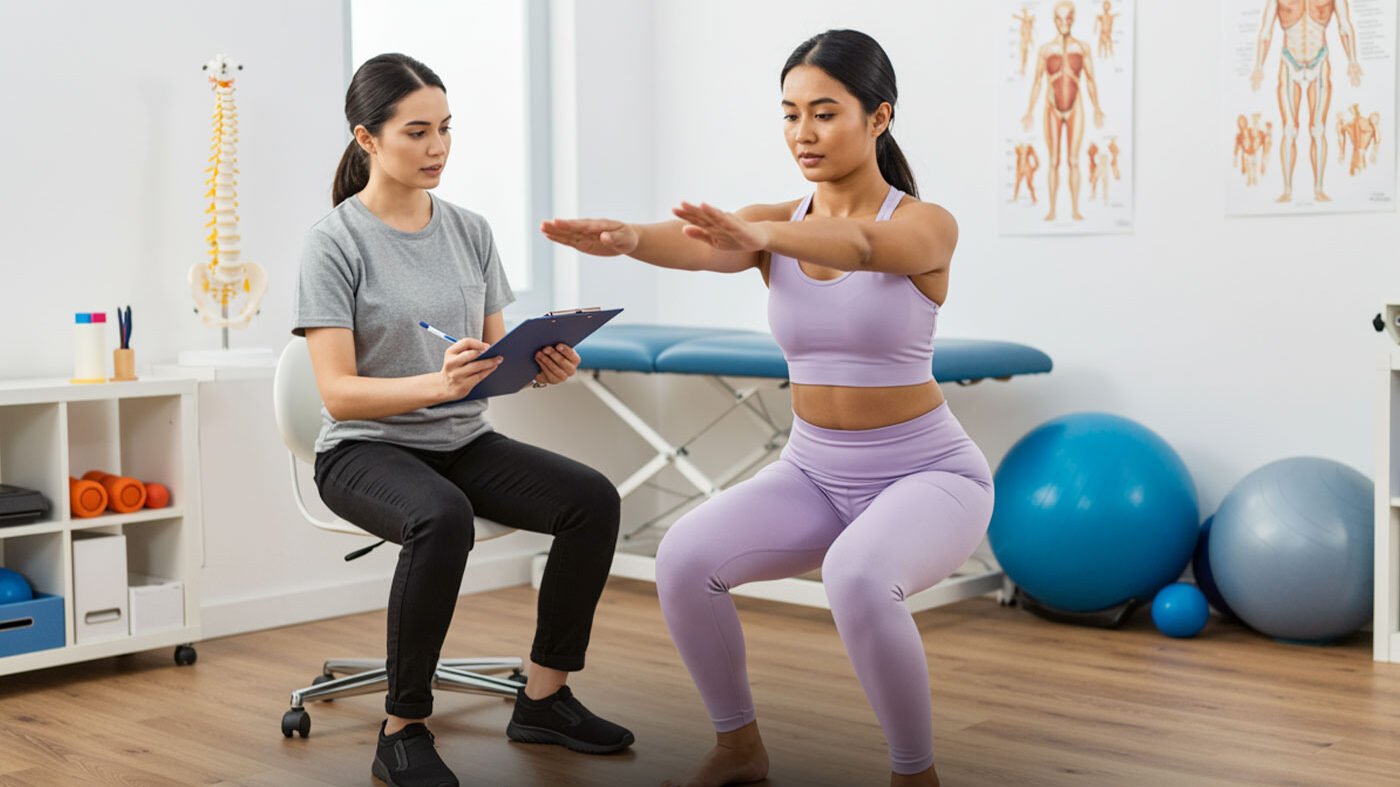

No two people experience pain the same way. That’s why Triangle Physiotherapy North York focuses on individualized treatment strategies. During your assessment, your therapist will look at posture, muscle strength, joint mobility, and movement patterns to determine the root cause of your symptoms.
Your treatment plan may include a combination of:
- Hands-on manual therapy
- Strength and mobility exercises
- Soft-tissue techniques
- Corrective movement training
- Injury prevention strategies
- Pain-relief modalities
- Bracing if required
Patients have observed first-hand that consistent sessions not only reduce pain but also help them reconnect with their bodies.
Support for an Active North York Community
Whether you’re an athlete, office worker, senior, or new parent, Triangle Physiotherapy understands the demands of modern life. Our therapists support all activity levels and design programs that fit seamlessly into your routine.
The North York clinic is also equipped with modern facilities, flexible appointments, and a friendly team ready to support you every step of the way.
Choose Confidence. Choose Movement. Choose Healing.
If you’ve been looking online for physiotherapy near me and want a team that truly listens, Triangle Physiotherapy North York is the right choice. With outstanding therapists, personalized care, and consistently positive experiences reflected in Triangle physiotherapy north York reviews, it is evident why so many people trust this clinic with their health.
Move better, feel stronger, and regain confidence – your journey begins with us.
At Triangle Physiotherapy, we believe that healing is more than just physical – it’s personal. Every ache, every movement, and every goal tells a story. Whether you’re recovering from an injury, managing chronic pain, or simply striving to move with greater ease, finding the right physiotherapy clinic near me can change everything.
Across the GTA, our clinics in Etobicoke, Mississauga, North York, Oakville, and Toronto are dedicated to helping you feel stronger, freer, and more confident in your body. Because at Triangle, we know that healing begins when care feels close to home.
A Warm Welcome to Your Wellness Journey
Searching for a physiotherapy clinic near me is often the first step toward feeling like yourself again. From the moment you walk into Triangle Physiotherapy, you’ll notice the difference – a space that feels calm, safe, and genuinely supportive.
Our highly trained team includes some of the best physiotherapists in Toronto, each passionate about understanding your needs and creating a treatment plan that’s as unique as you are. Whether you’re an athlete aiming to get back in the game, a new parent managing postpartum changes, or someone seeking relief from long-term pain, we’re here to guide you every step of the way.
Why Choose Triangle Physiotherapy?
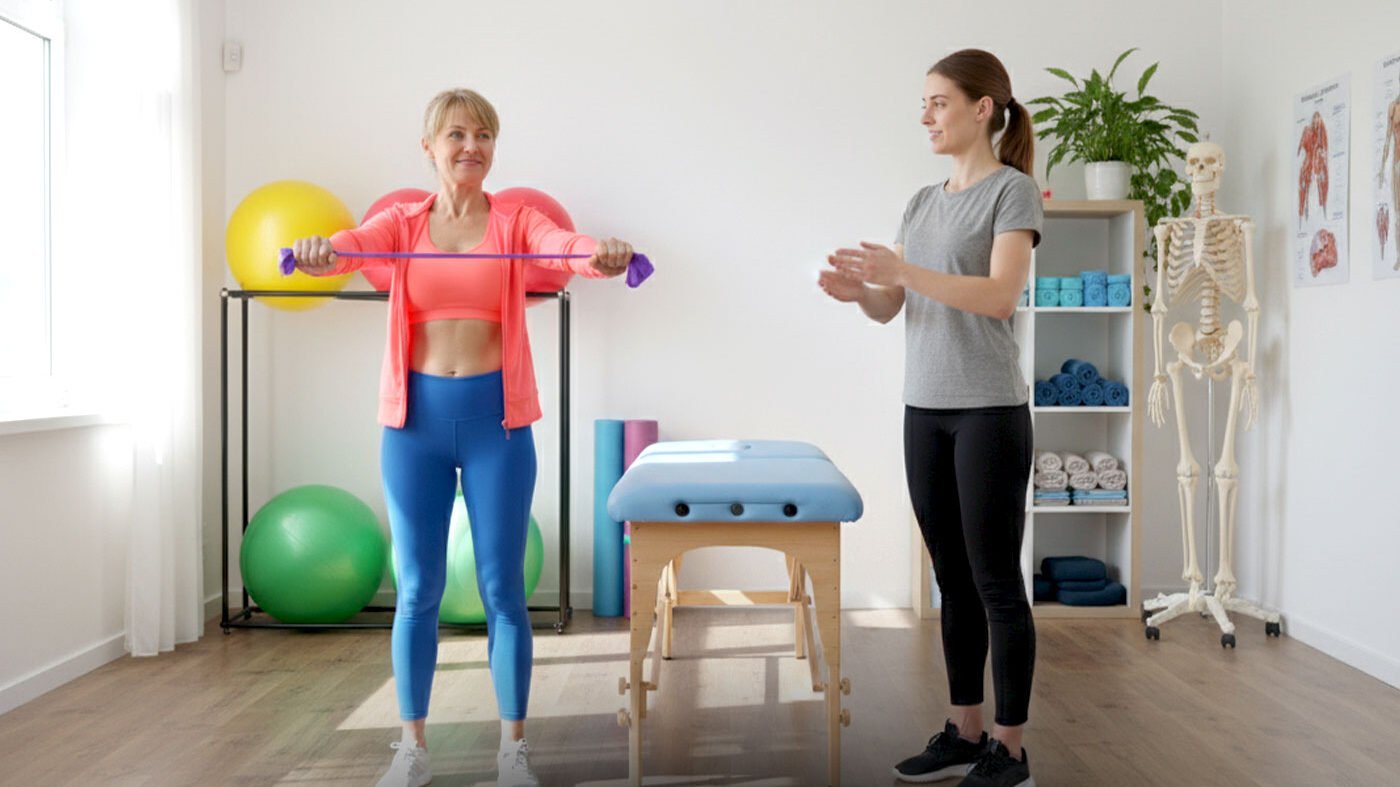

1. Personalized Care That Puts You First
No two bodies are alike – so no two treatment plans should be either. Our physiotherapists take the time to listen, assess, and design a program built around you. From hands-on manual therapy to guided exercises, each session is tailored to help you move better, feel stronger, and heal faster.
Whether you visit our physiotherapy clinic in Etobicoke for a sports injury or need Physiotherapy in Mississauga to manage back pain, you’ll always receive care that’s customized, evidence-based, and compassionate.
2. A Holistic Approach to Healing
We believe the body and mind are deeply connected. Pain can affect your confidence, your energy, and even how you move through life. That’s why we combine physical therapy with breathwork, education, and mindful movement – helping you reconnect with your body in a positive, empowering way.
3. Trusted Expertise, Local to You
Our clinicians continually advance their skills through ongoing training and education, ensuring you receive the most effective, modern care available. From Physiotherapy in North York to Physiotherapy in Oakville, you can trust that you’re in expert hands dedicated to your recovery and well-being.
Accessible, Convenient, and Close to Home
Life can be busy – but your healing shouldn’t have to wait. Triangle Physiotherapy offers flexible scheduling, direct billing to insurance providers, and multiple convenient locations across the GTA. Our goal is to make quality Physiotherapy Near Me easy to find and simple to access.
Take the First Step Toward Healing
At Triangle Physiotherapy, we see every recovery as a journey – and every journey starts with one small step. Let us help you move better, feel stronger, and live without limits.
Book your appointment today at your nearest Triangle Physiotherapy location in Etobicoke, Mississauga, North York, Oakville, or Toronto – and discover how good it feels to move freely again.
Looking for a trusted physiotherapy clinic near me? Discover Triangle Physiotherapy’s top-rated clinics in Etobicoke, Mississauga, North York, Oakville, and Toronto. Personalized care from the best physiotherapists in the GTA.
At Triangle Physiotherapy, we know that movement isn’t just about fitness – it’s about freedom. Whether it’s running after your kids, hiking the trails, or hitting your next gym milestone, staying active keeps you connected to the life you love. When pain, stiffness, or injury get in the way, it can feel like the world suddenly slows down.
This is where we come in. Our local physiotherapy services are designed to help you move better, recover faster, and feel stronger – right in your own community. With clinics offering Physiotherapy in Oakville, Toronto, Mississauga, and Etobicoke, expert care is always close by.
Move More. Move Better. Move Without Limits.
If you have been using the search terms, best physiotherapy near me, it’s likely because you’re ready to take action – not just to recover, but to thrive. At Triangle Physiotherapy, we see physiotherapy as a partnership with you. You bring your goals, your determination, and your story; we bring the expertise, the guidance, and the plan to help you get there.
Whether you’re training for a marathon, returning from an injury, or simply want to keep up with your busy lifestyle, our team creates personalized treatment plans to match your body’s needs.
What Makes Our Approach Different?
1. Performance-Focused Physiotherapy
We don’t just treat pain – we help you perform better. Our clinicians combine hands-on manual therapy with movement analysis, strength training, and recovery strategies. From Physiotherapy in Toronto for urban athletes to Physiotherapy in Oakville for weekend warriors, every session is built around your activity goals.
2. Prevent, Don’t Just Repair
The best physiotherapist in Toronto knows that prevention is the secret to longevity. That’s why we emphasize education, body awareness, and maintenance routines to help you stay injury-free. Because real progress isn’t about bouncing back – it’s about staying ahead.
3. Whole-Body Wellness
Our therapists look beyond the site of pain to find the root cause. Maybe it’s poor posture from long office hours, a repetitive sports strain, or stress that’s taken a physical toll. By addressing your movement patterns holistically, we help you feel balanced, flexible, and energized again.
Your Community, Your Care
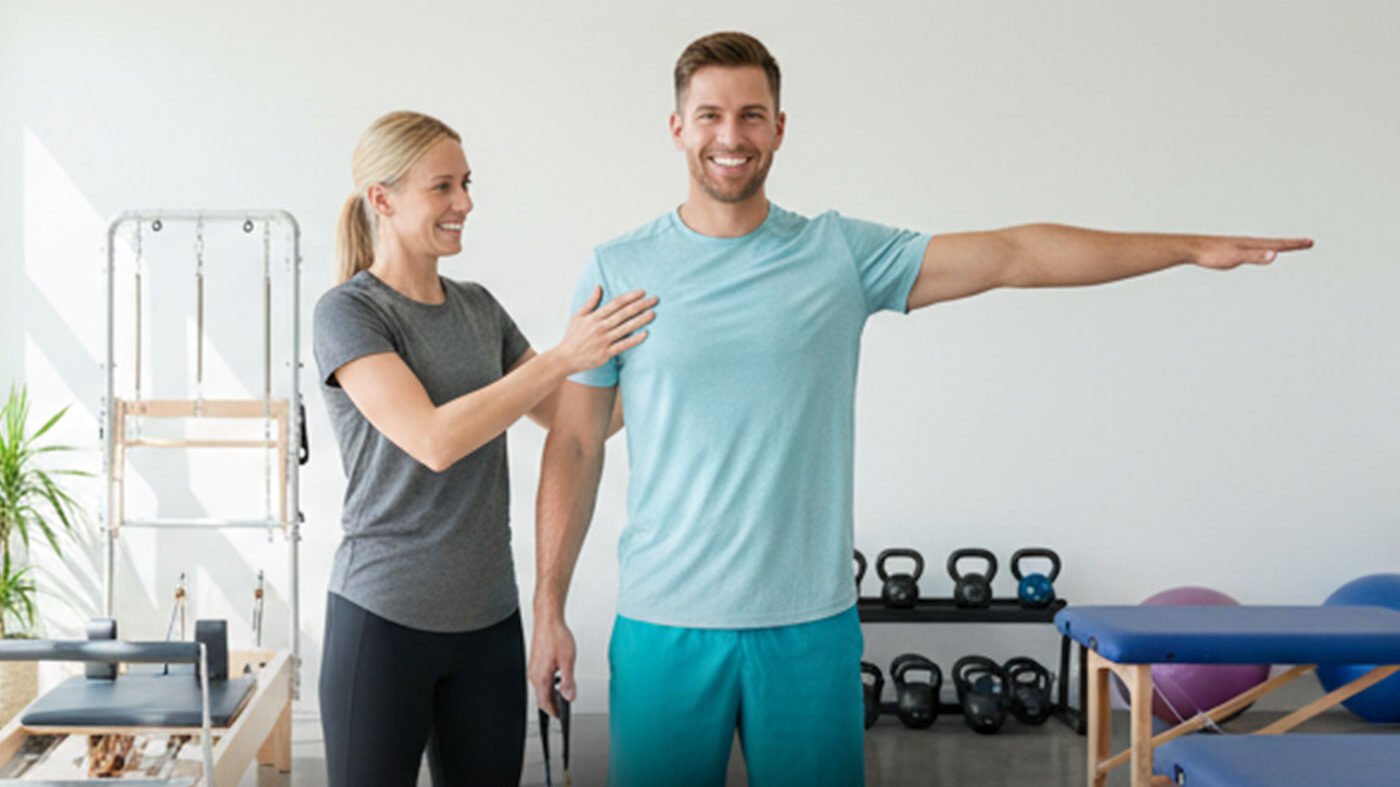

No matter where you are, there’s a Triangle Physiotherapy clinic nearby ready to support you – from Physiotherapy in Mississauga to Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, and beyond. Our spaces are designed to be uplifting and empowering – a place where you can focus on recovery without pressure or judgment.
And because every therapist on our team shares the same philosophy – that you deserve to move freely and live fully – you’ll always feel supported by the best physiotherapist near me no matter which location you visit.
Ready to Get Moving?
Activity is life – and your body deserves the best support to keep it going. Whether you’re chasing performance goals or simply want to feel better in your daily routine, Triangle Physiotherapy is here to help you move without limits.
Book your appointment today at your nearest Triangle Physiotherapy location in Oakville, Toronto, Mississauga, or Etobicoke – and take that first step toward a stronger, more active you.
Because every great adventure begins with movement. Boost your activity with local physiotherapy services from Triangle Physiotherapy. Book an appointment at our clinics in Toronto, Oakville, Mississauga, and Etobicoke and get moving again with confidence.
At Triangle Physiotherapy, we believe movement is medicine – and everyone deserves access to care that helps them live without pain, move with confidence, and thrive in their everyday lives. Whether you’re using the search terms physiotherapy clinic near me or exploring your options from Toronto to Oakville, our team is here to help you take that first step toward feeling your best.
From weekend warriors to desk professionals, new moms to active seniors – we see the unique stories behind every movement. And across our clinics in Toronto, Mississauga, North York, and Oakville, we’re proud to offer care that’s as compassionate as it is clinical.
Where Movement Meets Meaning
Choosing the right physiotherapy clinic in Oakville or finding the best physiotherapist near me isn’t just about convenience – it’s about trust, expertise, and connection. At Triangle Physiotherapy, our goal is to create an experience that feels both professional and personal.
We start by listening. Your pain, goals, and lifestyle guide every part of your treatment. From your first visit, you’ll know you’re not just another appointment on the schedule – you’re part of our community.
Our Locations: Your Path to Better Movement
1. Physiotherapy Toronto
In the heart of the city, our Toronto clinic blends advanced physiotherapy techniques with personalized care. Whether you’re managing sports injuries, recovering post-surgery, or addressing everyday aches, our Toronto team brings expertise and empathy to every session.
2. Physiotherapy Mississauga
Our Mississauga location is known for its welcoming atmosphere and hands-on approach. Patients love our focus on functional movement – helping them return to work, sport, and life with confidence and strength.
3. Physiotherapy North York
At our North York clinic, our therapists specialize in rehabilitation and preventative care. We don’t just treat injuries – we help you understand your body better so you can move efficiently, reduce pain, and prevent future setbacks.
4. Physiotherapy Clinic Oakville
Nestled in the heart of Oakville, our clinic offers a calm, supportive space where healing truly begins. Whether you’re dealing with chronic pain, recovering from an injury, or seeking postural correction, our Oakville physiotherapists design personalized plans to get you back to doing what you love.
Why Choose Triangle Physiotherapy?
We know you have choices when it comes to your health – but here’s what makes us stand out:
- Personalized care plans designed around your goals and comfort level.
- Expert clinicians who stay up to date on the latest physiotherapy methods.
- A holistic approach that considers the body, mind, and lifestyle together.
- Convenient locations across the GTA – so expert care is never far away.
When you search for the best physiotherapist near me, we want Triangle Physiotherapy to be your trusted answer – a place where you feel seen, supported, and empowered to move freely again.
Take the First Step Toward Better Movement
Healing doesn’t happen overnight – but with the right team by your side, it happens steadily and meaningfully. Whether you visit us in Toronto, Mississauga, North York, or Oakville, you’ll find a community of professionals ready to help you rediscover your strength.
Book an appointment today at your nearest Triangle Physiotherapy clinic and experience what personalized, compassionate care feels like.
Because when you move better – you live better.
Explore physiotherapy clinics from Toronto to Oakville with Triangle Physiotherapy. Find expert care at our clinics in Toronto, Mississauga, North York, and Oakville. Book today with the best physiotherapist near me for personalized treatment and lasting results.
The ulnar nerve runs from your neck, through your shoulder and elbow, and down into your hand. It’s responsible for sensation in your ring and pinky fingers and plays a key role in fine motor control.
When the nerve becomes compressed-especially around the elbow (in the cubital tunnel)-you may experience:
- Tingling or numbness in the ring and pinky fingers
- Weak grip strength
- Clumsiness when handling small objects
- Elbow pain that worsens when the arm is bent
This condition is called ulnar nerve entrapment, and it’s more common than you might think-especially in athletes, desk workers, and people with repetitive arm motions.
How Ulnar Nerve Therapy Helps
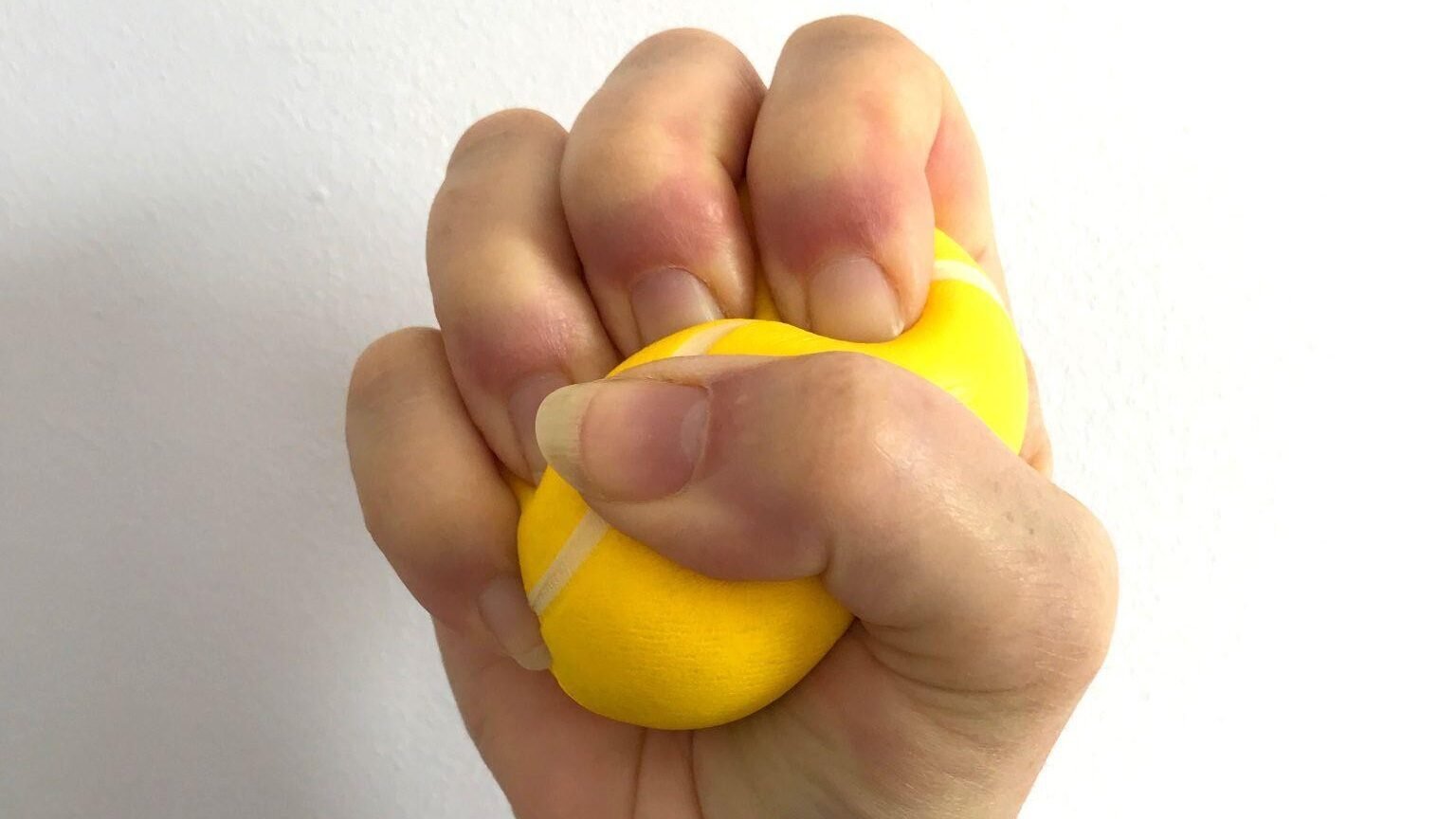

If you’re dealing with symptoms, don’t wait for them to go away on their own. At Triangle Physiotherapy, our team offers targeted, evidence-based ulnar nerve therapy to reduce pressure, improve mobility, and prevent long-term damage.
Here’s what your recovery journey might look like:
1. Assessment & Diagnosis
Your physiotherapist will evaluate your symptoms, movement patterns, posture, and arm function to pinpoint where the nerve is being compressed. This helps rule out other conditions like cervical spine issues or carpal tunnel syndrome.
2. Pain Relief & Protection
In the early stages, we focus on reducing inflammation and minimizing irritation:
- Activity modification (especially avoiding prolonged elbow flexion)
- Ergonomic advice for work and sleep positions
- Gentle modalities to calm irritated tissue
3. Ulnar Nerve Glides
One of the most powerful tools in your recovery toolbox? Ulnar nerve glides.
These are gentle, controlled movements that “floss” the nerve through its pathway-freeing it from areas of compression and restoring its mobility. You’ll learn how to perform them safely and effectively as part of your rehab program.
Bonus: These glides also improve circulation to the nerve, which can accelerate healing and reduce symptoms.
4. Strengthening & Mobility Work
As symptoms improve, your therapist will guide you through a tailored strengthening program to stabilize your shoulder, elbow, and wrist. This may include:
- Grip strengthening
- Postural retraining
- Core and scapular stabilization
- Stretching tight structures that may be contributing to compression
5. Return to Sport or Daily Activity
Whether you’re swinging a tennis racket, lifting weights, or typing for hours a day, we’ll help you safely return to your routine with confidence. We focus on:
- Rebuilding endurance
- Optimizing technique
- Preventing re-irritation
Where to Find Expert Ulnar Nerve Therapy in the GTA

Looking for physiotherapy in North York, Oakville, or Etobicoke? Triangle Physiotherapy has you covered.
Our experienced team offers hands-on treatment and personalized care to address ulnar nerve entrapment and get you back to doing what you love-pain-free and stronger than before.
How to Prevent Ulnar Nerve Issues Long-Term
- Avoid prolonged elbow flexion (especially during sleep)
- Keep good posture during desk work
- Strengthen your upper body to support your arms
- Perform ulnar nerve glides as recommended
- Listen to early signs-don’t ignore the tingling!
Ready to Take the Pressure Off?
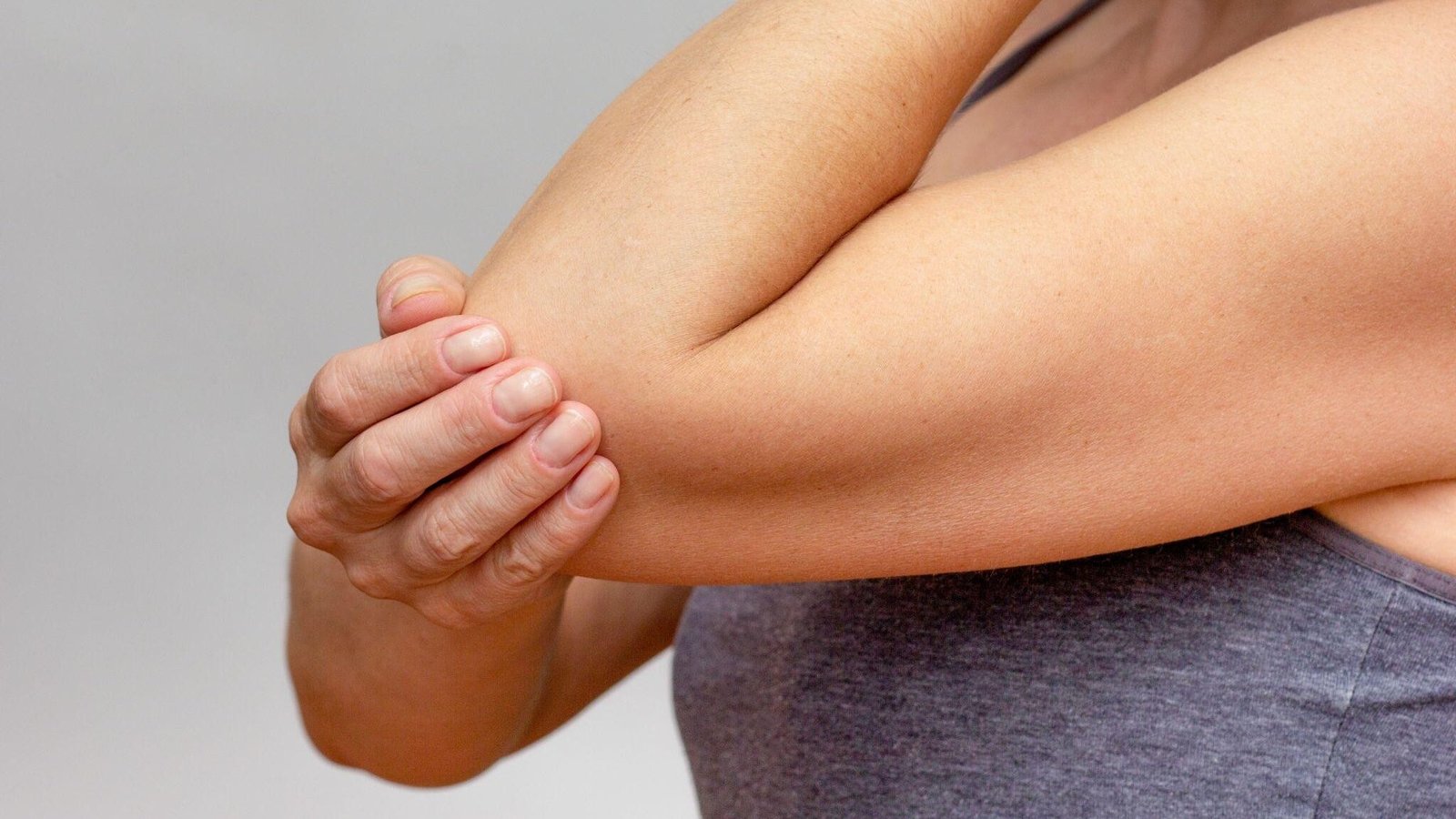

You don’t have to live with tingling hands, weak grip, or elbow pain. Whether you’re an athlete, a weekend warrior, or a dedicated desk worker, ulnar nerve therapy can make a life-changing difference.
Book your appointment today at Triangle Physiotherapy-serving patients across Etobicoke, North York, Oakville, and the Greater Toronto Area.
Let’s get your nerves firing on all cylinders again-no numbness, no limits.
If you’re an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or just someone who enjoys staying active, you know how frustrating sports injuries can be. Whether it’s a sprained ankle from a quick pivot, shoulder pain from weightlifting, or chronic knee strain from running, these injuries don’t just affect your physical performance – they impact your daily life. At Triangle Physiotherapy North York, our mission is to help you recover faster, move better, and prevent future injuries through personalized, expert care.
Why Physiotherapy Is Crucial in Sports Injury Recovery
Physiotherapy plays a vital role in every stage of sports injury rehab – from initial pain relief to long-term performance enhancement. At Triangle Physiotherapy North York, we take a full-body, functional approach to healing. Our experienced team doesn’t just treat your symptoms – we identify the root cause of the injury and build a custom rehab plan around your goals.
We combine advanced techniques like manual therapy, therapeutic exercise, soft tissue release, and even dry needling, all designed to get you back to doing what you love – whether that’s playing a sport, hitting the gym, or enjoying a pain-free walk.
Choosing the Right Sports Rehab Clinic: Why Triangle Stands Out
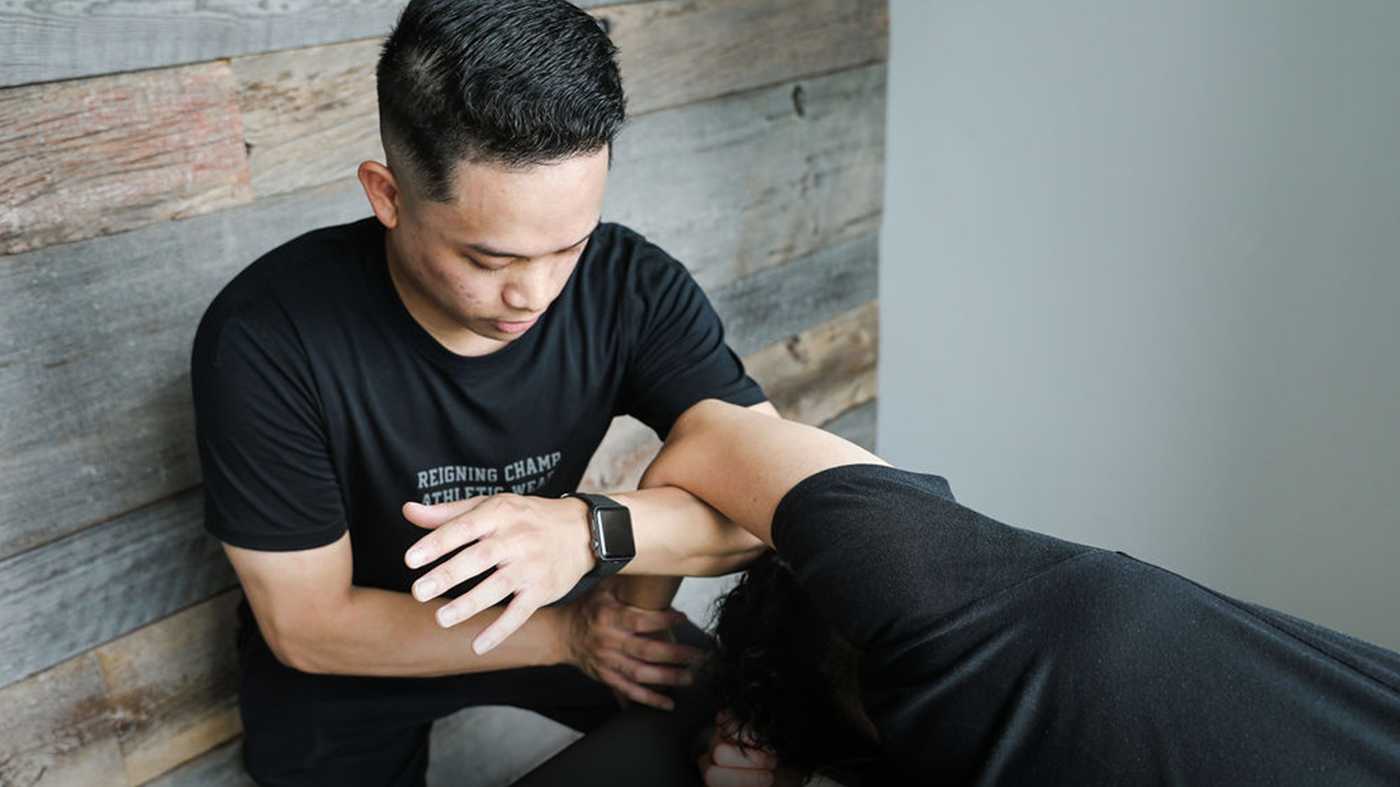

Much like choosing a clinic for back pain relief, selecting the right physiotherapy clinic for sports injuries is crucial to your recovery. Here’s how Triangle Physiotherapy North York makes the process easy and effective:
1. We Understand Your Unique Needs
No two injuries – or patients – are alike. Are you recovering from a torn ligament, muscle strain, or joint overuse? Are you prepping for a marathon or trying to get through your workday pain-free?
At Triangle, we take the time to understand your activity level, movement goals, and pain points. Our North York clinic offers everything from sports injury rehab and mobility training to preventative care and performance optimization – all tailored to your needs.
2. Experience and Evidence-Based Care
With a strong team of skilled and licensed physiotherapists, we deliver care that’s grounded in science and focused on results. Our treatment plans often include strength training, mobility work, posture correction, and ergonomic education – designed not only for short-term relief but long-term success.
Whether you’re recovering from a recent injury or managing chronic pain from overuse, our team in North York is ready to help you rebuild and return stronger.
3. A Supportive Environment That Motivates You
Healing doesn’t happen in a vacuum. That’s why the environment at Triangle Physiotherapy North York is designed to be welcoming, calm, and encouraging. From the front desk to your treatment sessions, our team ensures you feel heard, supported, and empowered throughout your recovery journey.
Ready to Get Back in the Game?
At Triangle Physiotherapy North York, we believe that recovery isn’t just about healing – it’s about thriving. Whether you’re aiming to return to sport, improve your performance, or simply move without pain, our personalized physiotherapy services are here to help.
Book your consultation today and take the first step toward a stronger, healthier, and more confident you.
At Triangle Physiotherapy, we believe that knowledge is the first step toward recovery. One condition that we often see in our clinic is ulnar nerve entrapment. This condition, while common, is often misunderstood. In this blog, we’ll explain what ulnar nerve entrapment is, how it happens, and how physiotherapy can help.
What is Ulnar Nerve Entrapment?
The ulnar nerve is one of the main nerves in your arm, running from your neck down to your hand. It controls the muscles in your forearm and hand, including those responsible for fine motor skills. Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when this nerve becomes compressed or irritated, typically at the elbow or wrist, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the hand and fingers.
This condition is sometimes referred to as “cubital tunnel syndrome” when it happens at the elbow, or “Guyon’s canal syndrome” when it occurs at the wrist. It’s important to address this problem promptly because if left untreated, it can lead to long-term nerve damage and functional impairment.
Causes of Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
Ulnar nerve entrapment can result from various factors, including:
- Repetitive motion: Activities that require repetitive arm movements, like typing, playing certain sports (e.g., tennis or golf), or assembly-line work, can put pressure on the ulnar nerve.
- Prolonged elbow flexion: When your elbow stays bent for long periods, such as when sleeping with your arm in a bent position, it can increase pressure on the ulnar nerve at the cubital tunnel.
- Direct trauma: A blow to the elbow or wrist can cause swelling or scar tissue that compresses the nerve.
- Anatomical issues: Some people are born with anatomical variations that make them more susceptible to ulnar nerve entrapment.
Symptoms of Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
The symptoms of ulnar nerve entrapment vary depending on the severity of the compression but commonly include:
- Numbness or tingling: You may feel a sensation of “pins and needles” in your ring and pinky fingers, especially when bending the elbow.
- Weakness: The muscles in your hand or forearm may feel weak, making it hard to grip or perform tasks that require fine motor skills, such as typing or buttoning a shirt.
- Pain: Sharp or aching pain may radiate from the elbow down to the hand, particularly when leaning on the elbow or holding the arm in a fixed position.
Treatment for Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
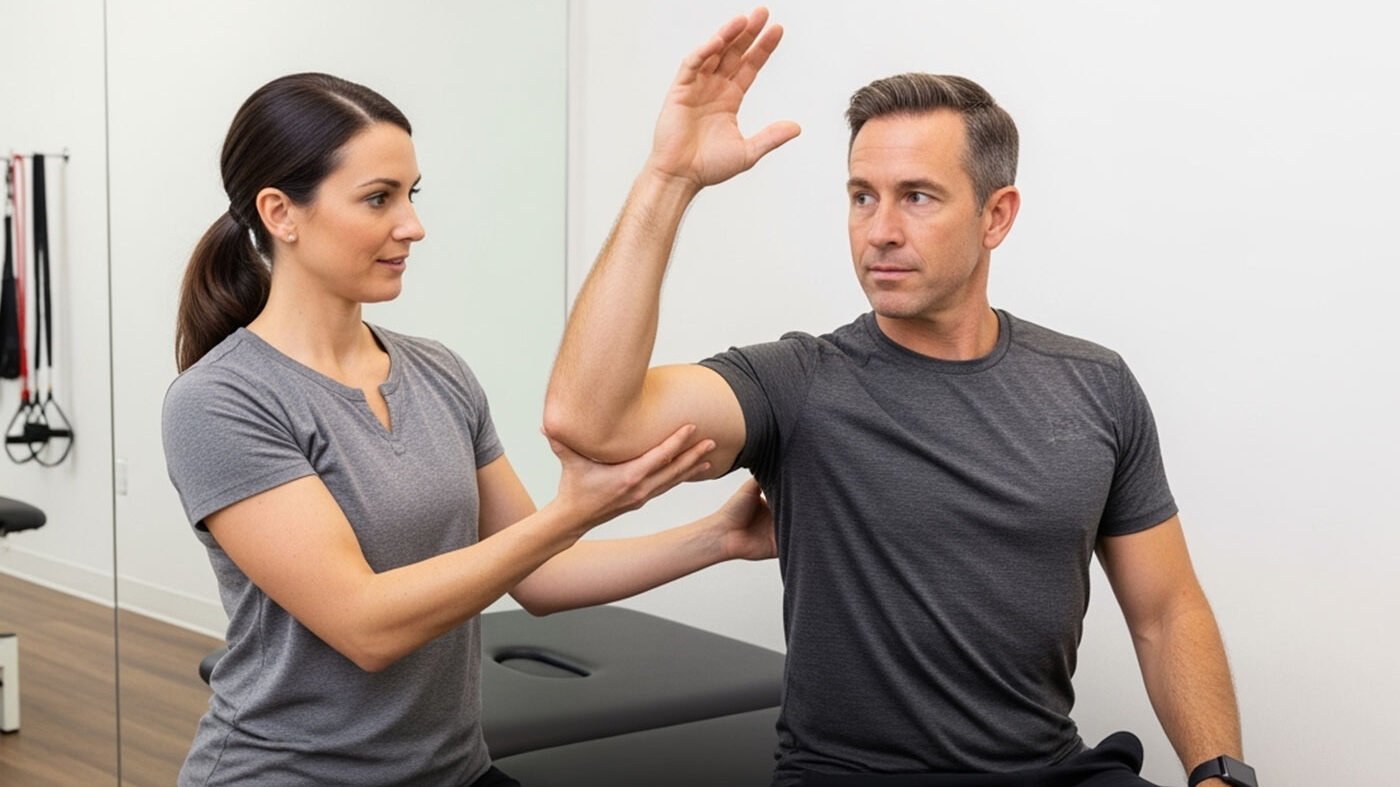

At Triangle Physiotherapy, our goal is to help you recover from ulnar nerve entrapment in a safe, effective, and non-invasive manner. Physiotherapy treatment often includes:
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to relieve tension, improve mobility, and reduce pressure on the ulnar nerve.
- Strengthening Exercises: A program designed to strengthen the muscles in the forearm and hand to help improve nerve function and prevent further injury.
- Stretching and Nerve Gliding Exercises: These exercises gently mobilize the ulnar nerve, helping to reduce tightness and improve circulation around the nerve.
- Ergonomic Advice: We provide recommendations on how to adjust your posture, workstation, or activity patterns to reduce stress on the elbow and wrist.
- IMS: Intramuscular stimulation not only helps you get rid of the symptomatic pain but also helps you trace the root cause of the problem. The results are golden.
In more severe cases, if conservative treatments like physiotherapy don’t bring relief, we may refer you to a specialist for further evaluation or suggest alternative treatments like injections or surgery.
Preventing Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
Prevention is always better than cure. Some simple tips to avoid ulnar nerve entrapment include:
- Taking breaks from repetitive activities
- Avoiding prolonged elbow flexion (e.g., don’t rest your elbow on hard surfaces for long periods)
- Using ergonomic supports like wrist splints during sleep. We help with custom braces especially for your measurements and it is also covered by your insurance.
Conclusion
If you’re experiencing symptoms like hand numbness, tingling, or weakness, ulnar nerve entrapment might be the culprit. The good news is that physiotherapy can be highly effective in alleviating symptoms and preventing future problems. At Triangle Physiotherapy, our team is here to provide personalized care and guide you through the healing process.
Don’t wait for the problem to worsen. Contact us today and take the first step toward a pain-free, more active life!
What to expect and how to feel empowered from day one
When it comes to pelvic health, there’s often a mix of curiosity, concern, and even confusion – especially if you’ve never seen a pelvic physiotherapist before. Whether you’re navigating postpartum recovery, persistent discomfort, or changes with age, know this: you’re not alone, and help is closer than you think.
At Triangle Physiotherapy North York, we know that walking into your first pelvic physiotherapy appointment can feel like a big step. That’s why we’ve created a safe, welcoming environment where education and empathy come first.
Here’s what to expect – plus some helpful prep tips so you can feel confident and informed ahead of your first visit.
What Is Pelvic Physiotherapy?
Pelvic physiotherapy focuses on the muscles, ligaments, and connective tissues that support the bladder, uterus (or prostate), and bowel. When these structures are weak, tight, or not working in coordination, it can lead to issues like:
- Bladder leaks or urgency
- Pain during sex
- Constipation
- Pelvic or lower back pain
- Heaviness or pressure in the pelvic region
- Discomfort during movement or exercise
Pelvic physiotherapy in North York is designed to assess and treat these concerns through a combination of hands-on therapy, targeted exercises, posture training, and patient education.
What Happens at Your First Appointment?
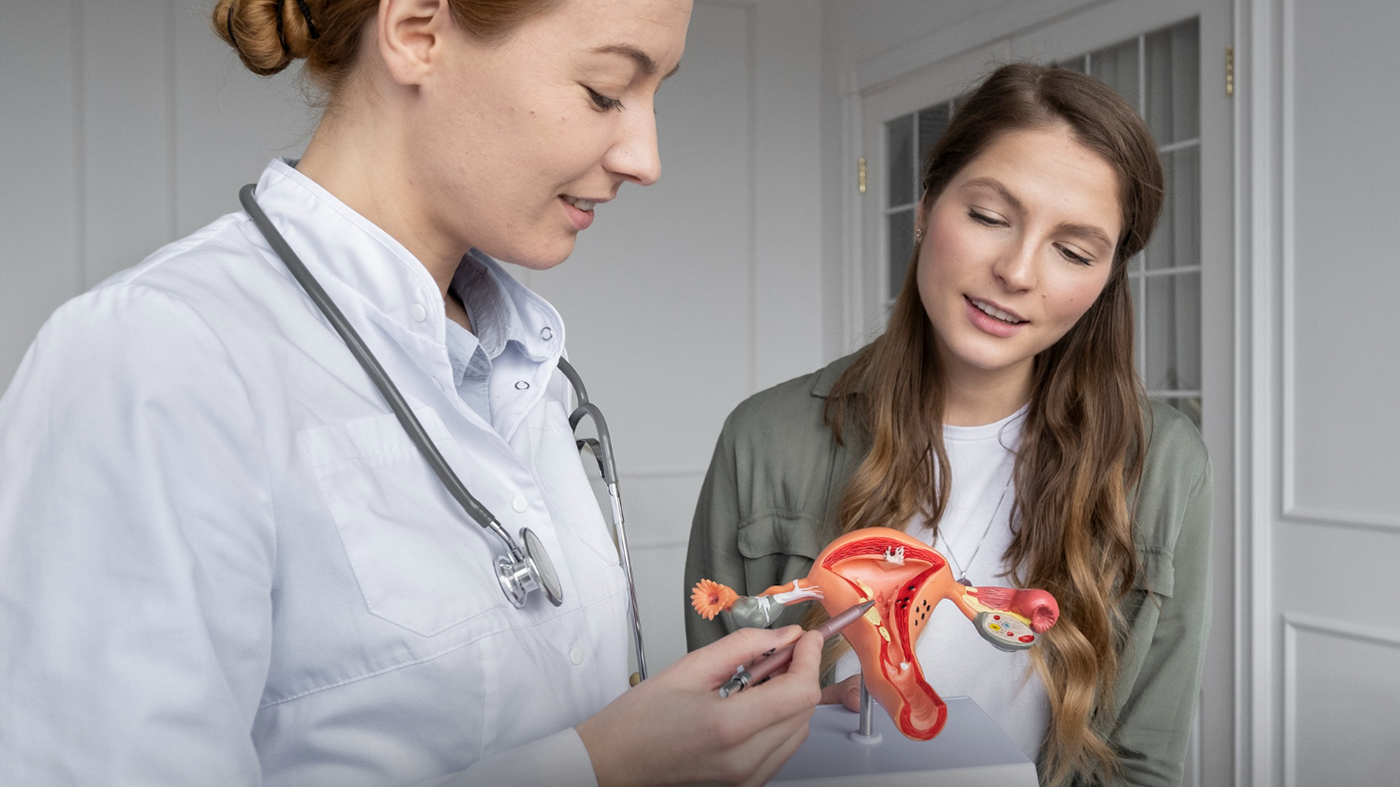

Your first session at Triangle Physiotherapy North York will feel a lot like a detailed conversation mixed with gentle movement-based assessment.
Here’s a breakdown of what to expect:
- History & Concerns: We start with your story. This includes your symptoms, medical background, lifestyle habits, and any previous injuries or surgeries.
- Education & Consent: We explain how the pelvic floor functions and what could be contributing to your symptoms. If an internal assessment is helpful, it’s discussed with complete transparency and only done with your full, informed consent.
- Movement & Posture Check: You may be asked to walk, squat, or move in certain ways so we can observe muscle coordination and alignment.
- Personalized Plan: Based on your needs, we build a care plan with treatment goals, exercises, and follow-up recommendations.
The goal? Helping you feel heard, informed, and never rushed. You’re in charge of your journey – we’re simply your support team.
Tips Before You Arrive
- Wear comfy clothes that let you move freely
- Bring a list of symptoms, questions, or goals
- Come with an open mind – pelvic physio is often gentler and more holistic than people expect
Why Triangle Physiotherapy North York?
We take pride in being a trusted name for pelvic physiotherapy in North York, with an emphasis on:
- Respectful, patient-centered care
- Highly trained pelvic health therapists
- Private, one-on-one sessions
- Flexible scheduling and direct billing options
- A clinic culture that prioritizes comfort, dignity, and real progress
Your First Step Starts Here
Taking care of your pelvic health is nothing to be shy about – it’s an important part of your well-being. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or just want to better understand your body, we’re here to help.
Book your initial pelvic physiotherapy session at Triangle Physiotherapy North York today. Your comfort, confidence, and health matter here.











