Who doesn’t want to stay flexible, especially as they age? Well, stretching is one very good way to stay flexible! According to the American College of Sports Medicine, it’s good to stretch all the major muscle groups at least two times a week. Stretching is an integral part of physiotherapy, and a physiotherapist is the perfect person to guide you on how to stretch. Physiotherapists recommend stretching regularly, as it keeps one’s hips and hamstrings flexible later in life, which is very important for easy movement in old age.
Apart from this stretching has many other benefits:
- It increases muscle flexibility
- It improves posture
- It also improves performance in sports & other activities
- It provides relief from stress
- It helps prevent injuries
- It prevents Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness or DOMS, which is the soreness and pain one suffers a few hours to a few days after hectic exercise.
Also read, Physiotherapy Etobicoke
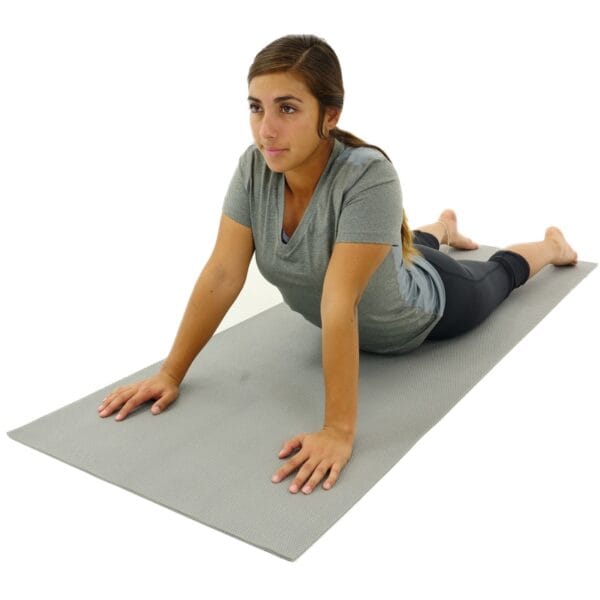

The first question that many wonder about, is what body parts should one stretch.
In physiotherapy, stretching the following body parts is considered essential –
- Neck
- Jaw
- Upper Back
- Shoulders
- Triceps
- Biceps
- Wrists
- Quadriceps
- Calves
- Hamstrings
- Hips
- Groin
The next thing to take into consideration is if there is the right amount of time to stretch. While there is no particular amount of time that physiotherapists suggest you stretch, recent studies show that 3 sets of 30-second stretches, 5 days per week for 4 weeks help to strengthen hamstring muscles greatly.
Also read, Physiotherapy Treatment Oakville
There are many kinds of Stretching that physiotherapists recommend.
Stretching a muscle to its full extent and holding it for 15 to 30 is known as the Static Stretch. You can exceed this time frame a bit but don’t stretch until it hurts, as you can end up doing more damage to your muscles than good by over stretching. However, don’t do Static Stretches before a run or sprint, as this can slow down your speed by tiring out the muscles.
Before warming up for a run or other sports, doing Dynamic Stretches is more suitable. Dynamic Stretches are stretches that you do, as you are moving, and hence are called dynamic.
Another effective way of stretching, often used in physiotherapy, is Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Stretching.
PNF stretching is an advanced type of stretching wherein the targeted muscle or muscle group, is stretched, contracted, and finally relaxed. This process is repeated at least 2 to 4 times before moving on to the next muscle group. PNF stretching helps to elongate one’s muscles and was first developed as a muscle therapy by athletes, but is now often used in physiotherapy as a means of increasing flexibility.
Stretching can be used as a preventative precaution, but also to help correct and recover from more serious issues. A physiotherapist can guide you more regarding the stretching exercises that will be best suited to your needs. So visit any of our locations in Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Mississauga & Toronto, and find out how you can get the most out of stretching!
Stretching with physiotherapy can help improve flexibility, prevent injuries, and enhance overall physical performance. If you’re looking for professional physiotherapy services to guide you in safe and effective stretching techniques, there are clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics provide expert care and personalized treatment plans to help you achieve your mobility and wellness goals.
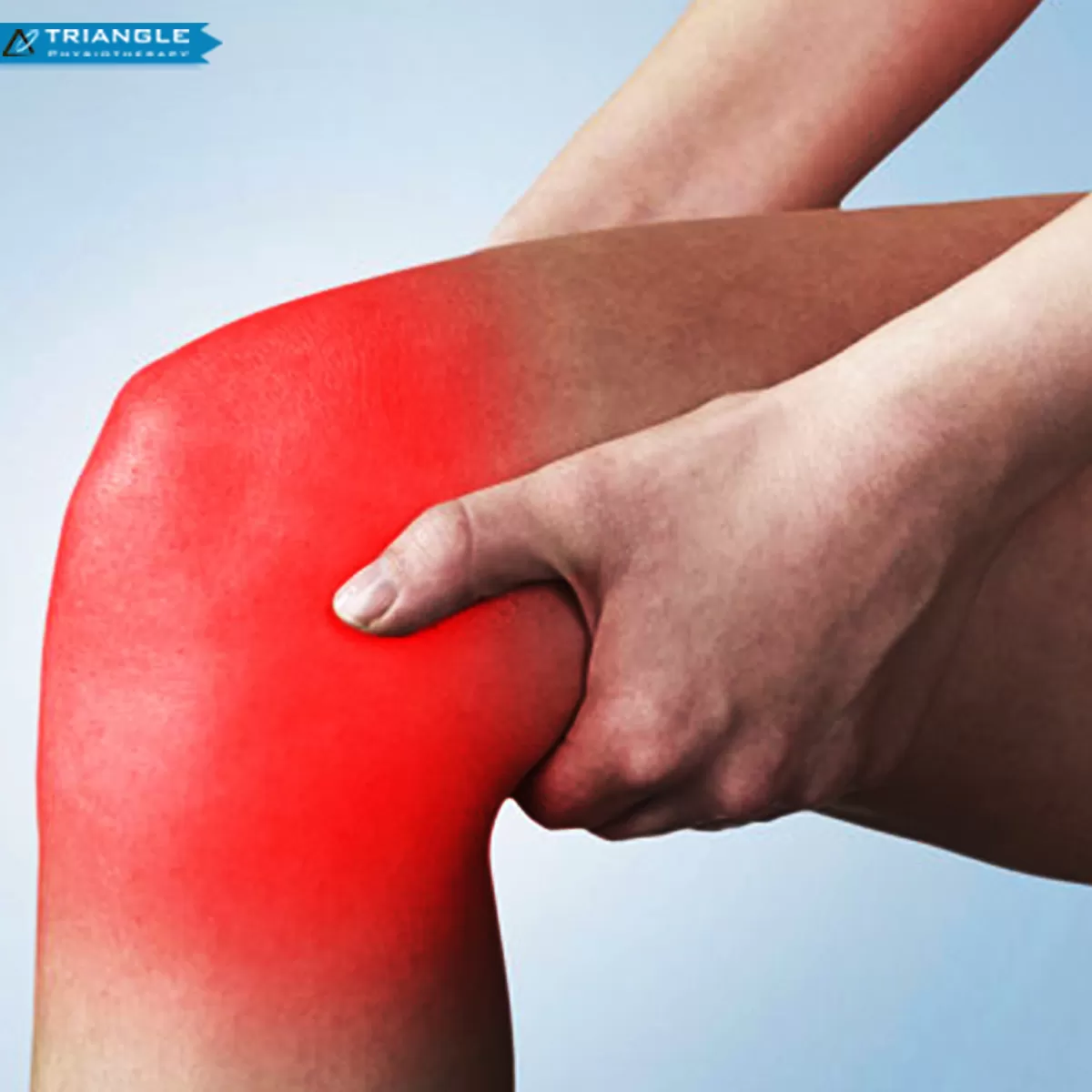
A knee sprain is an injury of the ligaments; tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect the bones of the upper and lower leg at the knee joint. One of the main forms of knee sprain is in the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ACL and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) bridge the inside of the knee joint, forming an, “X” pattern that stabilizes the knee against front-to-back and back-to-front forces.
There are certain movements in the knee that cause a sprain in the ACL such as:
- a sudden stop;
- a twist,
- pivot, or change in direction at the joint;
- extreme over-straightening (hyperextension);
- or a direct impact to the outside of the knee or lower leg.
These injuries are quite common among athletes in sports such as football, basketball, soccer, rugby, wrestling, gymnastics, and skiing.
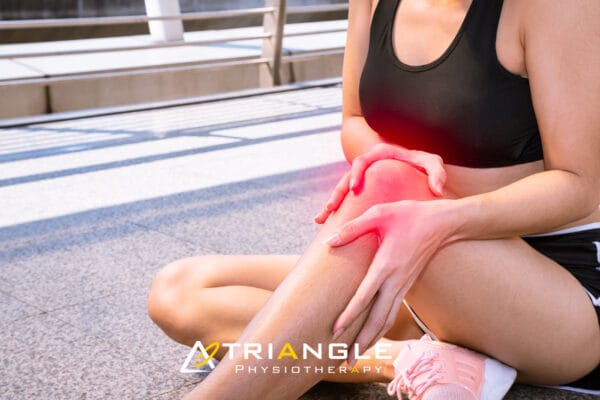

It is suggested that when one knee ligament suffers a sprain, there is a good chance that the other parts of the knee may also be injured, most commonly the ACL. Knee sprains are very common. ACL sprains tend to cause more significant symptoms compared to MCL injuries.
The most frequent signs of an ACL sprain are:
- A pop heard or felt inside your knee at the time of injury
- Significant knee swelling within a few hours after injury
- Severe knee pain that prevents you from continued participation in your sport
- Black-and-blue discoloration around the knee
- Knee instability- the feeling that your knee will buckle or give out
Treatment of an ACL Sprain
A physiotherapist will examine both knees, comparing the injured knee to the uninjured one. During this exam, the physiotherapist will check your injured knee for signs of swelling, deformity, tenderness, fluid inside the knee joint, and discoloration. If the patient does not have too much pain and swelling, a physiotherapist will then evaluate the knee’s range of motion and will pull against the ligaments to check their strength. During the exam, the patient will have to bend their knee and the physiotherapist will gently pull forward or push backward on their lower leg where it meets the knee.
Based on the results of the patient’s exam, diagnostic tests may need to be performed to further evaluate the condition of the patient’s knee. These tests may include standard X-rays to check for ligament separation from bone or fracture. Tests may also include an MRI scan or a camera–guided knee surgery (arthroscopy). The expected duration of recovery depends on the severity of the patient’s knee sprain, their rehabilitation program, and what type of sports the patients play. In general, milder sprains heal within 2-4 weeks, whereas other types may take 4-12 months.
There are many ways of preventing ACL knee sprain, to help sports related injuries you can:
- Warm up and stretch before participating in athletic activities
- Do exercises that strengthen the leg muscles around the knee, especially the quadriceps.
- Avoid sudden increases in the intensity of a training program. Do not push too hard or too fast. Gradually increase intensity.
- Wear comfortable, supportive shoes that fit your feet and fit your sport
About 90% of people with ACL injuries can expect a full recovery after proper treatment and a good physical therapy program. As a long-term complication, some patients who suffered from an ACL sprain eventually develop pain from osteoarthritis in the joint where the knee has been injured. This symptom may not become present until 15 to 20 years after the initial knee injury.
Call a professional when:
- Knee becomes very painful or swollen
- Cannot bear weight
- Feels as if it will buckle or give out.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Recovering from an ACL sprain involves targeted physiotherapy to restore knee stability, strength, and mobility. If you need professional physiotherapy services for ACL rehabilitation, consider clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics provide expert care and customized treatment plans to help you recover fully and return to your active lifestyle.