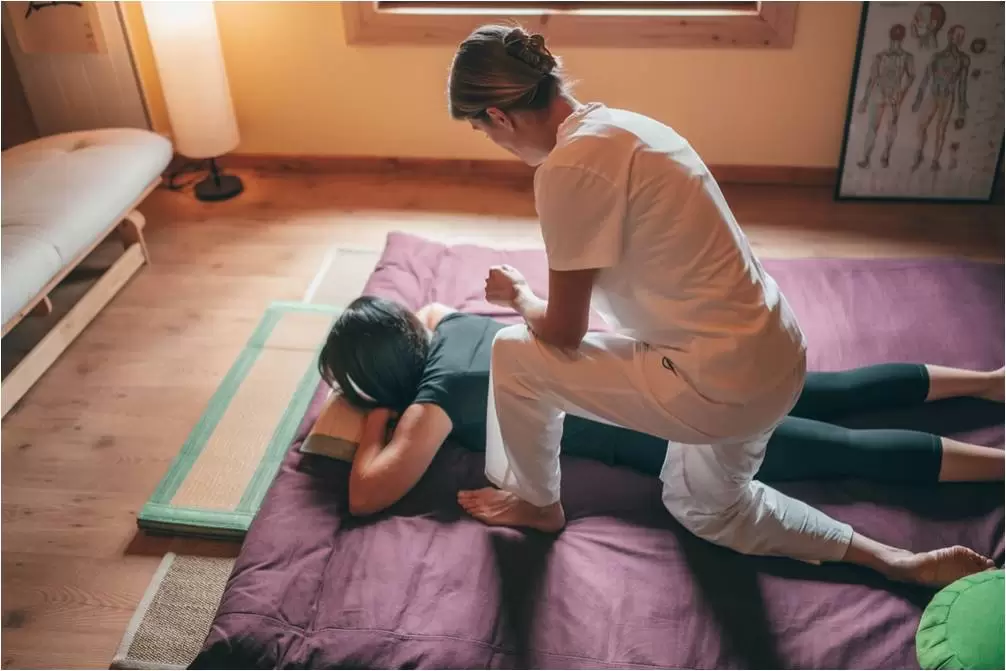
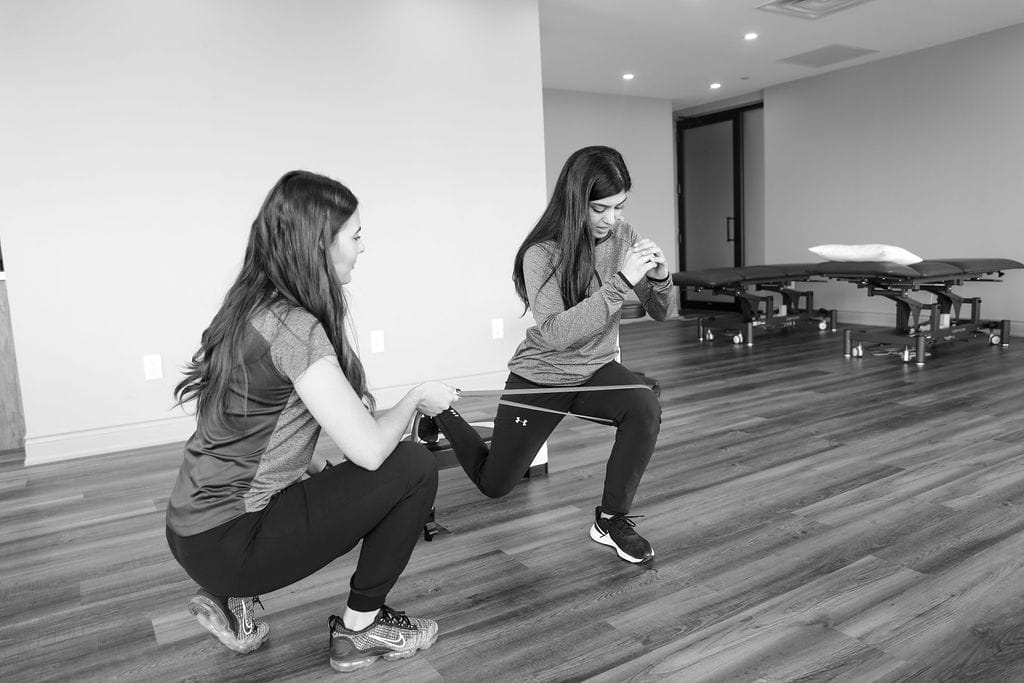
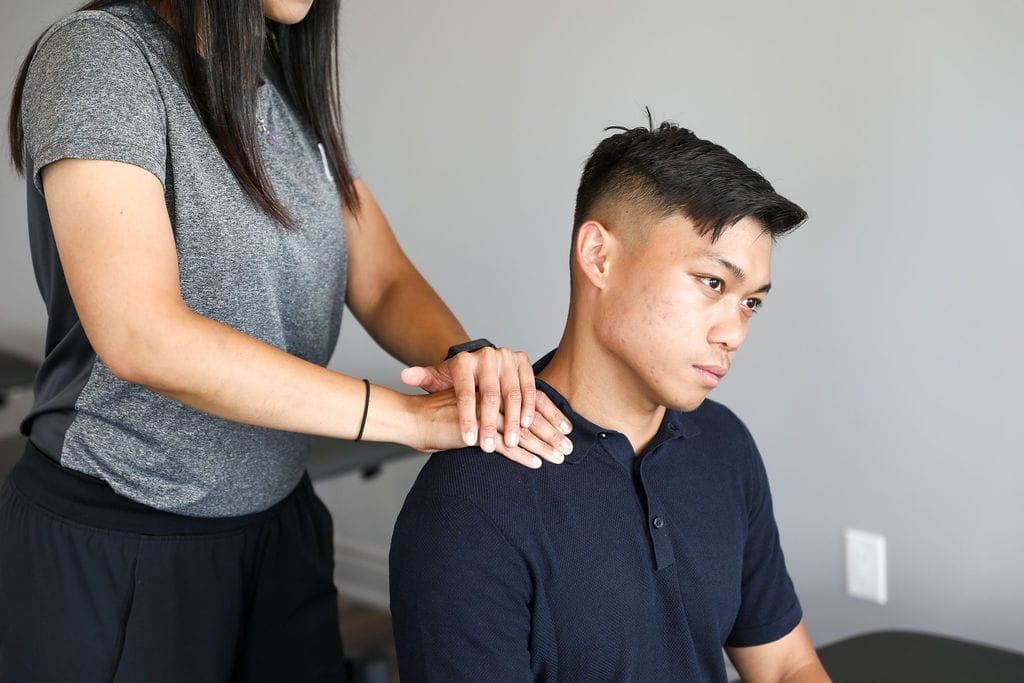
Should I go to a physiotherapist after a car accident?
If you met with a car accident and having problems related to the mobility of your body or if it causes obstacles to function properly and efficiently then you should definitely go for Physical Therapy.
Physical therapists are musculoskeletal experts and may help cure the underlying musculoskeletal injuries that may have occurred after meeting with a car accident. At Triangle Physiotherapy, our Physical Therapists will assure a one-to-one session where they will conduct an extensive whole-body analysis with a target of developing a customized treatment and detailed physical therapy programs which suit best to your condition and individual needs.
What can a physiotherapist do to help after a car accident?
The goal of physical therapy is to help you recover physically and strengthen damaged muscles and tissues.
A Few physical therapy exercise programs would include:
- Manual therapy to mobilize joints, decrease scar tissue, reduce inflammation and enhance healing of tissue.
- Custom exercises to address types of pain like neck and shoulder pain, back pain, spine dysfunction, or weakness.
- Postural training to resolve pain in the neck, shoulders, and back.

COMMON TYPES OF INJURIES
The list of injuries if you meet with a car accident are as follows:
- Whiplash
- Headaches
- Back Pain
- Neck Pain
- Shoulder Pain
- Knee Pain
What are the common symptoms related to WHIPLASH?
Common symptoms related to whiplash include:
- Stiffness to neck, arms, upper back, and the face.
- Numbness into arms, neck, and upper back.
- Headache, dizziness, nausea.
- Feelings of general weakness.
- Altered and disturbed sleeping habits and patterns.
- Difficulty with concentration.
Is it important to get physiotherapy as soon as possible after a car accident?
Although you may feel the immediate onset of pain or symptoms of injury, these symptoms may bring forth pain and mobility problems over the long haul.
Suppose if you met with a car accident, one may wonder that why is it necessary to get treated with Physiotherapy after an accident? If you’re considering Physiotherapy after a car accident, there are many reasons that you may want to begin or continue with the treatment.
The doctor will recommend that you receive Physiotherapy and you will realize the benefit of rehabilitation after a car accident. You may realize on your own that you can benefit from rehabilitative treatment.
Here’s why you should start Physical Therapy after a car accident:
- Physical Therapy After a Car Accident Can Help You Recover Faster
Going through Physical Therapy after a car accident can help you speed up your recovery time. It can help the body recover its lost strength so that you can reduce the amount of time it takes to improve and fully recover from the injuries caused by car accidents. Time and again patients don’t realize how bad their car accident injuries are until they return to their day-to-day activities.
If you are looking for a physiotherapist to help you with your injuries, our rehabilitation facility is one of the best physiotherapy clinics:
- Physical Therapy Can Help You Recover Better and Prevent Long-term damage
In order to help you recover faster, Physical Therapy programs ensure a better outcome after taking good care and following Physical Therapy exercises. It can also help you or prevent the long-term effects of your injuries like chronic pain and migraines. Unfortunately, car crashes can cause nagging damage if the patient’s injuries are not addressed right away. If you begin physical therapy immediately after your car accident, it’s more expedient to live a pain-free life for years.
- Boosting Mental Health and Improving Quality of Life
Some issues can create a problem after years of being a victim of a car accident and this can seriously affect the quality of life of a person. Physical therapy relieves these issues before becoming a serious health concern for an individual.
- Avoiding Surgery
Every so often injuries caused by car accidents can even require surgery, most injuries or a type of wear and tear but a few injuries, if left rampant, can lead to surgery and costly hospital bills. It is always advised to immediately check-up with a professional for the treatment. This will help with any claims you may wish to make later on. Physical therapy treatment is a much more cost-effective solution to recovery.
There are multiple benefits of physiotherapy and that’s why people are opting for this line of treatment for recovery and overall well-being.
Steps to take after a car accident and a few advantages of Physiotherapy:
- The Type of Injury
Car accident injuries can affect your recovery time and the time period that takes to complete your treatment. One of the most common car accident injuries is whiplash. A whiplash injury occurs when the force of the accident causes your head and neck to jerk violently forward and backward. This can cause the muscles and tendons in your neck to stretch outside their normal range of motion. Whiplash can also affect the spinal column in your neck and disc injuries can be serious. Depends on the intensity of the whiplash, it can take a few months to recover and get the accurate motion of the neck as it was before.
2. The Severity of the Accident
It is more likely to sustain a moderate to severe injury in a more serious car accident, even the smallest of the injury. A more severe accident can cause consequential harm to your body even if you are taking all precautions of car safety like wearing the seatbelt and the airbag deploys. More serious injuries like a dislocated knee or a broken foot can impact your daily routines.
3. Any Previous Injuries
A previous injury can leave behind scar tissue, that impacts how your body heals the new injury. Physiotherapy often takes longer if you have previous injuries, especially if they occur in the same area.
Few factors that effect are:
- The severity of the injury
- Location of the injury
- Patient’s current state of health
- Patient’s treatment goals
- Rate of progress
How can Physiotherapy help if you’ve met with a car accident?
Physiotherapy helps reduce the pain and discomfort usually felt after a car accident injury. A lack of physical activity when recovering from an injury can actually cause stiffness, which can lead to more discomfort when trying to return to your daily activities, so you should always try to keep your body in motion.
“Recovering from a car accident requires targeted physiotherapy to restore mobility and reduce pain. Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert care across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our experienced team provides personalized rehabilitation plans to help you recover effectively and regain your quality of life.”
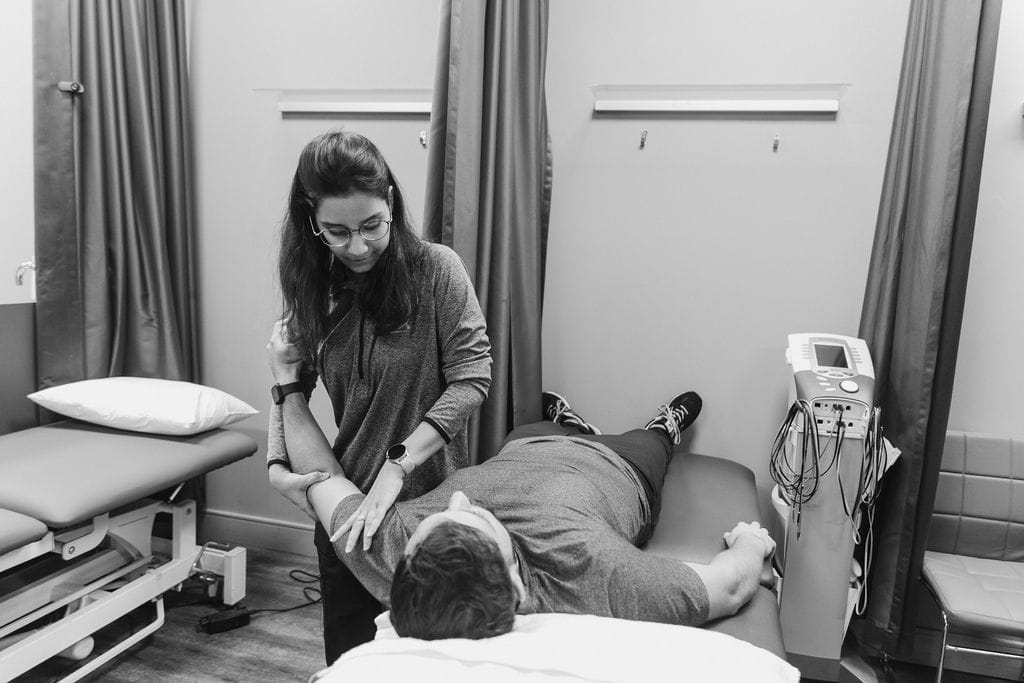
Physiotherapy and Physiology both have many similarities, but they have a set of differences too.

What is Physiotherapy and what does a physical therapist do?
Physiotherapy or Physical Therapy is a medical treatment where patients face problems of mobility, function, and well-being; pain in specific locations of a body especially body parts that are in constant motion like bones, tissues, etc. it helps through physical rehabilitation, injury prevention. Tests are carried out to determine the limitations of the patient which further helps in formulating the set of exercises that will aid in restoring movement.
Physiotherapist duties are:
- Detect the patient’s medical issues in order to help the patient recover from illness, accident, or injury.
- Provide a clear and well-organized exercise program with clearly defined goals and milestone targets.
- Set objectives for patient progress and document it.
- Set up an exercise session as a part of the treatment, and maintain detailed reports of future exercise planning.
- Prepare an evaluation document, and instruct patients to use exercise equipment such as walkers.
- Inform the patient about the benefits of exercise to mentally motivate them.
- Follow the doctor’s directions to prescribe exercises meanwhile assisting doctors and nurses if required.
What is Physiology and what does a Physiologist do?
Physiology is a medical treatment and a detailed study of the anatomy of the body’s organs and their cells, this treatment aims at preventing chronic diseases and providing physical health benefits suffering from injuries. It treats diseases like obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes.
Physiologist responsibilities are:
- Monitor and record patients’ health and medical performance while exercising and under medication, and make thorough observations over time to deliver results to the physician.
- Use medical equipment and machinery when going through the exercise of the lungs and heart.
- Performing tests to evaluate physical and mental stress levels.
- Simultaneously work with physiotherapists to evaluate results.
- Create a plan of types of exercises to be followed.
- Assess the treatment’s effectiveness to fetch the right results.
Differences between Physiologist and Physiotherapist
- Physiologists and exercise physiologist degree requirements both undertake 4 years of university training, both theoretical and practical, studying subjects such as anatomy, physiology, and biomechanics, etc. Both are recognized by Medicare, TAC, WorkCover, and private health funds, and require yearly professional development.
- Physiologists provide prescriptions and teach trigger point therapy and self-massage techniques, using exercise equipment such as foam rollers and trigger point balls. Physiotherapists, on the other hand, can deliver soft tissue mobilization through massage, acupuncture, dry needling, and ultrasounds, and guide you through self-massage techniques as well.
- Physiotherapists evaluate the injury diagnosis and prognosis, whereas Physiologists receive the injury diagnosis and deliver the rehabilitation prognosis.
- Physiologists specialize in providing lifestyle modification techniques to support those with a wide range of chronic health conditions to promote improved health and wellness and decrease risk. Physiotherapists will overall specialize in the acute phase of an injury, and can often also deliver long-term rehabilitation and health monitoring.
- Exercise physiology accreditation and the conditions they work with:
- Cancer treatment recovery
- Chronic pain and fatigue
- Managing osteoarthritis pain
- Osteoporosis and arthritis
- Diabetes
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Mental health
- Musculoskeletal
- Neurological (Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy)
- Obesity
- Pulmonary
- Cardiovascular

6. Conditions physical therapists work with:
- Mobility and balance concerns/falls
- Back or other spinal joint pain
- Sports injuries
- Chronic pain
- Post-surgery rehabilitation
- Cardiorespiratory issues
- Neurological (injuries) conditions – for example, stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Arthritis- for example osteoarthritis/rheumatoid arthritInjury Cycle – Acute Phase
Injury Cycle – Recovery Phase
The next phase of rehabilitation that is 3 to 4 weeks post-injury, is when a Physical Therapist will come into the play and provide treatment in order to introduce exercises to regain range of movement, including mobilization of soft tissue structures, and restore joint mobility and strength to optimize function.
All exercises prescribed by the Exercise Physiologist are made to achieve each individual’s activities of daily living and rehabilitation or performance goals.
Exercises recommended by Physical Therapists are made to achieve an individual’s daily life activities and rehabilitation or performance targets.
Difference between Physiology and Physiotherapy
| Physiotherapy | Physiology |
| Disorders concerning muscle and bones are treated by physiotherapy. This includes some medical conditions such as arthritis, joint aches, back pain, cardiorespiratory ailments like emphysema, asthma, neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and post-surgery complications, etc. | Physiology focuses on increasing metabolism and physical energy during the course of treatment along with rehabilitation. The diseases treated by physiological exercises are obesity, hypertension, diabetes, immunity complexities, arthritis, etc. |
| The techniques used by Physiotherapy are manipulation, electrotherapy, mobilization, therapeutic physiotherapy exercises, and gentle massage. These are performed by trained physiotherapists after evaluating the patient’s physical conditions. | Physiological treatments are not rendered after identifying the problem. The treatment to lower any kind of discomfort before a proper diagnosis is a part of physiology exercises. In physiology, a proper plan is designed with the mainstream treatment and changes in lifestyle and behavior. |
| Physiotherapy can be studied at the Bachelors’s level (BPT) course. | Physiology is a higher academic course at the Post Graduate level of medical science. One has to complete MBBS before opting for MD in Physiology. |
Why do you need a Physiotherapist and how can they help you?
Using these checklists is a great way to decide which health professional is best for you.
- Do you have pain that is new, unexpected, or not yet diagnosed?
- Or you have a type of sports injury, or have you recently undergone orthopedic surgery?
- Do you require hands-on treatment for symptomatic relief such as acupuncture, manipulation or massage?
If you have answered yes to any of the above questions, then a Physical Therapist may be for you!
It’s well known that exercising for the proper duration and intensity may help improve the quality and length of life – it may decrease the incidence of obesity and chronic health conditions. Accredited Exercise Physiologists can work with such conditions through prescriptions and proper training.
Our Exercise Physiologists are university-qualified health professionals who provide safe, effective exercise programs, tailor-made to meet your health goals.
Do you need a physiologist and a physiotherapist and how can they help you?
Using these checklists is a great way to decide which health professional is best for you.
- Are you recovering from an injury, or have a prior injury that you do not want to worsen, however, wish to get fit and healthy?
- Do you have a chronic health condition (such as diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, asthma, obesity, osteoporosis, etc.) that exercise could assist with?
- If you have goals around losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight?
- Do you seek a specifically drafted and prescribed exercise program that will meet your health and wellness needs?
At the end of the day, there is a degree of overlap between both professions as they aid in treating many different conditions and aspects of health and well-being. The key takeaway is to choose the right professional based on your stage of recovery. If you are in the acute stages of rehabilitation, a physiotherapist is the ideal person to seek treatment from. However, if you are in the sub-acute, recovery, or chronic stage of rehabilitation, receiving treatment from an expert physiologist who can provide a specific and individually tailored exercise program is what you need.
At Physiotherapy Oakville, our team collaborates with both physiotherapists and physiologists to ensure you receive comprehensive care at every stage of your recovery. Scientific evidence supports the importance of tailored treatment plans in achieving optimal health outcomes. By joining Physiotherapy Oakville, you benefit from a multidisciplinary approach that addresses your unique needs, ensuring effective treatment and a smooth recovery process.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North Yor
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
“Understanding the differences between a physiologist and a physical therapist is crucial for choosing the right care for your needs. Triangle Physiotherapy offers expert services across the GTA, including Physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. Our skilled physiotherapists are here to provide personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific health goals.”
When it comes to patient care, it is important to understand the different severities of injuries. This classification is important as it helps the medical practitioners to address and prioritize the efforts. Here, we are going to talk about the difference between injury and trauma and help you understand how does physiotherapy help in the treatment of both.
Unfortunately, the injuries caused due to trauma are very severe and require need complex medical treatment and longer recovery time. Therefore, anyone who undergoes a traumatic injury must consult the experts for their condition and avail the best physiotherapy treatment to ensure maximum and fastest recovery.
What is an injury?

What Is An InjuryIn simple terms, any instance that causes harm to the body can be classified as an injury. Injuries can be divided into different ranges, depending upon the severity and impact on the body. Some injuries might require immediate medical attention while some can heal naturally with minimum or less care. Some examples of injuries are cuts, burns, scrapes, minor concussions, broken bones and sprains. What may look like a minor injury could require urgent and special medical care. Therefore, it is suggested to visit a trained and experienced physiotherapist or practitioner in case of an injury.
What is a trauma?
Trauma can be explained as a more serious, possibly life-threatening injury, requiring urgent medical attention. A trauma is a critical injury and therefore most hospitals have a trauma center to attend and treat sensitive and urgent cases like these. Some of the examples of the trauma includes road accidents, severe cuts, burns, blunt-force trauma, serious falls, multiple broken bones, head injury, major concussions or stab wounds. Though the minor cuts or wounds can be handled by an effective first-aid kit or stitches, serious trauma like burns, bleeding artery or head injury may require extensive surgery followed by rehabilitation for a proper recovery.
Physiotherapy and Injury
When it comes to the recovery stage, physiotherapy is extremely beneficial. Many people believe that the road to recovery in injury passes through physiotherapy and the recovery can never be complete without physiotherapy. If a person has suffered from an injury from a broken bone or a sprained limb, he will face major challenges in routine activities. Simple tasks like walking or driving can be become arduous. This is where physiotherapy comes into picture. Physiotherapy provides the direction to exercise and mobilize specific muscles and tissues so that the body heals from the injury.
If a person suffers from an injury – major or minor, it is suggested that he should consult with the doctor about the recovery plan that must include physiotherapy. It is important to note that even a minimal physiotherapy helps in regaining strength and functionality post the injury. Injury recovery is not possible with a focused and dedicated physiotherapy program. For cases involving broken bones or sprains, physiotherapy is very useful to stretch and comfort the affected area and expedite the healing. Preventive physiotherapy is also beneficial for elderly patients and people at risk of injury. It helps in ensuring and maintaining balance, strength, agility and a complete range of motion while preventing injuries.
Physiotherapy and Trauma
Trauma injuries usually require more extensive and immediate surgery to fix the damage. Traumatic cases have extensive long recovery process. Patients suffer mental and physical anguish in injuries involving surgery. Based on the extent and severity of the injury, the recovery process may be anywhere from a few days to several years. In some unfortunate cases, some patients are never able to recover despite optimal surgery.
The time immediately after the injury and the subsequent surgeries is the most crucial one for people who have suffered a big physical trauma. It is this period that plays one of the biggest deciding roles in the duration and pace of the recovery. Therefore, it is suggested to consult an experienced and trained medical practitioner for the injury. Based on the injury and medical history, the doctor/medical practitioner prepares a recovery plan which starts immediately and involves a comprehensive active recovery like physiotherapy. Physiotherapy can be a painful and difficult process, but helps in regaining strength and mobility post traumatic injuries. They are a part of the recovery process in complicated cases like brain injuries and physical trauma.
Physiotherapy in GTA
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation care services can come in various forms based on the severity of the injury and medical history of the patient. For example, someone suffering from Tennis Elbow or Stress Fracture may need Shockwave Therapy Treatment, while someone who gets a head injury might need Vestibular Rehabilitation to cure dizziness and provide stability and balance to the mind. It is important to know that every situation is unique in its own way and therefore needs a different recovery plan and timeline. That is why one should be patient and adhere to the recovery plan chartered by the physiotherapist to get optimal results. At Triangle Physiotherapy, we offer a host of services aimed to provide relief from the pain and ensure preventive care for overall strength and well-being. Some of our services include –
- Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy – To encourage patients to successfully treat pelvic issues
- Vestibular Rehabilitation – To improve balance and reduce problems related to dizziness
- Shockwave Therapy – To reduce pain and promote healing shock waves are delivered to the injured soft tissues
- Chiropody – To lower the pain in the lower limbs and feet and cure mobility issues and infections
- Chiropractic – To treat the muscles, joints, bones and nerves through a non-invasive and conservative approach
- Naturopathic Medicine – To treat the root cause rather than covering up the symptoms using non-pharmacological interventions
- Massage Therapy – To promote deep relaxation, release tension and provide optimal well-being by working on the superficial and deep tissues
- Custom Bracing – To increase joint stability, improve alignment and reduce excessive movements
- Acupuncture – To help the body heal naturally by activating trigger points to relive muscle tightness
- Fascial Stretch Therapy – To achieve optimal strength, flexibility, performance and pain relief using table-based assisted stretching exercises
At Triangle Physiotherapy, we our trained and experienced physiotherapists will work with you to provide a comprehensive recovery program based on your conditions and medical history. Our services are tailor-made to provide relief and assistance to any type of injury or trauma and we ensure that you get the best recovery following our program. Our patients are our topmost priority and all our efforts are directed at providing them care and relief.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
If you are dealing with an injury or trauma, seeking professional physiotherapy can help you recover safely and effectively. Whether you’re located in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, or Liberty Village, there are physiotherapy clinics available to provide specialized care and personalized treatment plans to support your recovery journey.
Spondylolisthesis is a condition that leads to back pain caused by the instability in the vertebrae. According to an article published in Spine, 6 to 11.5% of the adult population experiences this condition. People who are involved in football or gymnastics are at a higher risk. While we understand that it’s a painful condition to be in, we don’t want you to stop doing what you love and therefore, we suggest you to book an appointment with our expert Physiotherapists at any of our nine rehabilitation clinics across the GTA ( Physiotherapy Etobicoke, Physiotherapy North York, Physiotherapy Mississauga, Physiotherapy King West, Physiotherapy Lawrence Park, Physiotherapy Erin Mills, Physiotherapy Queen Quay, Physiotherapy Oakville, Liberty Village).
When it comes to spondylolisthesis, exercise plays a very important role in improving the condition. However, one must remember here that not all exercises are safe and can even further damage the spine. We are going to make you learn Spondylolisthesis exercises that must be avoided for an effective Spondylolisthesis treatment. Before we move to exercises to avoid in spondylolisthesis, we must first understand what is spondylolisthesis.
Spondylolisthesis – an overview
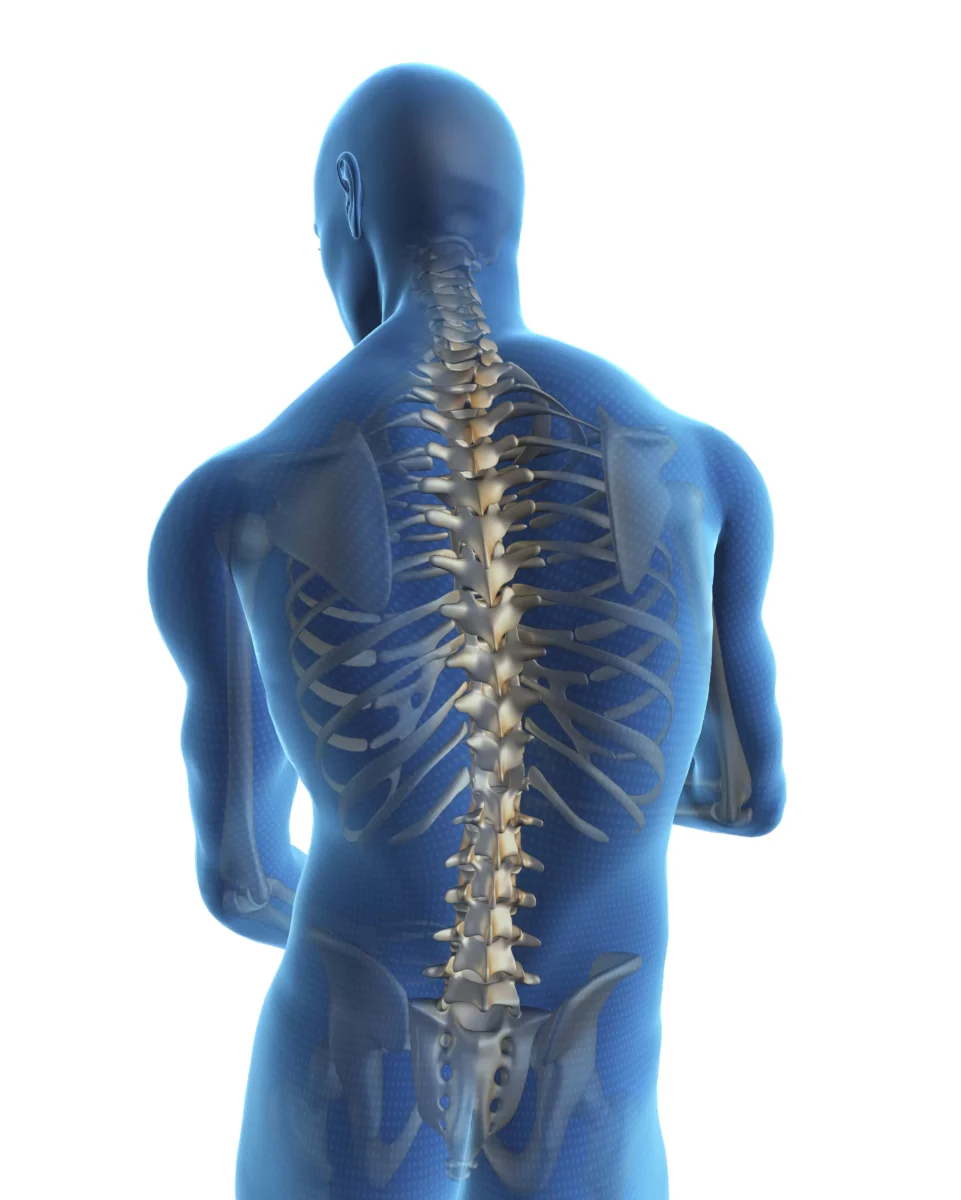
Is is usually caused by degeneration of the vertebrae or disc, due to trauma, injury or genetics. It makes a piece of the spinal bone, also known as vertebrae slips out of alignment and onto the bone below it. Spondylolisthesis usually occurs at the fifth lumbar vertebrae. As reported by the Cleveland Clinic, spondylolisthesis is one of the most common causes of back pain for teen athletes. Having said that, degenerative spondylolisthesis also results in low back pain in people older than 40 years.
Specific spondylolisthesis exercises are suggested to alleviate the pain and discomfort thereby improving the function and quality of life. Let’s now talk about the symptoms of spondylolisthesis.
Symptoms of Spondylolisthesis
Most of the spondylolisthesis symptoms include pain in the lower back that gets worse with standing and hyperextension. The pain may appear like a muscle strain. There are some other symptoms of spondylolisthesis that one must look out for –
• Tightness in hamstring
• Pain in posterior buttock
• Neurological changes including tingling down the legs and numbness
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms or have recently occurred an injury, consult our experienced physiotherapists at our rehabilitation clinics in different locations in GTA.
After a through examination, the physiotherapist suggests a personalised program to help reducing the pain and discomfort caused due to spondylolisthesis. Usually, the physiotherapists classify spondylolisthesis as low grade or high grade, depending on how much the vertebrae have slipped forward. Patients with lesser symptoms and low-grade slips respond well to conservative line of treatment, like exercise. However, patients who experience high grade slips witnessing numbness or tingling in the legs may require surgery.
Considering the potential risks, it is very important to know what exercises must be avoided in spondylolisthesis to prevent further damage or injury.
Spondylolisthesis Exercises to Avoid
If you are looking to rehabilitate a non-operative spondylolisthesis after consulting with the physiotherapist, expect it to take three to six months to heal, according to Sanford Orthopaedics Sports Medicine. It is suggested that the patient must take a break of at least three months from sports and athletics. The patients are also suggested to wear a brace for continuous stretch of time.
Other than rest and bracing, there are many other things to avoid in spondylolisthesis. We are now listing spondylolisthesis exercises to avoid to ensure proper and speedy recovery. These include lumbar extension movements that can take your spine past the neutral position. The lumbar extension movements may increase the pain and slow down the healing of the affected vertebrae.
Some other exercises to avoid in spondylolisthesis include –
- Prone press-ups (Push-up while lying on the stomach)
- Standing extensions
- Prone leg raises (Lifting legs while lying on the stomach)
- Back extension machine at the gym
It is also suggested that yoga asanas must also be avoided in spondylolisthesis. Yoga includes various back extension postures, like cobra and swan pose, which may not be safe to practice in spondylolisthesis.
There are some other exercises that must be avoided in spondylolisthesis. These includes weightlifting, exercises that need you to twist or bend, high impact activities that put a lot of stress on the healing back, like jumping rope or box jumps.
Now that we have learnt what exercises should be avoided for spondylolisthesis, we must also understand are the best to treat spondylolisthesis. Just like all the other injuries, physiotherapy is beneficial in the treatment of spondylolisthesis. Mostly, the rehabilitation focuses on increasing the core muscles without going past neutral along with hamstring stretches. One should expect up three to six months of rehabilitation before returning back to normalcy.
Spondylolisthesis Exercises to Do
We suggest the following spondylolisthesis exercises for a speedy and efficient recovery. We also suggest you to consult with your physiotherapist and not undertake any of these exercises without his approval.
- Pelvic tilt exercises – These exercises help in reducing the discomfort by stabilising the lower spine in a flexed position. Depending upon the pain and your preference, pelvic tilt exercises can be done in various positions.
- Crunches – Patients suffering from spondylolisthesis often face instability and pain caused by weak abdominal muscles. This can be strengthened with powerful crunch exercises. You must try to focus on proper form and moving slowly to engage the core muscles. Spondylolisthesis is a painful condition to be in and therefore we suggest not to force the body to move through full range of motion. This may increase the pain and slow down the recovery time.
- Hamstring stretch – Spinal instability often causes tension in the hamstrings to those suffering from spondylolisthesis. Hamstrings are the large muscles that run down the back of the thigh. Stretching hamstrings sitting on the ground can help to relieve tension and tightness caused due to spondylolisthesis. It also reduces the lower back pain.
- Multifidus activation – Multifidus muscles are the small but very important muscles lying next to the spine. These muscles help in bending and twisting movements thereby increasing the stability of the spinal joints. If suffering from spondylolisthesis, activating multifidi will ease the pain and provide the much-needed comfort.
- Double knee to chest – This spondylolisthesis exercise is suggested to decrease the instability and improve the strength. It works on the core muscles of the torso and is thus beneficial in spondylolisthesis.
Check with your physiotherapist before starting any exercise program for spondylolisthesis while recovering from this injury. You can aim for a gradual return to physical and sports activities, depending on the severity of the injury and how string your core is. Post healing core strengthening is also suggested to prevent future injuries.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
For those managing spondylolisthesis, seeking guidance from professional physiotherapists is essential. Whether you are looking for physiotherapy in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, or Liberty Village, there are specialized clinics available to help you avoid harmful exercises and support your recovery with personalized treatment plans.
Physiotherapy is the study of science of movements. It is a healthcare profession that includes different treatment modalities like massages, electrotherapy, heat therapy, exercises, patient awareness and advice for treating an ailment, deformity or injury.
When should I go to a Physiotherapist?
This is a very common yet important question. If you have suffered an injury or chronic pain that affects your daily chores, then you must consult a good physiotherapist. You can also avail the benefits of physiotherapy after surgery, like knee replacement or stroke.
At Physiotherapy Oakville, we have a team of dedicated and skilled physiotherapists who provide expert care tailored to your specific needs. Scientific research supports the role of physiotherapy in improving recovery outcomes and enhancing overall physical function post-surgery. By joining Physiotherapy Oakville, you gain access to personalized treatment plans and evidence-based practices that help you recover efficiently and resume your daily activities with confidence.
What will a Physiotherapist do?
Our experienced Physiotherapists provide case-based solution to your need. These are focused on preventive as well as rehabilitation. Some scenarios where a good Physiotherapist can help –
- Back and neck pain caused due to sprain in the skeleton or muscles
- Conditions like arthritis or after effects of amputation that results in discomfort in joints, muscles, knees and ligaments
- Lung disorders like asthma or bronchitis
- Disability resulting from heart problems
- Troubles occurred during childbirth like pelvic issue, bladder and bowel problems
- Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis or loss of mobility due to trauma to the brain or spine
- Pain, swelling, fatigue, loss of muscle strength and stiffness during palliative care or cancer treatment
What should I expect from my Physiotherapist?
Our trained Physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy provide specific and concerned answers to your core problems. This is what you can expect from your Physiotherapist-
- Your physiotherapist will understand your medical history
- Based on the medical history and symptoms, the physiotherapist will assess and diagnose your condition
- A treatment module will be set for you for your concern
- Specific exercises and assistive devices would be suggested to you based on your module
To understand what all things are done in Physiotherapy, let’s try to learn the various types of treatment modalities used in Physiotherapy.
- Manual Therapy – This technique is a very common one where the physiotherapists massage the affected joints to mobilise and manipulate using his hands. Our team of expert physiotherapists in Toronto are highly equipped and experienced in this therapy.
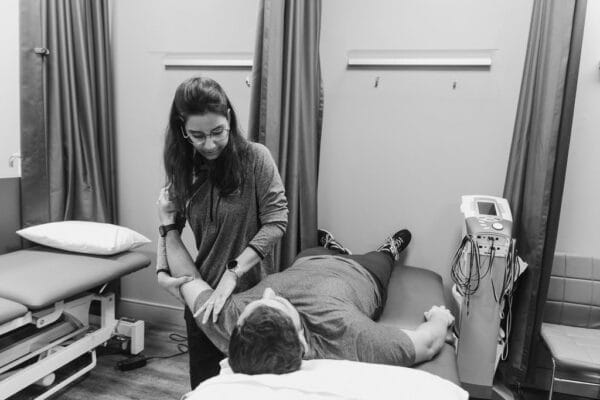
- Transcutaneous Electric Nerves Stimulation (TENS) Therapy – In this therapy, the physiotherapist uses a small device driven by a battery and place it on the skin surface of the patient. Low grade currents are sent through these electrodes to relive pain of the affected area.
- Magnetic Therapy – This therapy uses electromagnets of different sizes and types. These are used to limit the pain of the affected body part.
- Dry needling and acupuncture – In this therapy, the physiotherapist uses fine needles and insert them into specific body parts to alleviate the pain for a short time. You can consult with our physiotherapists at Etobicoke clinic for this specialized line of treatment.
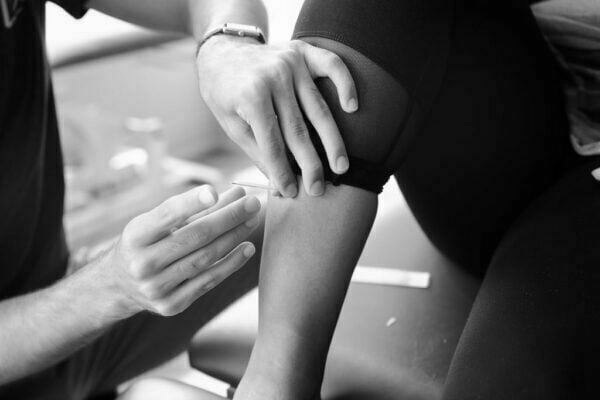

- Taping – This physiotherapy technique is highly popular as it promotes body’s inherent natural healing mechanism. Here, the physiotherapist uses a tape which lifts the skin away from the connecting tissue, thereby increasing the space and allowing the lymphatic fluid to move more functionally to ease the pain.
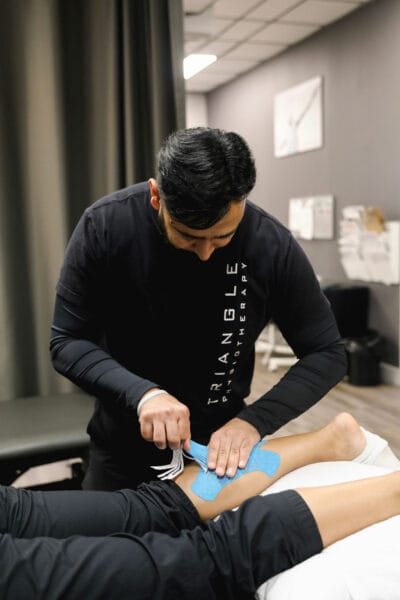
- Joint Mobilisation – This is a manual therapy technique where a physiotherapist mobilises the joint at different depths, speeds and amplitudes. It helps in restoring normal joint movement in the body. Our physiotherapists at Lawrence Park clinic are highly equipped and skilled in this technique.

- Stretches and exercises – This is a fairly common module where the physiotherapist teaches different exercises and techniques for body stretching which helps in restoring the joint movements.
- Rehabilitation – This includes a broad range of corrective, preventive and stretching exercises to reduce the sprain or pain in the affected area.
- Strengthening Program – This is one of the most important modalities in physiotherapy where the physiotherapist conducts specific program to make the patient understand about his personal responsibility towards his health and physical conditioning. This program is very useful as it helps the patient in improving overall heath, strength, balance, coordination and flexibility.

- Diathermy – In this technique, electrically induced heat or high-frequency electromagnetic currents are used to relive the pain and cure the condition. Our physiotherapists at North York clinic are efficient and skilled in this technique. If you are facing pain or recovering from a surgery, you can consult us.
- Ultrasound and phonophoresis – A frequency range of 0.5 – 3 MHz is used in this therapeutic ultrasound. This technique induces a deep heat to the target area to treat muscle spasm, promote healing at cellular level and lower the inflammation. It also increases the metabolism and improve the flow of blood towards the damaged tissue. Phonophoresis uses ultrasonic waves for better absorption of drugs that are applied topically during the treatment. This is a very useful technique as it helps in reducing the pain by allowing maximum absorption of drugs like anti-inflammatory and analgesics.
- Range of Motion exercises (RoM) exercises – A good physiotherapist would diagnose the patient and recommend Range of Motion exercises to improve the mobility of joints and reduce the stiffness in the muscles. There are various types of RoM exercises, like Passive Range of Motion (PROM) exercises, Active Assistive Range of Motion (AAROM) exercises and Active Range of Motion (AROM) exercises.
- Soft tissue mobilization – This highly effective technique in physiotherapy helps in alleviating pain, reducing swelling and relaxing the tight muscles in the body.
To summarize, Physiotherapy is a special treatment to maintain, restore and make the most of a person’s function, mobility, strength and well-being. It helps through various techniques and aid in recovery as well as strengthen the body for w holistic living.
Now that we have established what all is done and expected in Physiotherapy, we would like to hear from you. Please write to us if you have any questions regarding Physiotherapy. You can also check our services and locations for any line of treatment.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Physiotherapy encompasses a wide range of techniques, including manual therapy, exercise prescription, and patient education, to promote healing and recovery. For those seeking physiotherapy services, there are numerous clinics available in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These locations offer expert care and customized treatment plans to help patients achieve optimal health and mobility.
Imagine you have the power to control your pain, and stiffness.You will not have to spend months in therapy. You will not need to buy or use expensive equipment. You will not have to rely on needles, injections or surgery.You will use your own skills and resources when you gain knowledge and guidance from a Certified McKenzie Provider.
What is the McKenzie method?
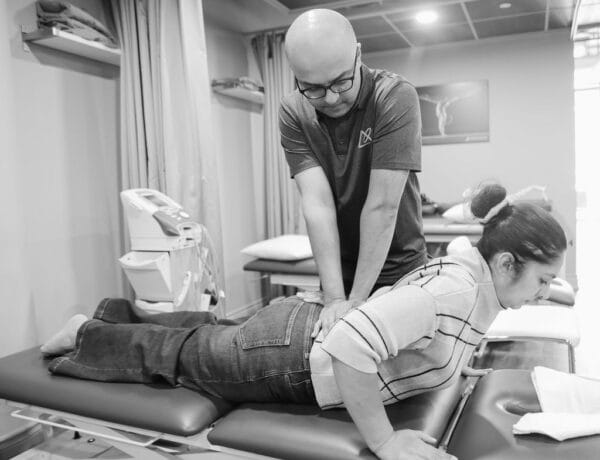
The Mckenzie method utilizes repeated movements for assessment , diagnosis and treatment. It is a comprehensive and clinically reasoned evaluation of patients where the emphasis is on patient independence , avoidance of therapist dependency, and use of minimal intervention.
Also read, Best Physiotherapy Clinic in Etobicoke
What lower back problems can we treat with Mckenzie?
Developed by world-renowned expert physiotherapist Robin McKenzie in the 1950s, this well-researched MDT is a reliable assessment process intended for all musculoskeletal problems, including pain in the back, as well as issues associated with sciatica, sacroiliac joint pain, arthritis, degenerative disc disease, muscle spasms and intermittent numbness in feet. If you are suffering from any such issues, then a MDT assessment may be right for you!
How does it work?
Most musculoskeletal pain is “mechanical” in origin, which means it is not due to a serious pathology like cancer or infection but a result of abnormal forces or mechanics occurring in the tissue. Further, it means that a position, movement or activity caused the pain to start. If a mechanical force caused the problem then it is logical that a mechanical force may be part of the solution. The MDT system is designed to identify the mechanical problem and develop a plan to improve it. In the simplest and most common instance, this may mean that moving in one direction may provoke and worsen the pain, and moving in the opposite direction may eliminate the pain and restore function.
Also Read, Best Clinic for Physiotherapy in Oakville
Assessment, treatment and prevention.
The McKenzie assessment process begins with the trained clinician taking a detailed history about your symptoms and how they behave. This enables the clinician to identify specific pain patterns, which then helps the clinician develop a treatment plan specific to your pattern of presentation. The clinician will prescribe specific exercises and advice regarding appropriate postures and ergonomics.If your problem has a more difficult mechanical presentation, a certified McKenzie clinician can provide advanced hands-on techniques to help manage the problem until you can self-manage.The aim is to be as effective as possible in the least number of treatment sessions. By learning how to self-treat your current problem, you gain hands-on knowledge to minimize the risk of recurrence and rapidly deal with symptoms if they recur putting you in control safely and effectively. The chances of problems persisting can more likely be prevented through self-maintenance.
Take control of your pain, empower yourself and get back to the life you love with the McKenzie Method of Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy.
Book an appointment with our McKenzie Certified Physiotherapist, Ankit Doshi, BPT, MClSc (Adv Healthcare Practice), FCAMPT, CGIMS, Cert. MDT
Related Tags : Physiotherapy Toronto, physiotherapy Oakville, physiotherapist Toronto, physiotherapist North york, physiotherapists Toronto, physiotherapists Oakville, physiotherapy exercise Toronto, physiotherapy exercise Oakville
The McKenzie Method is a proven approach for managing low back pain through specific exercises and posture correction. If you are seeking professional physiotherapy to help with back pain, there are excellent clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics provide personalized care and expert guidance to help you manage pain and improve your quality of life.
Shoulder Prehabilitation (prehab) involves the process of implementing a physical, psychological, nutritional intervention before an individual goes into surgery. The goal behind prehab programs is to maximize an individual’s physical and psychological fitness/health before surgery in order to reduce pain, increase physical function and allow you to return to your normal activities sooner following surgery.
Although there is limited evidence regarding shoulder prehab programs, there is promising and growing evidence that suggests prehab programs for hip, knee, and spinal surgery may improve pain, function and reduce the total cost of healthcare spending in the post-operative period.
Also Read, Physiotherapy Clinics in Etobicoke
Types of Surgeries for Shoulder
- Reverse arthroplasty
- Total shoulder arthroplasty/replacement
- Rotator cuff repair
- SLAP repair
- Bicep tendon repair
- Tenotomy
What Prehab Programs look like:
Most prehab programs can be anywhere from 2-8 weeks leading up to surgery and could potentially involve:
1) Exercise training (2-3x/week)
- Strengthening and stabilization exercises for the rotator cuff and muscles supporting your shoulder blade
- Home exercise program tailored to your needs
- Exercise training 1 on 1 with a physical therapist
2) Education: information delivered regarding
- Shoulder anatomy and mechanics
- Pain science education
- The process of your operative procedure
- Patient-therapist expectations
- Post-operative protocol
- Detailed exercise program and technique
Also read, Best Physiotherapist near Mississauga
3) Nutritional support
- Consultation with a registered dietician
- Detailed nutrition programs to optimize physical and mental health
- Nutritional supplements as indicated
4) Psychological support
- Consultation with psychologist/ psychotherapist
- Anxiety and stress reduction
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Relaxation techniques
- Coping strategies for surgery
Shoulder Prehab is a set of exercises and movements designed to strengthen and condition the shoulder joint and surrounding muscles, helping to prevent injury or improve recovery from a previous injury. Prehabilitation may include:
- Shoulder rotator cuff strengthening exercises such as internal and external rotation with light weights.
- Scapular stability exercises to improve posture and reduce stress on the shoulder joint.
- Stretching to improve flexibility and range of motion.
- Plyometric exercises to improve power and explosiveness.
- Core stability exercises to improve overall body control and stability.
Prehabilitation should be performed regularly, especially if you have a history of shoulder injuries or plan to participate in overhead activities such as weightlifting or throwing. By taking care of your shoulder before it becomes a problem, you can help prevent injury and improve your performance.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Shoulder prehabilitation is essential for preventing injuries and optimizing recovery, especially for those undergoing surgery or managing shoulder pain. If you’re looking for professional physiotherapy services for shoulder prehabilitation, there are several clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These locations offer specialized care to help you strengthen your shoulders and maintain overall joint health.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is caused by the wear and tear of the cartilage and can affect all joints in the body. The most commonly affected areas are the knees, hips, low back, neck, and the digits of the hands and feet. Osteoarthritis affects 3.3%-3.6% of the population globally. The risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, gender, weight, anatomy, and history of trauma. The severity of osteoarthritis can be evaluated through medical imaging.
The following are characteristics and clinical presentation of OA:
- Use-related pain
- Stiffness
- Crepitus
- Decrease range of motion and flexibility
- Instability, Weakness
- Deformity
- Swelling
- Local

Also read, Best Physiotherapy Clinic in Mississuaga
OA can be managed conservatively through physiotherapy or chiropractic interventions. Pharmacological or surgical intervention may also be of benefit depending on the severity of the joint. Assistive devices can aid in offloading the damaged joint. Physiotherapy and chiropractic treatment for osteoarthritis focuses on reducing pain and increasing physical function through education and exercises. An individualized exercise program consisting of stretching and strengthening the muscles surrounding the affected joint will improve the well-being of the individual.
Tell me more about the GLA:D™ for knee and hip osteoarthritis.
- Good Life with osteoArthritis in Denmark (GLA:D™), developed in Denmark, is an education and tailored neuromuscular exercise program designed for individuals with hip or knee osteoarthritis
- The program is unique because it provides education and targeted exercise that can be applied to movement in everyday activities
- The program is suitable for individuals with early to late stages of OA
The following are the benefits of an individualized exercise program:
- Decrease pain and stiffness
- Increase mobility and function
- Improve muscles length and elasticity
- Improve cartilage
- Reduce risk of injury
- Delay surgical intervention
A physiotherapist and chiropractor can help identify the main issues affecting an osteoarthritic joint and create a treatment program based on your needs and goals.
Contact us today if you would like to see one of our physiotherapists or chiropractors to help you manage your osteoarthritis & relieve your pain.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Managing osteoarthritis effectively requires a comprehensive treatment approach, including physiotherapy to alleviate pain and improve mobility. If you’re looking for professional physiotherapy services to support your osteoarthritis management, clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village offer expert care and personalized treatment plans to help you achieve better joint health and quality of life.
Knee ligament injuries are quite common, and they can occur at any age. These injuries can be caused by a variety of factors, such as sports injuries, accidents, or falls. Knee ligaments connect the bones in the knee, and when they are injured, they can cause severe pain, swelling, and instability in the joint.
Anatomy of the Knee
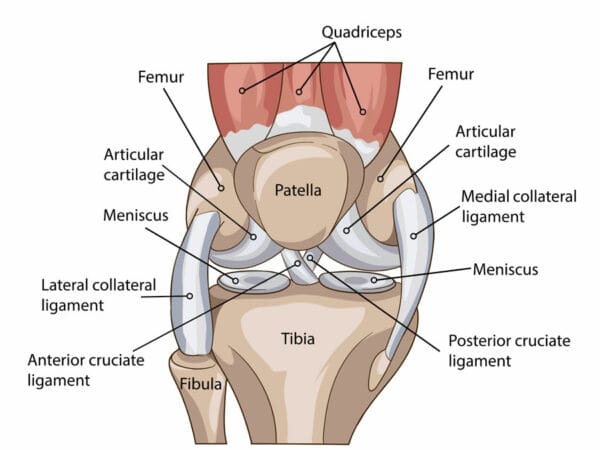
There are four primary ligaments in the knee, and they are the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), the medial collateral ligament (MCL), and the lateral collateral ligament (LCL). Each of these ligaments serves a vital function in the knee joint, and an injury to any one of them can cause significant problems.ACL injuries are common in sports that require sudden stops and starts, such as football, basketball, and soccer. A sudden change in direction or a twisting motion can cause the ACL to tear or sprain. Symptoms of an ACL injury include a popping sound in the knee, severe pain, swelling, and difficulty walking or standing.
PCL injuries are less common than ACL injuries but can occur in the same types of sports. The PCL is located at the back of the knee and is responsible for stabilizing the knee joint. Symptoms of a PCL injury include pain, swelling, and instability in the knee joint.
MCL injuries are often caused by a direct impact to the outer side of the knee, such as during a tackle in football. Symptoms of an MCL injury include pain, swelling, and difficulty straightening the knee.LCL injuries are less common than MCL injuries but can occur in the same types of sports. The LCL is located on the outer side of the knee and is responsible for stabilizing the joint. Symptoms of an LCL injury include pain, swelling, and instability in the knee.
What is the best treatment for Knee ligament injuries?
Treatment for knee ligament injuries varies depending on the severity of the injury. In mild cases, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) may be all that is necessary to relieve pain and swelling. In more severe cases, surgery may be required to repair the damaged ligament.
Physical therapy is an essential component of treatment for knee ligament injuries. A physical therapist can help the patient regain strength, mobility, and flexibility in the knee joint. Exercises that focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee can help reduce the risk of future injuries.
How do I prevent knee injuries from recurring?
Preventing knee ligament injuries is also essential, especially for athletes who participate in high-impact sports. Wearing appropriate protective gear, such as knee pads, can help reduce the risk of injury. Stretching before and after exercise can also help prevent injuries.
In conclusion, knee ligament injuries can be a significant source of pain and disability. It is essential to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect you have a knee ligament injury. With the right treatment and rehabilitation, most people can recover from these injuries and return to their normal activities. Preventing knee ligament injuries is also crucial, and taking appropriate precautions can help reduce the risk of injury.
Book an appointment to see one of our physiotherapists to get that knee injury treated.
Recovering from knee ligament injuries requires proper physiotherapy to restore strength, stability, and function. For those seeking professional care, there are numerous physiotherapy clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics provide expert physiotherapy services and personalized rehabilitation programs to help you recover effectively and return to your active lifestyle.
Knee pain is a very common complaint. It is something that can originate from many different structures in and around the knee. The knee joint is made up of the interaction between the femur (thigh), the tibia (shin), and the patella (kneecap). All the tissues around these areas can be contributing to your knee pain.

Common structures that can be contributing to your knee pain include but are not limited to: Ligamentous support around the knee (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL), Meniscus Patellar Surfaces, Bursa Patellar or Quadriceps tendon. Pain in the knee could also be referral from other structures in the body such as the low back, or soft tissues further up or down the kinetic chain. Because of this, it is important to speak to a knowledgeable physiotherapist or chiropractor who can provide a detailed assessment.

People with knee pain commonly complain of inability to perform physical activity, pain when walking, standing, going up or down stairs, along with stiffness and lack of range of motion. A lot of these people are able to return to previous levels of physical function with a graded rehab program provided by a skilled practitioner. With a proper program, they are able to exceed their prior levels of function.
Physiotherapists are trained to assess, diagnose and treat musculoskeletal conditions, including knee pain. They use a variety of techniques and exercises to help alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent further injury. Some common techniques used by physiotherapists for knee pain include manual therapy, stretching and strengthening exercises, taping, and the use of modalities such as heat, cold, and electrical stimulation. Additionally, physiotherapists may provide education on proper body mechanics, ergonomics, and lifestyle modifications to help prevent future injury.
If you are struggling with knee pain, be sure to seek out a physiotherapist or certified FRC practitioner who can help you reach your physical activity goals.