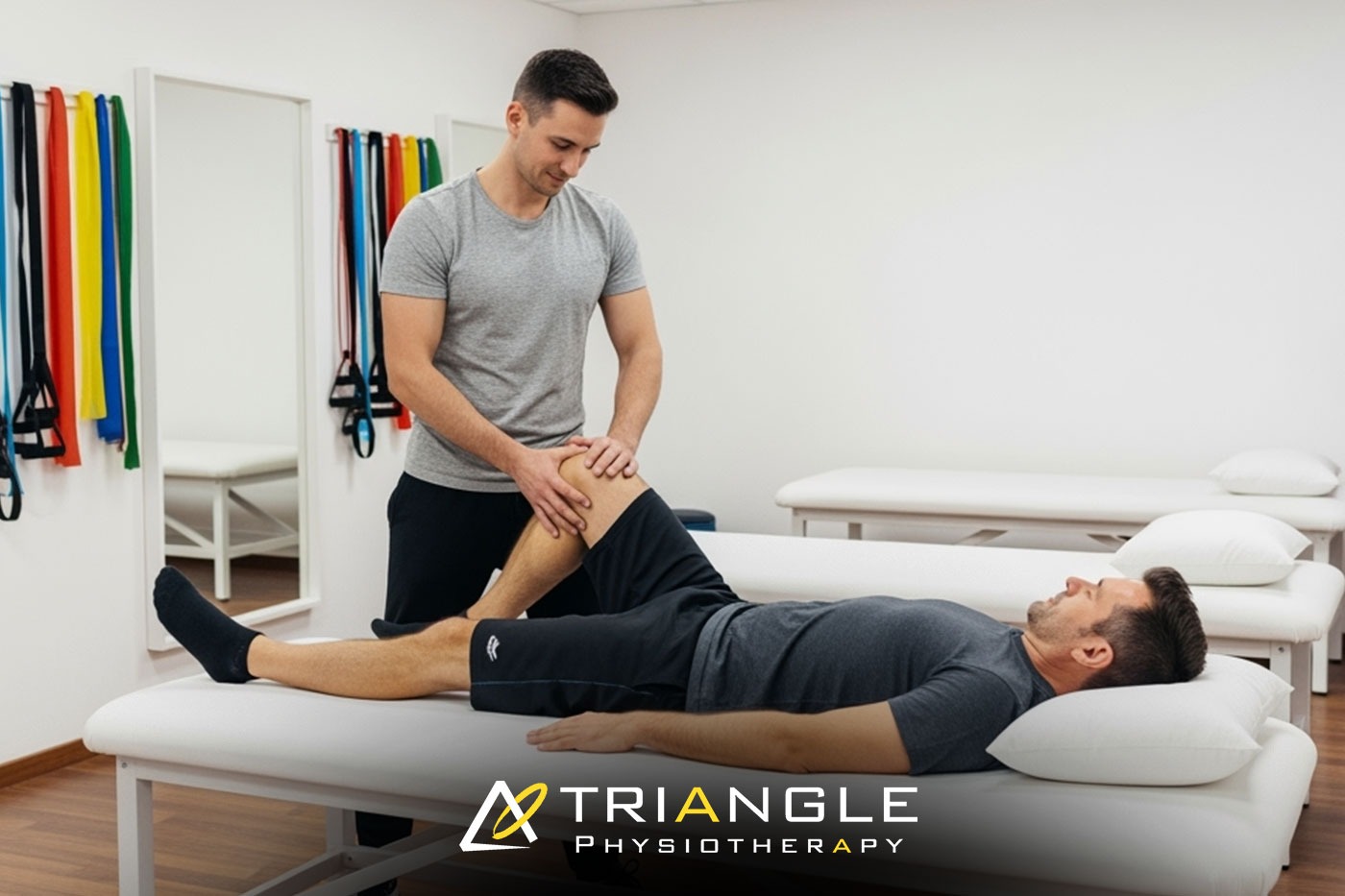
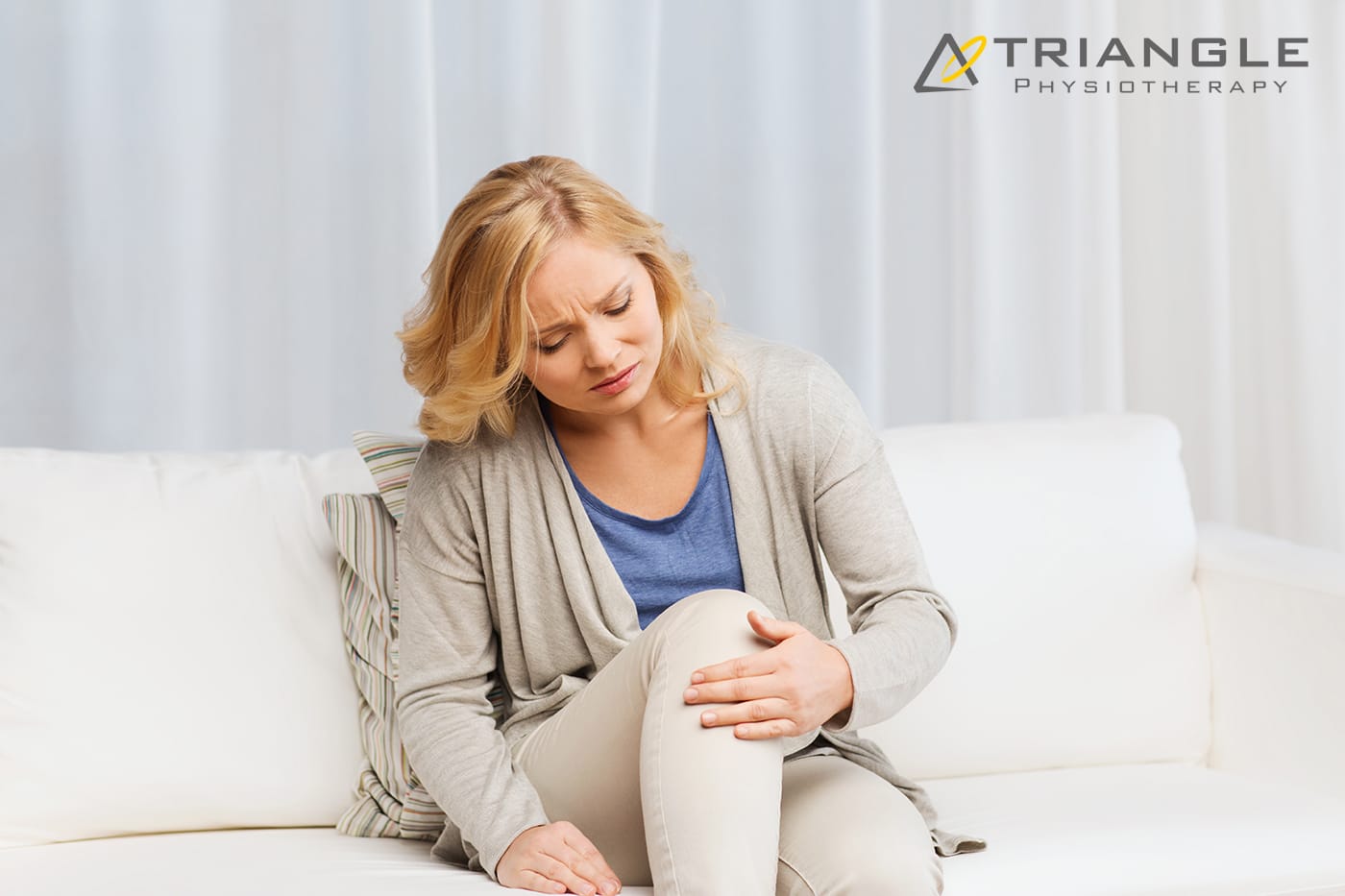
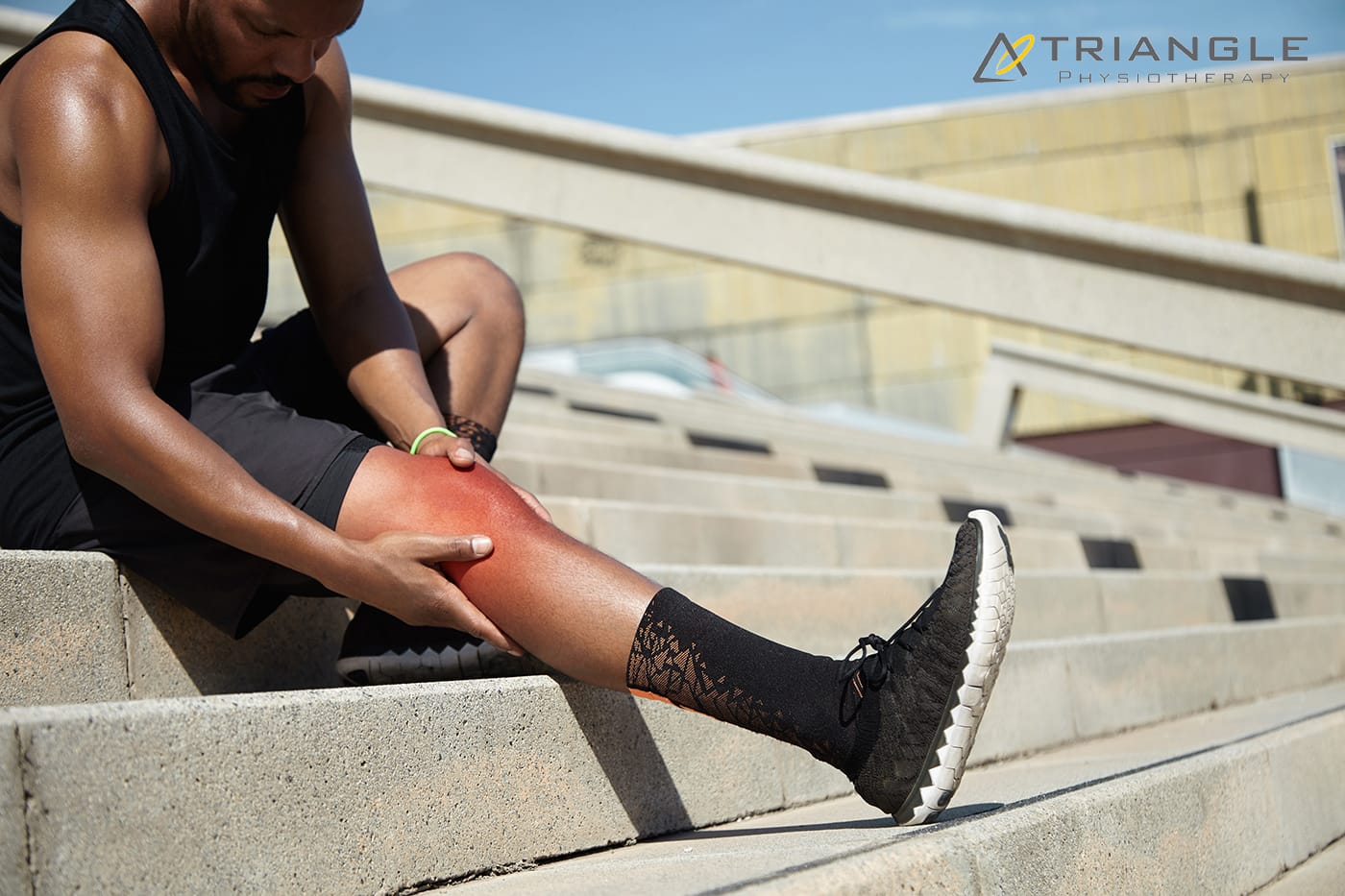
Knee discomfort can impact each step you take – whether it arises from aging, sports injuries, or chronic issues. If you’re looking for physiotherapy in Mississauga or asking, “Where can I find a top physiotherapist close to me?“, you’re not alone. Millions of Canadians suffer from knee discomfort annually, and physiotherapy provides one of the most effective, non-invasive means for sustainable relief.
In this article, we’ll examine how the skilled physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga can assist you in restoring mobility, alleviating pain, and returning to the activities you enjoy.
Understanding the Causes of Knee Pain
Knee discomfort can originate from multiple sources, and recognizing the underlying cause is crucial for successful treatment.
Some of the most prevalent causes include:
- Osteoarthritis
- Meniscus tears
- Ligament injuries (ACL, MCL)
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome
- Overuse injuries or repetitive strain
These conditions can affect adults and seniors, restricting independence and diminishing quality of life. That’s where skilled physiotherapy becomes essential.
Why Choose Physiotherapy for Knee Pain?
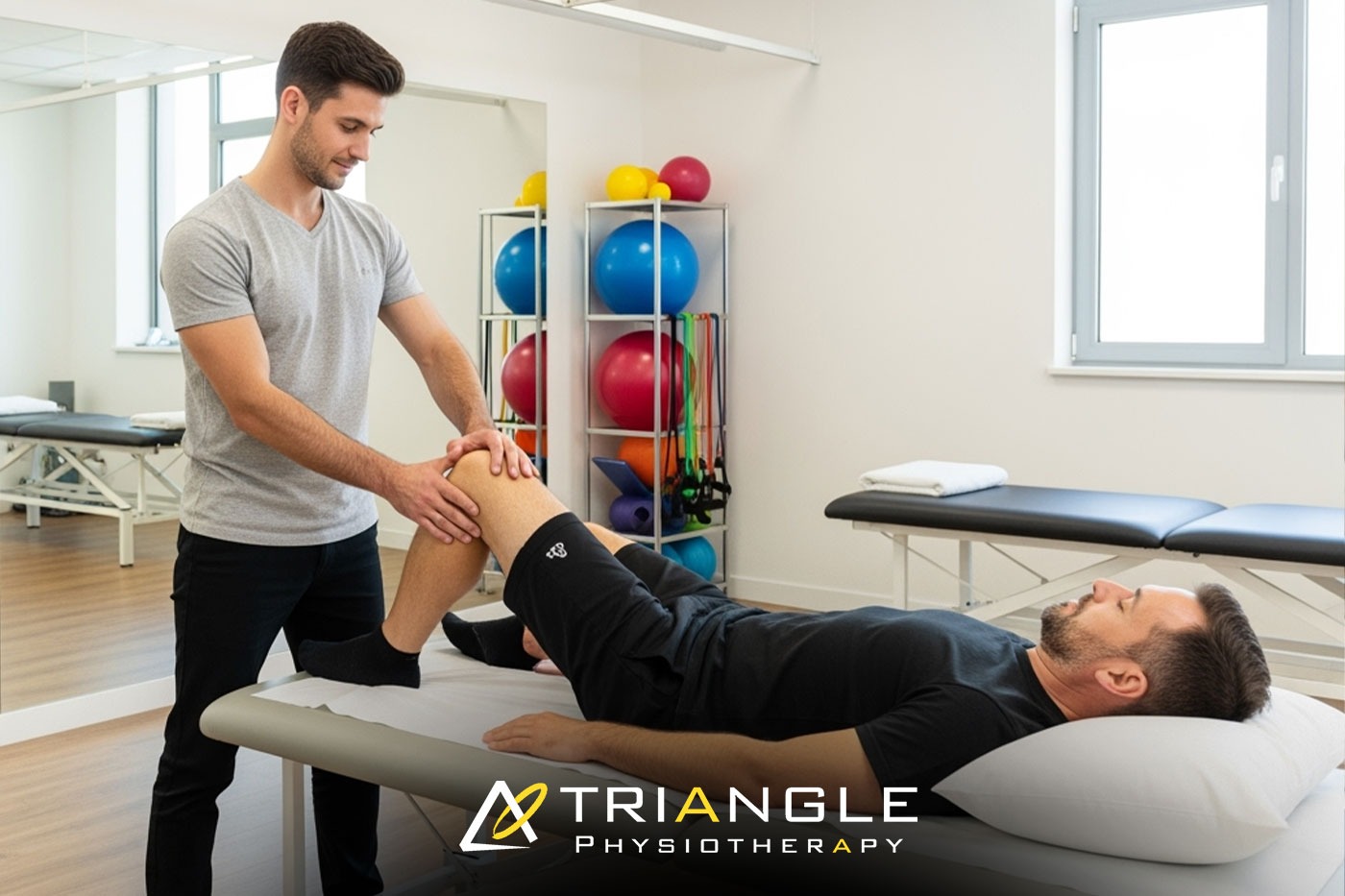

Whether you’re coping with chronic knee discomfort or healing from an injury, physiotherapy nearby is often the initial approach to treatment.
Here’s why:
- Targeted Treatment Plans: Customized exercises and manual therapy concentrated on your specific condition.
- Non-Invasive Relief: Avoid surgical procedures with effective physiotherapy methods.
- Enhanced Mobility and Strength: Restore function to muscles and joints for long-term well-being.
- Pain Management Without Medication: Decrease or eliminate the reliance on pain medications.
At Triangle Physiotherapy, our knowledgeable team adopts a patient-centered approach to care.
What to Expect at Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
When you schedule your initial visit at our physiotherapy clinic in Mississauga, here’s what you will experience:
- Thorough Evaluation Our certified physiotherapists conduct a complete assessment of your knee, gait, posture, and overall biomechanics to pinpoint the issue’s source.
- Customized Treatment Strategy We create a plan that suits your requirements, which may encompass – Manual therapy – Therapeutic ultrasound – Intramuscular Stimulation – Joint mobilization – Strength and flexibility exercises – Taping and bracing (if necessary)
- Continuous Support & Education We equip you with exercises for home and preventive advice to guarantee lasting results. Our team tracks progress and modifies your treatment as necessary.
Are you on the lookout for a top physiotherapist nearby? Triangle’s team in Mississauga boasts extensive expertise in treating various knee injuries and age-related conditions.
Benefits of Physiotherapy for Seniors with Knee Pain
As we age, joint degeneration tends to become more frequent – especially in weight-bearing joints such as the knees.
Seniors in Mississauga looking for physiotherapy nearby can reap benefits including:
- Enhanced balance and stability
- Decreased pain and inflammation
- Greater range of motion
- Improved quality of life
Triangle Physiotherapy provides a secure, encouraging environment for older adults to recover and strengthen.
When to See a Physiotherapist
If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, it’s time to schedule an assessment:
- Ongoing or worsening knee pain
- Swelling or stiffness
- Trouble walking or ascending stairs
- Popping or grinding sounds in the knee
- Limited mobility or strength
Don’t postpone addressing the pain that could take over your life – physiotherapy in Mississauga is only a phone call away.
Why Triangle Physiotherapy Is Your Best Choice
Are you using the search terms “physiotherapy clinic near me” that focuses on knee discomfort? Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga distinguishes itself by:
- Skilled, certified physiotherapists
- Individualized care and bespoke treatment
- Convenient location and adaptable appointment times
- Advanced equipment and evidence-based methodologies
Book Your Appointment Today
Don’t let knee pain hold you back. Whether you’re an active adult, a senior, or recovering from an injury, Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga is here to help. Our expert team is ready to guide you every step of the way toward lasting relief.
📍 Looking for physiotherapy near me or the best physiotherapist near me?
📞 Contact Triangle Physiotherapy today and take the first step toward pain-free movement.
After menopause, women face an increased risk of knee injuries due to hormonal changes, decreased muscle strength, and other age-related factors. These changes, combined with weight gain and joint instability, can make the knees more vulnerable. However, with the right prevention strategies, knee injuries can be minimized, allowing you to stay active and pain-free. Give us a call at one of our Toronto locations and our physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy can help you.
What Causes Knee Injuries in Post-Menopausal Women?
Several factors contribute to knee injuries in post-menopausal women, including:
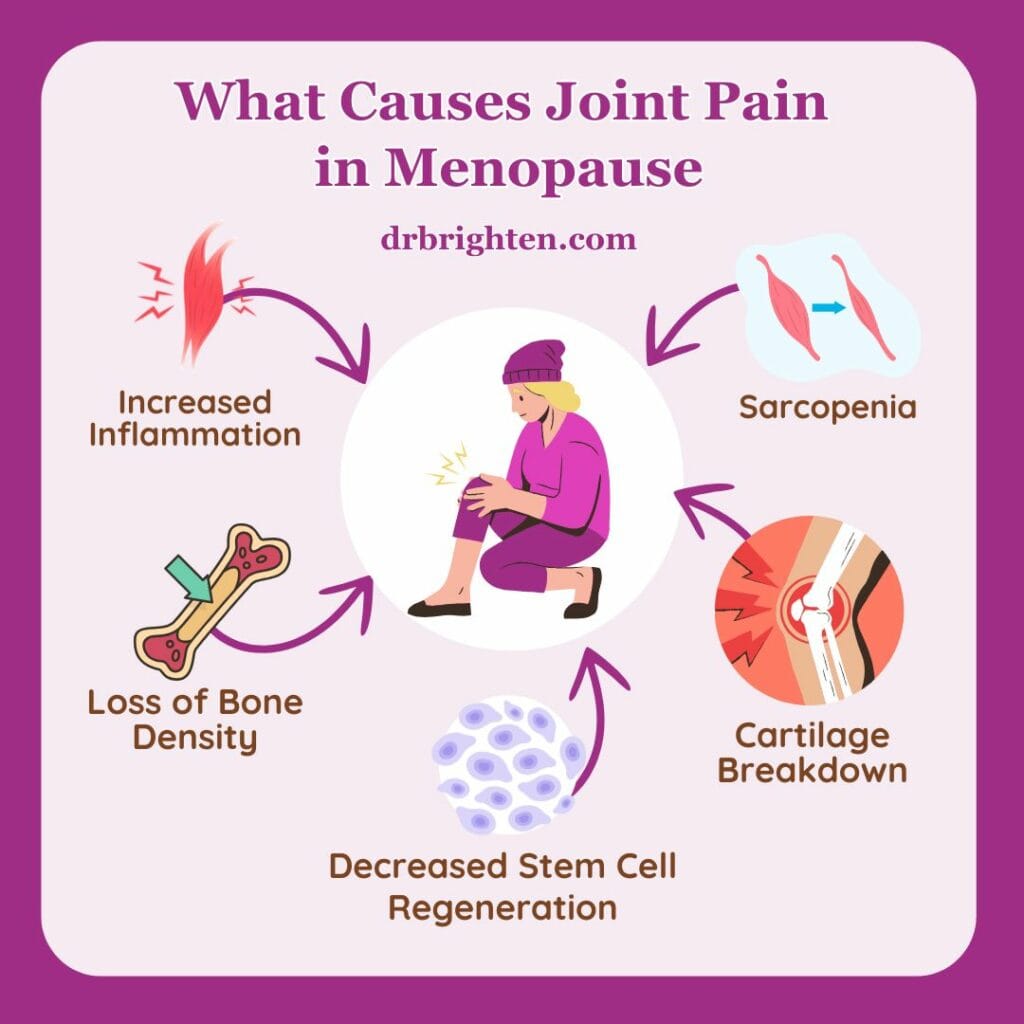
- Hormonal Changes: The drop in estrogen after menopause can weaken bones, muscles, and ligaments, increasing the risk of knee injuries.
- Muscle Weakness: Aging leads to a natural decline in muscle mass, which weakens the muscles surrounding the knee, leaving it less supported.
- Joint Instability: Weakened muscles and bones contribute to joint instability, making the knee more prone to sprains, strains, and tears.
- Weight Gain: Many women gain weight after menopause, which places added stress on the knee joints, leading to pain and increasing the risk of conditions like osteoarthritis.
Common Knee Injuries Post-Menopause
Some of the most common knee injuries women face include:
- Osteoarthritis: A condition where the knee’s cartilage wears down, causing pain and stiffness.
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Pain around the kneecap often caused by overuse or poor alignment.
- Ligament Injuries: Sprains or tears in the knee’s ligaments, such as the ACL or MCL, from sudden movements or falls.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons, usually due to overuse or muscle imbalances.
Preventing Knee Injuries
Here are some essential physiotherapy tips to help prevent knee injuries post-menopause:
- Strengthen Muscles Around the Knee: Build strength in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves through exercises like squats and lunges to support the knee joint.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight adds stress to the knees, so managing weight through diet and exercise can reduce knee strain.
- Increase Mobility: Stretching the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves can prevent tightness, but having overall mobility helps keep the joints healthy.
- Low-Impact Exercises: Activities like swimming, cycling, or walking are easier on the knees while still strengthening muscles and improving cardiovascular health.
- Strengthen Core and Hips: Strong core and hip muscles improve overall stability, reducing strain on the knees.
- Wear Supportive Footwear: Shoes with proper arch support and cushioning can reduce stress on the knees, especially during physical activities.
- Use Proper Technique: Ensure correct form when exercising, lifting, or performing daily tasks to avoid unnecessary stress on the knees.
- Balance Exercises: Improve stability and prevent falls with exercises that challenge balance, such as standing on one leg.
Managing Knee Injuries
If knee pain or injury occurs, here are some strategies for managing it:
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can design a program to improve strength, flexibility, and mobility, helping you recover and prevent further injury.
- Braces or Sleeves: Knee supports can provide stability and reduce pain during activity.
Conclusion
Post-menopausal women are at higher risk for knee injuries, but with proactive care, the risk can be minimized. Strengthening the knee muscles, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good form are key to keeping your knees healthy. If knee pain occurs, working with a physiotherapist and using the right treatments can help you stay active and injury-free. Book an appointment with one of the physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy in Toronto to get help today!
Knee pain can significantly impact your daily activities and overall quality of life. Whether it’s due to an injury, arthritis, or overuse, finding effective relief is essential. Physiotherapy is a valuable tool in managing knee pain, providing strategies to alleviate discomfort and improve function. Whether your knee pain is from a fall, a sports injury, arthritis or everyday aches and pains, our physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy are here to help you navigate your recovery.
Understanding Knee Pain
Knee pain can arise from various conditions, including ligament injuries, tendonitis, bursitis, post-surgery or osteoarthritis. The pain may manifest as sharp, dull, or throbbing sensations, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment. Physiotherapy takes a comprehensive approach to address not only the symptoms but also the root cause of the pain.
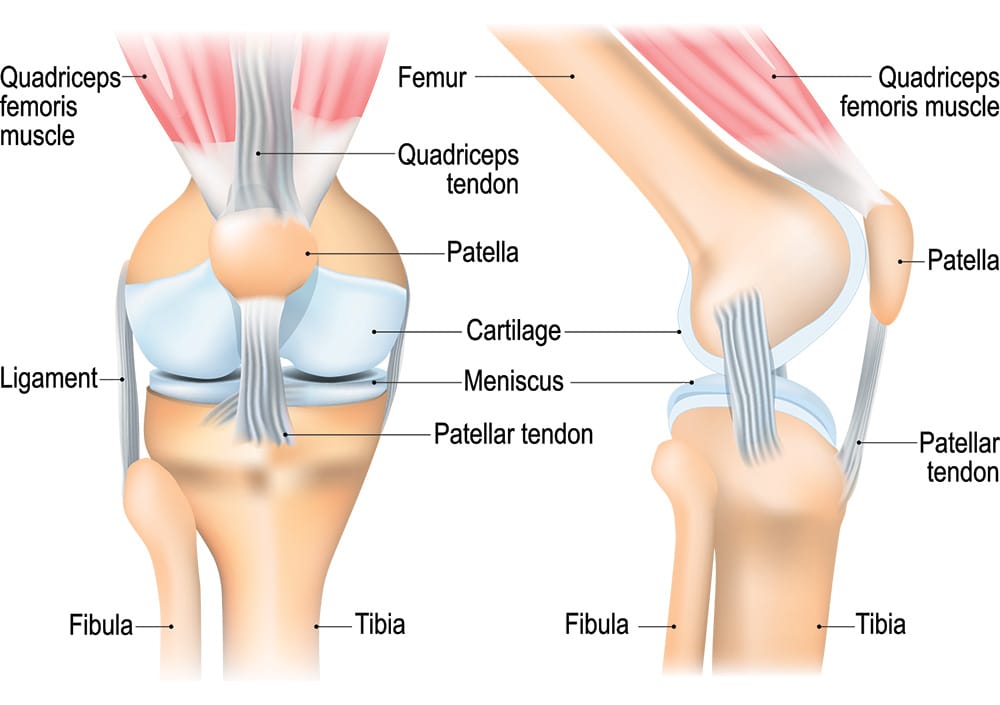
The Role of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy offers a structured treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. A physiotherapist will conduct a thorough assessment, reviewing your medical history and evaluating your knee’s function. Based on this assessment, they will develop an individualized treatment plan focused on relieving pain, restoring mobility, and strengthening the muscles around the knee.
Pain Management Techniques for Knee Pain
Physiotherapists employ various techniques to manage knee pain effectively. These can include:
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to mobilize the knee joint and surrounding tissues, reducing stiffness and improving range of motion.
- IMS: Intra muscular Stimulation is an effective tool to trace and treat the root cause, reducing recurrence.
- Modalities: Methods such as ultrasound, heat, or cold therapy can help alleviate pain and inflammation. Read about PEACE and LOVE protocol instead of PRICE.
- Education: Learning about your condition, including proper body mechanics and strategies to avoid aggravating your knee, is vital for long-term management.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee is crucial for stability and pain relief. Physiotherapists will guide you through targeted exercises that focus on the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves. These exercises help improve strength and support the knee joint, reducing strain and preventing further injuries.
Mobility and Flexibility
Maintaining mobility and flexibility in the knee is essential for functional movement. Physiotherapy includes stretching exercises and gentle range-of-motion activities to help restore flexibility and reduce stiffness. This focus on mobility not only alleviates pain but also enhances your overall physical activity levels.
Knee Pain Prevention Strategies
Preventing future knee pain is a key aspect of physiotherapy. Your physiotherapist will educate you on proper techniques for daily activities, including walking, climbing stairs, and exercising. They will also address any risk factors, such as muscle imbalances or poor posture, to help you avoid re-injury.
FAQs
Can a physiotherapist help with my knee pain?
Yes, physiotherapists specialize in treating knee pain through tailored rehabilitation programs that target the underlying causes and symptoms.
What should I expect during my first visit to Triangle Physiotherapy?
During your first visit, you’ll undergo a comprehensive assessment, where your physiotherapist will evaluate your knee’s condition, discuss your medical history, and outline your treatment goals. A personalized plan will be created based on this information.
How many sessions will I need?
The number of sessions varies depending on the severity of your knee pain and your progress. Some patients may notice improvement in a few sessions, while others may require ongoing treatment. Your physiotherapist will provide an estimate during your assessment.
Do I need a referral to see a physiotherapist?
No, you do not need a referral to access physiotherapy services. You can book an appointment directly, unless required by your insurance for billing purposes.
How soon can I expect pain relief?
Many patients report relief within a few sessions, but the timeline may vary based on individual circumstances and the underlying cause of the knee pain.
How can I ensure effective management of my knee pain?
Engaging in physiotherapy, adhering to your rehabilitation plan, and performing prescribed exercises regularly are vital for managing knee pain effectively. Open communication with your physiotherapist will also help track your progress.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy is a powerful resource for managing knee pain. By understanding the nature of your condition and engaging in a tailored treatment plan, you can alleviate pain, restore function, and improve your quality of life. If you’re struggling with knee pain, consider the benefits that physiotherapy can provide in your recovery journey. To get help for your knee pain, you can call any of the locations of Triangle Physiotherapy or simply Book An Appointment online.
IT Band Syndrome (Iliotibial Band Syndrome) is a common condition among athletes and active individuals, characterized by pain on the outside of the knee. This pain is typically caused by inflammation of the IT band, a thick band of connective tissue running along the outer thigh from the hip to the shin.
Understanding the causes, effective treatment strategies, and prevention methods can help you manage and avoid this frustrating condition. Let’s delve into what IT Band Syndrome is, how to treat it, and strategies to prevent it from recurring.
Causes of IT Band Syndrome
IT Band Syndrome often develops due to repetitive stress and overuse of the knee joint. Several factors can contribute to this condition:
- Overuse: Repeatedly performing activities that involve knee flexion and extension, such as running or cycling, can lead to IT band irritation.
- Biomechanical Issues: Abnormalities in your gait or foot mechanics, like overpronation or leg length discrepancies, can increase stress on the IT band.
- Muscle Imbalances: Weakness or tightness in the muscles of the hip, thigh, or calf can affect the alignment and function of the IT band.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or cushioning can contribute to the development of IT Band Syndrome.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: Rapidly increasing the intensity or duration of physical activity without proper conditioning can strain the IT band.
Importance of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a crucial component in both the treatment and prevention of IT Band Syndrome. A physiotherapist can help by:
- Assessing and Diagnosing: They will evaluate your movement patterns, muscle strength, and flexibility to pinpoint the underlying issues contributing to your symptoms.
- Developing a Treatment Plan: A tailored treatment plan may include exercises, manual therapy, and advice on activity modifications to alleviate pain and prevent recurrence.
- Education and Guidance: Physiotherapists provide valuable education on injury prevention, proper technique, and ways to incorporate exercises into your routine.
Key Principles of Physiotherapy
- Pain Relief: The initial focus is on managing pain and inflammation. This might involve rest, ice application, and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Gradual Loading: Gradually reintroducing activity is important to avoid further strain. This includes slowly increasing exercise intensity and duration.
- Muscle Balance and Alignment: Addressing any muscle imbalances and ensuring proper alignment can help reduce the stress on the IT band.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles around the hip and knee can help support the IT band and reduce the risk of future injuries. Effective exercises include:
- Clamshells: Lie on your side with knees bent and feet together. Lift the top knee while keeping your feet touching. This strengthens the hip abductors.
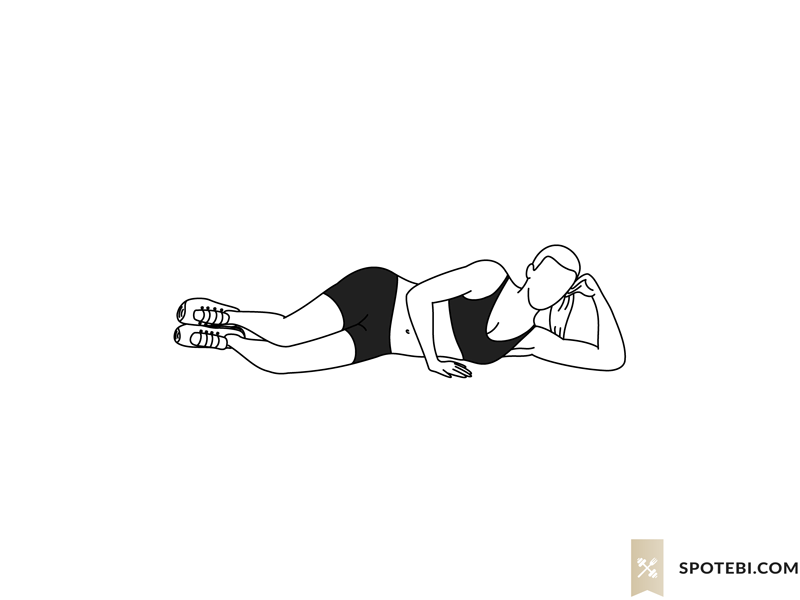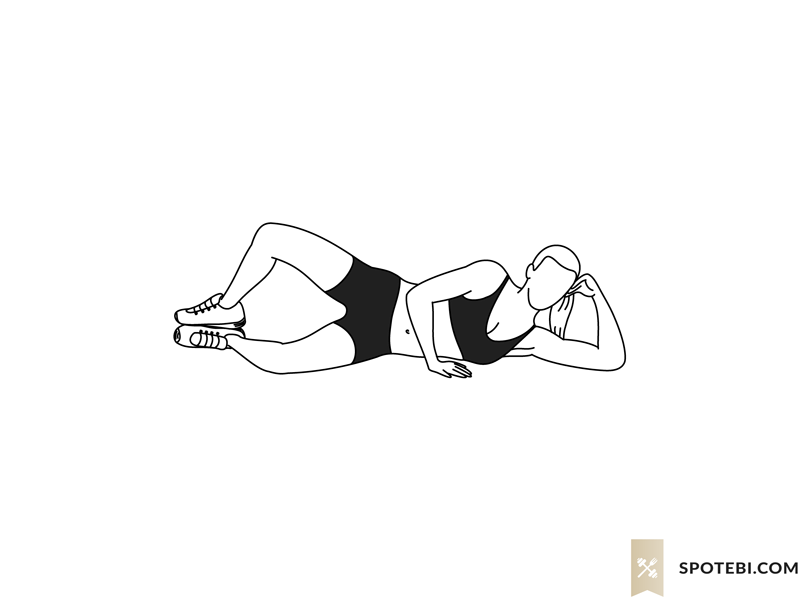
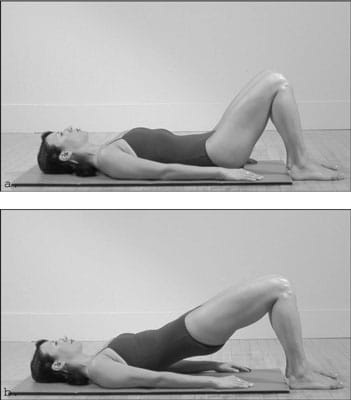
- Bridges: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Lift your hips towards the ceiling, then lower them back down. This exercise targets the glutes and hamstrings.
Neuromuscular Exercises
Neuromuscular exercises improve coordination and muscle function, which can aid in injury prevention and recovery:
- Single-Leg Squats: Perform squats on one leg to enhance balance and strength. Start with a small range of motion and gradually increase as strength improves.
- Step-Ups: Step onto a platform with one foot and then back down. This exercise helps improve the strength and control of the hip and knee.
Proprioceptive Exercises
Proprioceptive exercises help improve your body’s awareness of its position, which is vital for maintaining proper movement mechanics:
- Balance Board Exercises: Stand on a balance board and try to maintain stability. This enhances proprioception and ankle stability.
- Bosu Ball Work: Perform exercises such as squats or lunges on a Bosu ball to challenge your balance and coordination.
Incorporating Mobility
Maintaining and improving joint mobility is essential for overall function and injury prevention:
- Foam Rolling: Use a foam roller to massage and release tightness in the IT band and surrounding muscles.
- Dynamic Stretching: Incorporate dynamic stretches such as leg swings and hip circles into your warm-up routine to improve flexibility and range of motion. Try performing the static stretch for ITB in standing as well. Ensure to work on glute medius and hip flexors along with ITB. Learn to brace the core well. Avoid full/deep ROM exercises till you feel better. Using a half foam roller to squat down is better than squatting through pain.
Understanding IT Band Syndrome and implementing effective treatment and prevention strategies can help you manage this condition and maintain an active lifestyle. Physiotherapy plays a vital role in addressing pain, improving function, and preventing future issues. By focusing on strengthening, neuromuscular, proprioceptive exercises, and incorporating mobility work, you can support your recovery and reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Remember to follow safety tips and consult with healthcare professionals to tailor a plan that best suits your needs. With the right approach, you can overcome IT Band Syndrome and get back to enjoying your favorite exercises.
Are you ready to get that IT Band Injury resolved? Contact Triangle Physiotherapy to schedule an Initial Assessment and get on the road to recovery!
Our Toronto locations are conveniently located with easy transit access:
An ACL tear can be a significant setback, especially for athletes and active individuals. The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament), located in the knee, plays a crucial role in stabilizing and allowing movement. When it’s torn, physiotherapy becomes essential for a successful recovery. In this guide, we’ll explore the causes of ACL tears, prevention strategies, and the various physiotherapy techniques that can aid in recovery.
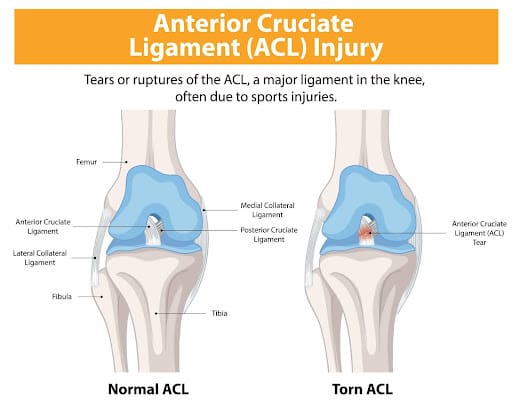
Causes of ACL Tears
What It Is: The ACL is a ligament in the knee that helps stabilize the joint and control movement. An ACL tear is a common knee injury, particularly in sports.
Common Causes:
- Sudden Stops and Starts: Rapid changes in direction or sudden stops can put excessive stress on the ACL.
- Direct Impact: A blow to the knee or a collision, common in contact sports like football or basketball, can cause the ACL to tear.
- Improper Landing: Landing awkwardly from a jump or fall can also strain the ACL.
Prevention Strategies
How to Reduce Risk: While not all ACL tears can be prevented, taking certain measures can significantly lower your risk.
- Strength Training: Strengthen the muscles around your knee, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles, to provide better support and stability.
- Proper Technique: Learn and practice proper techniques for jumping, landing, and pivoting to reduce stress on your knee.
- Warm-Up: Always warm up before engaging in sports or strenuous activities to prepare your muscles and joints for the demands ahead.
Resistance Exercises
Purpose: Resistance exercises help build strength in the muscles surrounding the knee, which is crucial for stabilizing the joint and aiding recovery. The ones mentioned below are to be performed in the latter stages of rehab, with professional help.
Examples:
- Squats: Perform squats with proper form to strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Leg Press: Use a leg press machine to work on lower body strength while controlling the range of motion.
- Lunges: Lunges help in building strength and balance in the legs, targeting various muscle groups around the knee.
How to Do Them Safely: Start with light weights or bodyweight, gradually increasing the resistance as your strength improves. Focus on maintaining proper form to avoid additional strain.

Neuromuscular Exercises
Purpose: Neuromuscular exercises enhance the communication between your brain and muscles, improving coordination and balance.
Examples:
- Balance Boards: Standing on a balance board helps improve stability and proprioception (awareness of your body’s position in space).
- Single-Leg Stands: Practice standing on one leg to strengthen stabilizing muscles and improve balance.
- Agility Drills: Incorporate ladder drills or cone drills to enhance agility and neuromuscular control.
How to Do Them Safely: Start with easier exercises and gradually progress to more challenging ones as your balance and coordination improve.
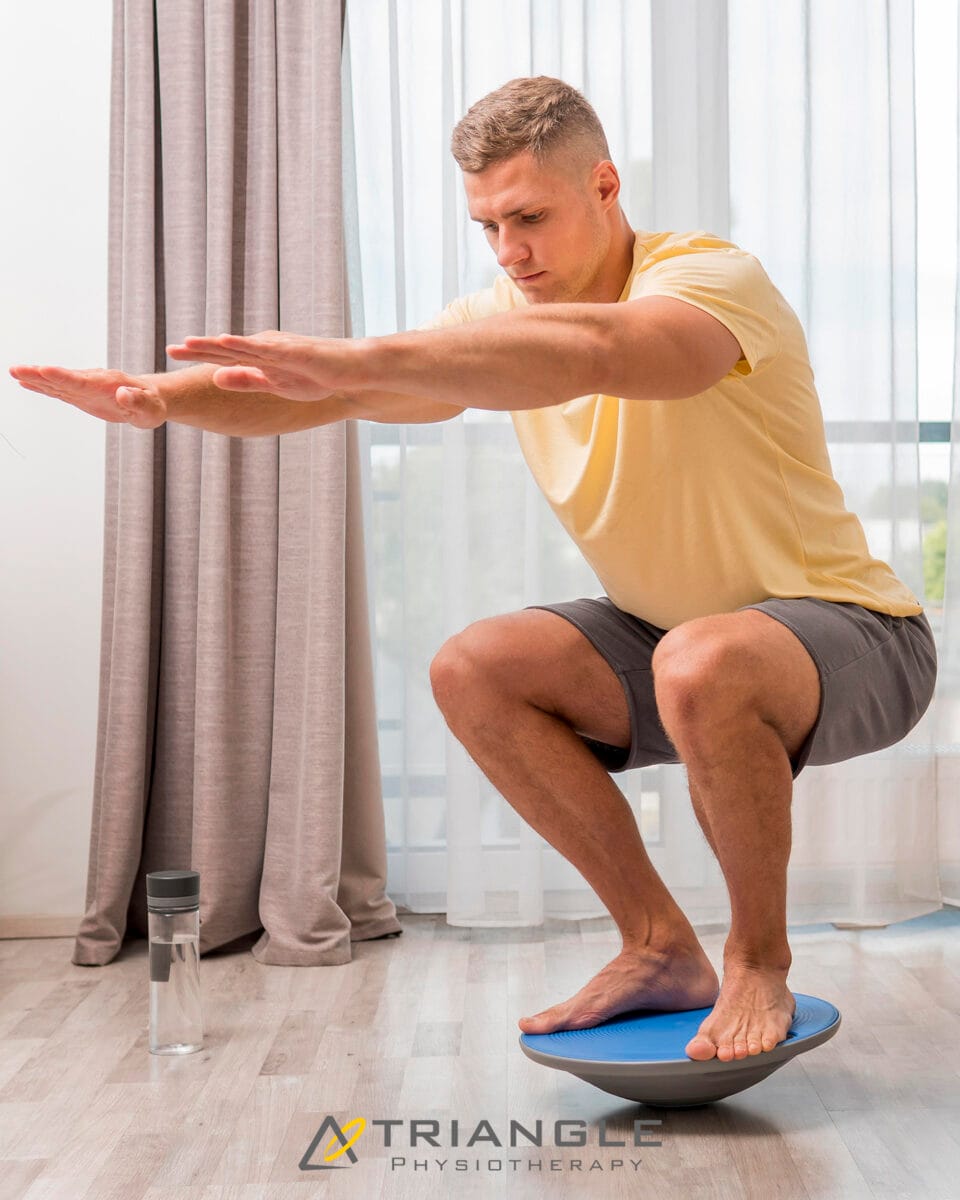

Progressive Exercises
Purpose: Progressive exercises are designed to gradually increase in difficulty, helping to build strength and endurance while avoiding overexertion.
Examples:
- Step-Ups: Begin with low steps and gradually increase the height as your strength and stability improve.
- Resistance Bands: Use resistance bands to add progressive resistance to leg exercises, adjusting the band’s tension as needed.
- Cycling: Start with short, low-resistance cycles and progressively increase duration and resistance.
How to Do Them Safely: Follow a structured program that gradually increases the intensity and complexity of exercises to prevent overuse injuries.
Stretching and Strengthening
Purpose: Stretching maintains flexibility and prevents stiffness, while strengthening exercises build the muscle support necessary for knee stability.
Examples:
- Hamstring Stretch: Gentle stretching of the hamstrings can help maintain flexibility and reduce tension in the knee.
- Quadriceps Stretch: Stretch the quadriceps to keep the front of the thigh flexible and balanced.
- Strengthening Exercises: Incorporate exercises like leg lifts and bridges to build muscle strength around the knee.
How to Do Them Safely: Perform stretching exercises slowly and hold each stretch for 20-30 seconds. Strengthening exercises should be done with controlled movements and proper form.
Mobility Routine
Purpose: A mobility routine focuses on improving the range of motion and function of the knee joint.
Examples:
- Knee Circles: Perform gentle knee circles to increase flexibility and mobility.
- Heel Slides: Lie on your back and slide your heel towards your buttocks to improve knee flexion.
- Straight Leg Raises: Lift your leg while keeping it straight to maintain and improve knee range of motion.
How to Do Them Safely: Ensure you’re performing exercises within a comfortable range of motion and avoid pushing through pain.
Tips for Safely Performing Activities
How to Stay Safe: As you recover and resume activities, following these tips can help prevent re-injury and ensure a safe return to your routine.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any pain or discomfort and modify your activities as needed.
- Gradual Return: Ease back into your regular activities and sports gradually to allow your knee to adjust.
- Use Supportive Gear: Consider using a knee brace or support during high-impact activities for added stability.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Work with a physiotherapist to develop a personalized rehabilitation program and get advice on technique and progression.
Physiotherapy Treatment of an ACL Sprain
A physiotherapist will examine both knees, comparing the injured knee to the uninjured one. During this exam, the physiotherapist will check your injured knee for signs of swelling, deformity, tenderness, fluid inside the knee joint, and discoloration. If the patient does not have too much pain and swelling, a physiotherapist will then evaluate the knee’s range of motion and will pull against the ligaments to check their strength. During the exam, the patient will have to bend their knee and the physiotherapist will gently pull forward or push backward on their lower leg where it meets the knee.
Based on the results of the patient’s exam, diagnostic tests may need to be performed to further evaluate the condition of the patient’s knee. These tests may include standard X-rays to check for ligament separation from bone or fracture. Tests may also include an MRI scan or a camera–guided knee surgery (arthroscopy). The expected duration of recovery depends on the severity of the patient’s knee sprain, their rehabilitation program, and what type of sports the patients play. In general, milder sprains heal within 2-4 weeks, whereas other types may take 4-12 months.
Looking to have an ACL Injury treated? Schedule an appointment today!
Contact our clinic to book an appointment with one of our physiotherapists to help you recover from your ACL injury!
Our Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics are located at:
Hiking is a wonderful way to explore nature and stay active, but it’s not without its risks. Understanding common hiking injuries, their causes, symptoms, and effective prevention strategies can make your outdoor adventures safer and more enjoyable. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you stay injury-free on the trails.
Understanding Hiking Related Injuries
Hiking can lead to various injuries, often related to the terrain, equipment, or physical condition of the hiker. Common hiking injuries include:
- Sprained Ankles: Caused by uneven ground, rocks, or roots.
- Knee Injuries: Such as patellar tendonitis or meniscus tears from repetitive strain.
- Muscle Strains: Typically in the calves, thighs, or lower back due to overexertion.
- Blisters and Hotspots: Resulting from friction and poorly fitting footwear.
- Sunburn and Heat Exhaustion: Due to prolonged exposure to the sun and inadequate hydration.
- Back Injuries: Resulting from improper lifting of heavy backpacks or poor posture.

Causes and Symptoms
Each type of injury has specific causes and symptoms:
- Sprained Ankles: Twisting the ankle on unstable ground, causing pain, swelling, and difficulty walking.
- Knee Injuries: Overuse, sudden twists, or impacts leading to pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
- Muscle Strains: Overstretching or overloading muscles, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
- Blisters and Hotspots: Friction from ill-fitting socks or boots causing painful, fluid-filled sacs on the skin.
- Sunburn and Heat Exhaustion: Excessive sun exposure leading to red, painful skin, dehydration, dizziness, and nausea.
- Back Injuries: Lifting heavy loads improperly, causing pain, stiffness, or spasms in the lower back.
Importance of Physiotherapy for Hiking Injuries
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in treating hiking injuries by promoting recovery, restoring mobility, and preventing future problems. Benefits include:
- Pain Relief: Through targeted exercises and techniques.
- Restoration of Mobility: Enhancing flexibility and range of motion.
- Improvement in Strength: Strengthening muscles to support injured areas.
- Prevention of Recurrence: Teaching proper movement patterns and injury prevention strategies.
Key Principles of Physiotherapy Exercises for Pain Relief
Physiotherapy exercises focus on alleviating pain and promoting healing:
- Stretching and Range of Motion Exercises: Improve flexibility and joint function.
- Proprioception Training: Enhance balance and stability to prevent re-injury.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage or joint mobilization to reduce pain and inflammation.
Strengthening Exercises
Building strength is essential for recovery and injury prevention:
- Core Strengthening: Supports the back and improves posture.
- Lower Body Exercises: Target muscles in the legs and hips for stability.
- Resistance Training: Uses bands or weights to strengthen specific muscle groups.
Neuromuscular Exercises for Pain Management and Prevention
These exercises improve coordination and control:
- Balance Exercises: Enhance stability on uneven terrain.
- Functional Movements: Mimic hiking motions to improve efficiency and reduce strain.
Progressive Resistance Training
Gradually increasing resistance builds strength:
- Incremental Loading: Challenges muscles without causing undue stress.
- Specificity: Tailors exercises to mimic hiking movements and demands.
Incorporating Stretching and Flexibility Exercises in Your Routine
Regular stretching maintains muscle elasticity and joint flexibility:
- Pre-hike Stretching: Warms up muscles and prepares them for activity.
- Post-hike Stretching: Helps muscles recover and prevents stiffness.
Tips for Safely Performing Physiotherapy Exercises

Follow these guidelines to avoid further injury:
- Consult a Professional: Get a personalized exercise plan from a physiotherapist.
- Start Gradually: Increase intensity and duration of exercises as tolerated.
- Listen to Your Body: Stop if you feel pain beyond normal discomfort.
- Stay Consistent: Perform exercises regularly for best results.
Hiking injuries can be prevented and managed effectively with the right knowledge and preparation. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for common hiking injuries, along with incorporating physiotherapy exercises into your routine, you can enjoy the trails safely and confidently. Remember, safety and preparation are key to a rewarding hiking experience—happy trails!
Conclusion
Don’t let these physical conditions ever ride on you. You can consult any of our locations of Triangle Physiotherapy or simply Book An Appointment online.
“Whether you’re dealing with hiking-related injuries or any other physical discomfort, Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert care at multiple locations across the GTA. Our clinics provide Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Visit us to receive tailored treatment that helps you get back on your feet and enjoy the activities you love.”
Hiking is a fantastic way to enjoy the great outdoors and stay fit, but it can also pose some risks. Whether you’re new to hiking or a seasoned backpacker, there are numerous factors to take into account before heading out on the trails. You need to evaluate your backpack’s weight, choose appropriate footwear, plan your food and hydration, check the weather, and map out your routes. Additionally, since hiking often takes you off the beaten path, it’s essential to take precautions against three common hiking injuries: knee pain, ankle sprains, and sore feet.
Is it necessary to warm up before hiking?

Yes, it is necessary to warm up before hiking. Warming up helps prepare your muscles and joints for physical activity, reducing the risk of injury. Here are some reasons why warming up is important before hiking:
Benefits of Warming Up Before Hiking
- Increases Blood Flow: A proper warm-up increases blood flow to your muscles, delivering oxygen and nutrients that help them perform better.
- Enhances Flexibility: Warming up loosens your muscles and increases your range of motion, making it easier to navigate uneven terrain.
- Reduces Injury Risk: Warm muscles are less prone to strains, sprains, and other injuries.
- Prepares Your Heart: Gradually increasing your heart rate helps prepare your cardiovascular system for the more strenuous activity of hiking.
- Improves Performance: A good warm-up can improve your overall performance, making your hike more enjoyable and less exhausting.
What are some effective warm up exercises to do before hiking?
Effective Warm-Up Exercises
- Walking or Light Jogging: Start with 5-10 minutes of brisk walking or light jogging to get your blood flowing.
- Dynamic Stretches: Perform dynamic stretches like leg swings, arm circles, and torso twists to loosen up your muscles and joints.
- Ankle Rotations: Rotate your ankles in circles to prepare them for the uneven terrain.
- Hip Circles: Rotate your hips to loosen the hip joints, which are crucial for hiking.
- Calf Raises: Perform calf raises to warm up your calves, which are heavily used during hiking.
Taking a few minutes to warm up before you start your hike can make a significant difference in your overall hiking experience and help prevent injuries.
What are the most common hiking injuries?
Some of the most common hiking injuries are:
- Knee Pain
- Ankle Sprain
- Foot Pain
Knee Pain when Hiking
Knee pain is a common issue among hikers, especially on longer or more challenging trails. Here’s a comprehensive approach to understanding, preventing, and managing knee pain when hiking:
Causes of Knee Pain While Hiking
- Overuse and Strain: Continuous stress on the knee joint from uphill climbs, downhill descents, or long sessions of hiking.
- Improper Biomechanics: Poor hiking technique, such as improper foot placement or stride, can strain the knee joint.
- Previous Injuries: Past knee injuries or conditions like arthritis can flare up during hiking.
- Improper Gear: Worn-out or inappropriate footwear lacking proper cushioning and support.
Ankle Sprain when Hiking
An ankle sprain can be a painful and frustrating injury, especially when hiking in rugged terrain. Here’s how to understand, prevent, and manage ankle sprains while hiking:
Causes of Ankle Sprains While Hiking
- Uneven Terrain: Stepping on uneven surfaces, rocks, or roots can twist or roll the ankle.
- Fatigue: Muscles that support the ankle can become tired, leading to less stability and increased risk of injury.
- Inadequate Footwear: Wearing shoes or boots without proper ankle support or that are worn out.
Foot Pain when Hiking
Foot pain while hiking can be uncomfortable and distracting. Here’s how to understand, prevent, and manage foot pain effectively:
Causes of Foot Pain While Hiking
- Improper Footwear: Shoes or boots that are too tight, loose, worn out, or lacking proper cushioning and support.
- Overuse or Strain: Prolonged walking or hiking, especially on challenging terrain, can strain the muscles and joints of the feet.
- Blisters: Friction from improperly fitting shoes or moisture buildup can lead to painful blisters.
If you get injured while hiking, consult one of our physiotherapists who can help you with treating the injuries as well as advise and educate you on prevention so you can enjoy your outdoor activities without pain and discomfort.
Click here to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Physiotherapy can be highly beneficial for individuals suffering from knee osteoarthritis (OA) by addressing pain, improving function, and enhancing the overall quality of life.
What is Knee Osteoarthritis (OA)?
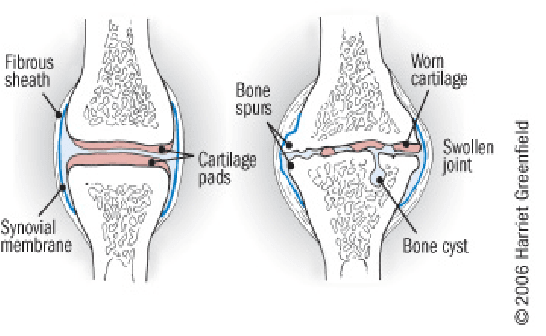
Knee OA is a degenerative joint disease that is typically a result of wear and tear and causes progressive loss of the articular cartilage of the joint.
What are the causes of Knee OA?
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a complex condition influenced by a variety of factors. Here are the primary causes and contributing factors:
1. Aging
- Natural Wear and Tear: As people age, the cartilage that cushions the knee joint gradually wears away, leading to OA.
- Decreased Ability to Heal: Older cartilage has a reduced ability to repair itself, making it more susceptible to damage.
2. Genetics
- Family History: Genetic predisposition can play a significant role. If OA runs in your family, you might be more likely to develop it.
- Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic mutations can affect cartilage production and maintenance.
3. Joint Injuries
- Previous Injuries: Injuries such as fractures, ligament tears, or meniscus damage can increase the risk of OA.
- Repetitive Stress Injuries: Repeated stress or overuse of the knee joint, often due to occupational or recreational activities, can lead to OA.
4. Obesity
- Increased Joint Load: Excess body weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, accelerating cartilage breakdown.
- Inflammation: Fat tissue produces inflammatory chemicals that can contribute to joint damage.
5. Mechanical Factors
- Joint Alignment: Abnormal joint alignment, such as bowlegs or knock-knees, can increase stress on certain parts of the knee.
- Muscle Weakness: Weak muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps, can lead to increased joint stress.
6. Gender
- Higher Risk in Women: Women, especially those over 50, are more likely to develop knee OA compared to men. Hormonal differences might contribute to this increased risk.
7. Metabolic and Systemic Factors
- Metabolic Syndrome: Conditions like diabetes and metabolic syndrome are associated with an increased risk of OA due to systemic inflammation and metabolic disturbances.
- Inflammatory Diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can predispose individuals to secondary OA.
8. Lifestyle Factors
- Physical Activity: Both excessive and insufficient physical activity can affect joint health. High-impact sports can lead to joint injuries, while sedentary lifestyles can weaken muscles and joints.
- Diet: Poor nutrition can affect joint health. For example, deficiencies in vitamins D and C can impair cartilage maintenance and repair.
9. Joint Biomechanics
- Meniscus Tears: Damage to the meniscus can disrupt joint mechanics and contribute to OA.
- Ligament Damage: Injuries to ligaments, such as the ACL, can destabilize the knee and lead to abnormal wear patterns.
10. Inflammation
- Low-Grade Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation can contribute to the breakdown of cartilage and other joint tissues.
Understanding these causes and contributing factors can help in the prevention and management of knee osteoarthritis, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding joint injuries, and seeking early intervention for symptoms.
What are the most common symptoms of Knee OA?
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) typically presents with a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity from mild to severe. The most common symptoms include:
1. Pain
- Activity-Related Pain: Pain that worsens with activity or weight-bearing and improves with rest.
- Persistent Pain: Chronic pain that may be present even at rest or during the night in more advanced stages.
2. Stiffness
- Morning Stiffness: Stiffness in the knee that is usually worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity and typically lasts less than 30 minutes.
- Post-Activity Stiffness: Stiffness that occurs after prolonged sitting or resting.
3. Swelling
- Joint Swelling: Swelling around the knee joint due to inflammation or increased production of joint fluid.
- Effusion: Accumulation of excess fluid within the knee joint, leading to noticeable swelling.
4. Reduced Range of Motion
- Limited Flexibility: Difficulty bending or straightening the knee fully.
- Loss of Motion: Progressive decrease in the knee’s range of motion over time.
5. Grinding Sensation (Crepitus)
- Audible Cracking or Popping: A sensation of grinding, cracking, or popping sounds when moving the knee, often due to roughened cartilage surfaces.
6. Weakness or Instability
- Feeling of Giving Way: A sensation that the knee might buckle or give out, often due to muscle weakness or joint instability.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles surrounding the knee, particularly the quadriceps.
7. Deformity
- Joint Deformities: Changes in the shape of the knee joint, such as bowlegged (varus) or knock-kneed (valgus) appearance, due to uneven wear and joint damage.
8. Tenderness
- Joint Tenderness: Tenderness or pain when pressing on or around the knee joint.
9. Functional Impairment
- Difficulty with Activities: Challenges with everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs, sitting, or standing due to pain and stiffness.
- Reduced Mobility: Decreased ability to perform normal daily activities and exercise.
10. Fatigue
- General Fatigue: Feeling of tiredness and reduced energy levels, often due to chronic pain and sleep disturbances.
These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and ability to perform daily activities. Early recognition and management of knee OA symptoms can help slow disease progression and improve function and comfort.
What are the treatment options for Knee OA?
The number 1 treatment option is conservative management (ie. Patient education, therapeutic exercise, activity modification, weight loss, bracing), surgery should be considered after a conservative approach (talk to your orthopaedic specialist for more information).
Physiotherapy can help by providing you with education about osteoarthritis, tailor an exercise program that is suitable for you, help you consider the best options for activity modifications, provide you with education on bracing, address psychosocial factors such as fear-avoidance, promote patient autonomy and get you back to doing the things you love to do!
Manual therapy- joint mobilization to help with stiffness. Muscle energy technique to help stretch surrounding muscles.
Modalities – heat/ice for pain relief, TENs/IFC for pain relief and inflammation control. Ultrasound for pain relief.
Exercises – help with improving mobility, ROM, strength, balance, aerobic capacity, promoting physical function, reducing knee pain and inflammation.
Click here to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Physiotherapy can be a highly effective treatment for managing knee osteoarthritis by improving mobility, reducing pain, and enhancing overall function. Whether you are looking for physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, or Liberty Village, there are experienced physiotherapists ready to help you manage osteoarthritis and improve your quality of life.
Golf is known for its emphasis on skill, strategy, and etiquette, and it is enjoyed by millions of people worldwide. Apart from the swing, optimal golf performance involves perfect coordination between physical fitness, technique, and mental focus. Physiotherapy is increasingly used by golfers to enhance their game, to optimize golf performance.

What are the key physical attributes essential to a good golf game?
- Core Strength and Stability for Swing Power
- Spine and Cervical Rotation for Swing Rotation
- Wrist and Forearm Mobility for Control
- Lower Body Mobility for Distance
- Pelvic Tilt for Power and Control
- Single Leg Balance for Stability
What are the most common golf injuries?
The most common Golf injuries are:
Tendinitis:
Tendinitis is caused by overuse or repetitive movements, especially during activities such as sports, gardening, or typing, notably in elbows (tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow) and wrists. The symptoms are: aching, tenderness, and swelling around the affected joint during and after play.
How to prevent tendinitis:
- Warm-up and cool-down: stretch before and after each round.
- Proper form: Ensure that you use proper technique and form. Improper technique can put excessive stress on tendons and increase the risk of tendinitis.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any signs of discomfort or pain during physical activity. If you experience persistent pain or discomfort in a tendon, stop the activity and rest. Continuing to push through pain can exacerbate the injury and lead to more severe problems.
Shoulder Injuries:
Shoulder injuries related to golfing are relatively common, particularly among avid golfers or those who engage in the sport frequently without proper technique or conditioning. The golf swing involves complex movements that can place stress on various parts of the body, including the shoulders.
How to prevent shoulder injuries:
- Warm-up: perform a thorough warm-up routine that includes dynamic stretches and exercises to prepare your muscles and joints for the golf swing.
- Maintain good posture: PWork with a golf instructor to ensure that your golf swing technique is sound and biomechanically efficient. Proper swing mechanics can help reduce stress on the shoulders and decrease the risk of injury. Pay attention to your posture, grip, and rotation throughout the swing.
- Gradual progression: Pace yourself during your round of golf and avoid swinging too forcefully, especially if you’re fatigued.
Back Pain:
The repetitive motion of the golf swing, combined with the rotational forces generated by the movement, can place stress on the muscles, ligaments, and joints of the back, leading to discomfort or injury. The symptoms are: Aching, stiffness, or sharp pain in the lower back, sometimes radiating down the legs.
How to prevent back injuries:
- Core strengthening exercises
- Posture: Avoid excessive rounding or arching during swings.
- Proper lifting techniques: Avoid bending from the back during activities.
Knee Problems:
Knee problems are caused by pivoting motions and uneven terrain stress knees, causing tendonitis, patellar instability, and arthritis. The symptoms are:
- Symptoms: Knee pain, swelling, and stiffness, especially during weight-bearing activities.
How to prevent knee problems:
- Strengthening exercises: Target hamstrings, quads, and calves for knee stability.
- Proper footwear: Select supportive shoes with good traction for uneven surfaces.
- Warm-up and cool down: Prepare knee joints before play and stretch after the game.
How do I prevent golf injuries?
Seeing a physiotherapist before golfing season is highly recommended. Your physiotherapist will help you with:
- Strengthening: Strengthen core, shoulder, and leg muscles with planks, lunges, and rotator cuff exercises. A strong foundation makes your body resilient to swing demands.
- Flexibility: Maintain spine, hip, and shoulder range of motion for a smoother swing. Incorporate gentle stretches and yoga poses to reduce muscle strains.
- Balance and Proprioception: Improve balance and body awareness with single-leg stances and wobble board exercises. Prevent awkward falls on the course.
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Improving your golf game this spring can greatly benefit from the right physical conditioning and expert guidance. For personalized support, consider physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, or Liberty Village. Skilled physiotherapists in these areas can help you enhance your strength, flexibility, and overall performance on the golf course.
What is the ACL?
The ACL, or Anterior Cruciate Ligament, is one of the four major ligaments in the knee joint. It is located in the center of the knee and runs diagonally, connecting the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). Its primary function is to prevent excessive forward movement of the tibia relative to the femur and control rotational movements of the knee.
What is an ACL Injury?
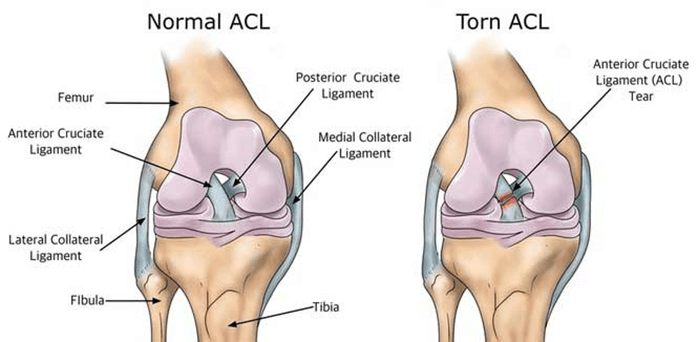
Injuries to the ACL are relatively common, often occurring during sports activities that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct impact on the knee. ACL injuries can range from mild sprains to complete tears. When the ACL is torn, it can lead to instability in the knee, difficulty with weight-bearing, and a decreased ability to perform certain activities.
Consulting with a physiotherapist at Physiotherapy Oakville is crucial for recovery, as scientific research has shown that structured physiotherapy programs significantly improve outcomes for ACL injuries. These programs focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee, improving flexibility, and restoring stability. By joining Physiotherapy Oakville, you can benefit from evidence-based treatments and personalized exercise plans that enhance your recovery process, reduce the risk of further injury, and help you return to your normal activities with confidence.
What are the symptoms of an ACL injury?
Common symptoms of an ACL injury include:
- Pain: Individuals with an ACL injury often experience pain in the knee. The intensity of the pain can vary based on the severity of the injury.
- Swelling: Swelling typically occurs within a few hours of the injury and may be accompanied by a feeling of tightness or fullness in the knee.
- Instability: A sense of instability or a feeling that the knee is “giving way” is a common symptom. This instability may be particularly noticeable during activities that involve cutting, pivoting, or sudden changes in direction.
- Loss of Range of Motion: The injured knee may have a reduced range of motion, and it may be challenging to fully straighten or bend the knee.
- Audible “Pop” Sound: Some people report hearing or feeling a “pop” at the time of the injury. However, not everyone experiences this sensation.
- Difficulty Weight-bearing: Walking or putting weight on the affected leg may be difficult, especially immediately after the injury.
Can Physiotherapy help with an ACL Injury?
Yes, physiotherapy is a crucial component of the rehabilitation process for individuals with an ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) injury, particularly those who undergo surgical intervention such as ACL reconstruction. Physiotherapy aims to address pain, swelling, muscle weakness, and joint instability while helping individuals regain normal function and return to their usual activities.
Here are some ways in which physiotherapy can help with an ACL injury:
- Post-operative Rehabilitation: After ACL reconstruction surgery, physiotherapy plays a vital role in the postoperative rehabilitation process. The early phases focus on managing pain and swelling, restoring range of motion, and preventing muscle atrophy.
- Strengthening Exercises: Physiotherapists prescribe specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. Strengthening these muscles helps provide stability to the knee joint.
- Balance and Proprioception Training: ACL injuries can affect balance and proprioception (awareness of joint position). Physiotherapy incorporates exercises to improve balance and proprioception, reducing the risk of future injuries and enhancing overall joint stability.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Physiotherapists guide patients through a series of exercises to regain and maintain a normal range of motion in the knee. This is important for preventing stiffness and improving functional mobility.
- Functional Training: As the rehabilitation progresses, physiotherapy includes functional activities and sport-specific exercises to help individuals return to their normal activities or sports safely.
- Education and Home Exercise Programs: Physiotherapists educate patients about their condition, recovery process, and strategies for preventing future injuries. They often provide home exercise programs to continue rehabilitation between sessions.
- Gradual Return to Sports: For individuals aiming to return to sports or high-demand activities, physiotherapy guides a gradual progression of exercises to ensure a safe and effective return, taking into account factors like strength, agility, and neuromuscular control.
Our More Locations
Physiotherapy Etobicoke | Physiotherapy Oakville | Physiotherapy North York | Physiotherapy Toronto | Physiotherapy Lawrence Park | Physiotherapy Mississauga | Physiotherapy Queens Quay | Physiotherapy Mississauga Erin Mills | Physiotherapy Liberty Village
How do I book an appointment with a Physiotherapist near me?
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist or chiropractor at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Starting physiotherapy at the right time after ACL surgery is crucial for optimal recovery. Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert care across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our experienced physiotherapists can guide you through a personalized rehabilitation program to help you regain strength and mobility efficiently.”