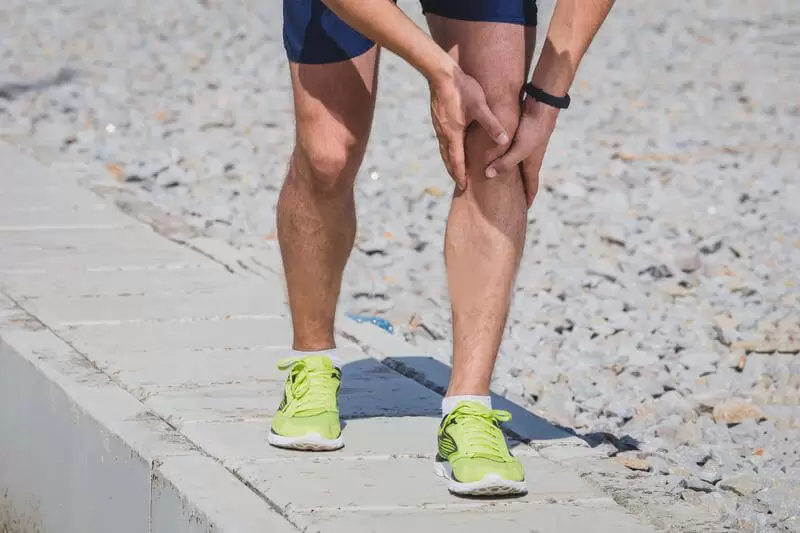
Pacifying the Pain – All about Patella Tendon Tears
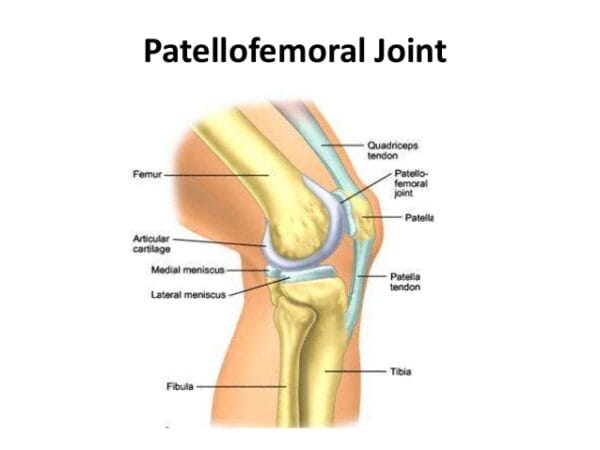
Despite it being named a “Tendon”, the patella tendon is both a ligament and a tendon. It connects to two different bones, the patella and the tibia. The patella tendon works in unison with the quadricep muscles and quadriceps tendons allowing them to straighten the knee. The tear within the patella tendon is either partial or complete and can be a disabling injury:
- Partial tear- More frayed and not complete, (think of a rope that is not completely torn)
- Complete Tear- The tissue is torn into two complete pieces
There are numerous causes that can contribute to the tear of a patella tendon:
- Falls
- Jumping
- Patellar tendonitis- inflammation of the patellar tendon thus weakening the tendon, causing small tears.
- Chronic disease – Chronic renal failure, rheumatoid arthritis, Diabetes mellitus & metabolic disease, etc.
- Infection
- Surgery
Also read, Best Physiotherapy Clinic Mississauga
Most patients have stated that they had felt a popping or tearing sensation when the patella tendon has torn. Additional symptoms recorded were:
- Indentation at the spot where the patella tendon is located
- Bruising
- Tenderness
- Cramping
- Shift of the kneecap to thigh, due to un-attachment
- Difficulty walking due to weakness in the knee
Also read, Physiotherapy Oakville
Once the initial pain and swelling has subsided, physiotherapy treatments can be started. Physiotherapy can restore strength and range of motion. Depending on the intensity of the injury, a brace may need to be worn. While the brace is worn, straight leg exercises are often prescribed to strengthen the quadriceps muscles. As the patellar tendon heals, eventually the brace may be removed, allowing the patient to move freely with a greater range of motion, with more exercises being put into use as healing progresses.
Recovery from patellar tendon tears is possible, and most individuals are able to return to work and regular activities. Even though patients may feel stiffness in the region after recovery, most regain nearly equal motion compared to the uninjured leg. At Triangle Physiotherapy, we are able to dispense custom-fit braces to aid in the recovery of patellar tendon tears. For more information visit our custom braces page at: http://www.trianglephysiotherapy.com/services/custom-bracing
Recovering from a patella tendon tear requires a comprehensive approach, including effective physiotherapy to restore strength and mobility. If you’re seeking professional physiotherapy services for tendon injuries, there are clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These locations offer expert care and customized treatment plans to help you recover fully and get back to your active lifestyle.
What exactly are shin splints? Are they treatable?
Shin splints are a condition characterized by damage and inflammation of the connective tissue joining muscles to the inner shin bone (tibia). Shin splints are known by many different names such as: Medial Tibial Tenoperiostitus, MTSS, Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome, Tenoperiostitus of the Shin, Inflammatory Shin Pain, Traction Periostitis, and Posterior Shin Splint Syndrome.
Several muscles lie at the back of the lower leg, and are collectively known as the calf muscles. The tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallicus, and soleus are muscles that lie deep within the calf and attach to the inner border of the tibia. Connective tissues are responsible for attaching these muscles to the tibia known as the tenoperiosteum. Every time the calf contracts, it pulls on the tenoperiosteum. When the tension becomes forced too much or is repeated frequently, the damage is caused to the tenoperiosteum. The results are inflammation and pain. Shin splints can also occur in combination with other pathologies that cause shin pain such as compartment syndrome and tibial stress fractures.
Patients who suffer from shin splints experience pain along the inner border of the shin. In other cases, the patient may experience an ache or stiffness along the inner aspect of the shin that increases with rest (typically and night or first thing in the morning). Areas of muscle tightness, thickening, or lumps may also be felt in the same area of pain.

There are several factors that predispose patients to shin splints:
• Excessive training or exercise
• Poor foot posture (especially in patients with flat feet)
• Inappropriate footwear
• Inadequate warm-up• Training on hard or inappropriate surfaces
• Muscle weakness (especially in calve muscles)
• Tightness in specific joints (such as ankle)
• Tightness in specific muscles (calves especially)
• Poor lower limb biomechanics
• Poor training techniques or methods
• Leg length differences
• Poor balance
• Being overweight
• Deconditioning
• Poor core stability
Also read, Physiotherapy Clinic in Oakville
Physiotherapy treatment for patients with shin splints is vital to speed up the healing process. Physiotherapy will ensure the most optimal outcome and reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Treatment may comprise of the following:
- Deep tissue massage
- Joint mobilization
- Dry needling
- Electrotherapy
- PNF stretches
- Arch support taping
- The use of orthotics or shock-absorbing insoles
- Crutches
- Biomechanical correction
- Ice or heat treatment
- Exercises to improve flexibility, balance, strength, and core stability
- Activity modification advice
- Anti-inflammatory advice
- Footwear advice
- Weight loss advice where appropriate
Also read, Physiotherapy Clinic in Mississauga
If you happen to suffer from shin splints and you are looking for a way to relieve pain, stress, and improve overall health, try adding physical therapy to a routine wellness plan. Our physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy can be a powerful ally when combating daily stress, muscle pain, and general health issues when it comes to shin splints. Not only does physical therapy relieve pain, increase energy levels, and improve overall physical and mental performance, it prevents further injuries.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Physiotherapy can play a crucial role in treating and preventing shin splints by addressing muscle imbalances and improving biomechanics. If you’re looking for professional physiotherapy services to help manage shin splints, there are clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics offer expert care and tailored treatment plans to support your recovery and enhance your running or athletic performance.
Do your legs tingle, become numb, or feel weak? You may be experiencing Sciatica. The term Sciatica describes leg pain that originates from the lower back and travels through the buttock and down the large sciatic nerve in the back of each leg. Sciatica is not a medical diagnosis in and of itself –it is a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Common lower back problems such as: lumbar herniated disc, degenerative disc disease, and spondylolisthesis can cause sciatica symptoms.
Sciatica is often characterized by one or more of the following symptoms:
• Constant pain in only one side of the buttock or leg (rarely in both legs)
• Pain that becomes worse when sitting
• Leg pain that is described as burning, tingling, or searing
• Weakness, numbness, or difficulty moving the leg, foot, and/or toes
• A sharp pain that may make it difficult to stand up or walk
• Pain that radiates down the leg and possibly into the foot and toes
Physiotherapy exercises incorporating a combination of strengthening, stretching, and aerobic conditioning are a central component of almost any sciatica treatment plan.
• Strengthening exercises- Most of these back exercises focus not only on the lower back, but also the abdominal muscles, and the buttock and hip muscles.
• Stretching exercises- Stretches for sciatica are designed to target muscles that cause pain when they are tight and inflexible.
• Low-impact aerobic exercise- Some form of low-impact cardiovascular exercise such as: walking, swimming, or pool therapy is usually a component of recovery, as aerobic activity encourages the exchange of fluids and nutrients to help create a better healing environment.
Also read, Physiotherapy Clinic Etobicoke
When patients engage in a regular program of gentle exercises, they can recover more quickly from sciatica pain and are less likely to have future episodes of pain. As sciatica is due to pressure on the sciatic nerve, it stands to reason that treatment involves removing this pressure. Your physiotherapy treatment aims to achieve this by reducing nerve pressure caused by poorly moving spinal joints as well as easing muscular tension in the lower spine, buttock, and leg.
If you are suffering from sciatica please do not delay. You can achieve the best results when you address the symptoms early!
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Dealing with numbness can be challenging, but physiotherapy can help by improving circulation, reducing nerve compression, and enhancing mobility. For those seeking professional physiotherapy services to address numbness or related conditions, there are clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These locations offer expert care and personalized treatment plans to help you regain sensation and improve your quality of life.
Patellar tendinopathy aka, Jumpers Knee, (also known as patellar tendonitis, and tendonitis) is an overuse injury affecting the knee. The patella tendon is a short but very wide tendon that runs from the patella (kneecap) to the top of the tibia. It works with the muscles at the front of the thigh to extend the knee so it can perform physical acts like kicking, running, and jumping. Due to these elements, the patellar tendon has to absorb a lot of this loading and as a result, is prone to injury in runners and jumpers. Unlike many running injuries, patellar tendonitis is somewhat more common in men than in women.
The stress on the patellar tendon results in small tears, which the body attempts to repair, but as the injury multiplies, it causes pain from inflammation and weakening of the tendon. When this tendon damage persists for more than a few weeks, it is called, “tendinopathy”.

Initial symptoms of patellar tendonitis can be:
- Anterior knee pain over the patella tendon
- Pain increased from jumping, landing or running activity, and on occasion prolonged sitting
- Onset of pain can be gradual and commonly relates to an increase in sports activities
- Localised tenderness over the patella tendon
- The tendon feeling stiff, mostly first thing in the morning
- The affected tendon may appear thickened in comparison to the unaffected side
Also read, Physiotherapy Clinic in Oakville
Typically, tendon injuries occur in three areas:
- Musculotendinous junction (where the tendon joins the muscle)
- Mid-tendon (non-insertional tendinopathy)
- Tendon insertion (eg. Into the bone)
If you try to work through your pain, ignoring your body’s warning signs, you could cause increasingly larger tears in the patellar tendon.
Knee pain and reduced function can persist if the problem is not addressed , which can progress to more serious patellar tendinopathy.
Treatment of Jumpers Knee
Treatment of this condition has two objectives: to reduce inflammation and to allow the tendon to heal. Rest is a must when the knee is painful and swollen. Avoid stair climbing and jumping sports. Keep your knee straight while sitting, and avoid squatting.
Icing the knee for twenty minutes two to three times a day is recommended, especially after any sporting activities. Exercises can also be used to stretch and balance the thigh muscles.
It is advisable, however, to contact a physical therapist & approach proper physical therapy before you attempt any of these remedies, to avoid any further damage.
Happy Healing!
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Jumper’s knee can be a persistent issue for athletes, but physiotherapy can help by strengthening the knee, improving flexibility, and reducing pain. If you’re looking for professional physiotherapy services to treat jumper’s knee, consider clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These locations provide expert care and customized treatment plans to help you recover and return to your sport stronger than ever.
There are many forms of fractures, each causing a dilemma in our lives and requiring the help of a physiotherapist in order to heal safely and adequately. One of the most common types of fractures seen in sports medicine today is called a “hairline” or “stress” fracture. Hairline fractures are caused by repetitive strain and excess training. Hairline fractures are minute cracks on the bones, which can become severe if not immediately treated. The main causes of hairline fractures are:
- Traumatic Incidents
- Repetitive Stress
- Pathological
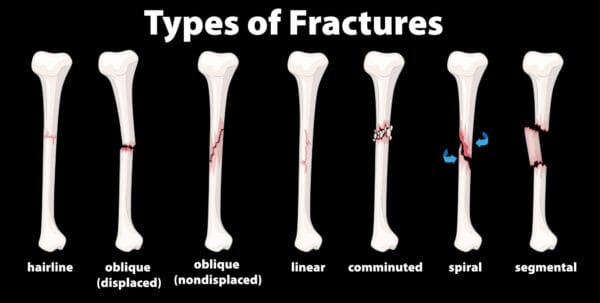
Also read, Physiotherapy Clinic in Mississauga
Causes of Fractures
Basically, hairline fractures are caused by the depressed response of the bone with the ground reaction forces that are applied to the bones during certain activities such as: running, jumping, or walking. Symptoms may include pain and tenderness to the affected bone. Repetitive stress or a sudden fall or strike to the area can also cause hairline fractures.
Treatment of Fractures
The best way to treat a hairline fracture is to refrain from any activities that can aggravate the injury. Recovery time can span from two weeks to a month and a half. Once the bone is healed from its minute cracks, you can gradually resume normal activities. In extreme circumstances, the affected area must be put at rest and must be immobilized by casting or bracing. The stages of healing a fracture through physiotherapy are as follows:
- Muscle Assessment
- Joint Mobilisation
- Massage Therapy
- Heat and Electro Therapy
- Gait Education
Also read, Physiotherapy Oakville
Shoe inserts like supportive orthotics and walking crutches may also be recommended by your physiotherapist. Treatment through physiotherapy is advised through strengthening exercises that are non-weight bearing like swimming. Luckily, hairline fractures rarely need surgery because they can easily be mended with just two weeks of rest. However, the injury can worsen if not given the proper medical attention.
If you happen to suffer from a hairline fracture and you are looking for a way to relieve pain, and recover from an injury, adding physiotherapy to a routine wellness plan can maximize recovery time and optimize your healing process. Our physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy can be a powerful ally when combating daily stress, muscle pain, and general health issues regarding hairline fractures. Not only does physiotherapy relieve pain, increase energy levels, and improve overall physical and mental performance, it prevents further injuries.
Our More Locations
Physiotherapy Etobicoke | Physiotherapy Oakville | Physiotherapy North York | Physiotherapy Toronto | Physiotherapy Lawrence Park | Physiotherapy Mississauga | Physiotherapy Queens Quay | Physiotherapy Mississauga Erin Mills | Physiotherapy Liberty Village
The experienced, professional physiotherapists at Triangle Physiotherapy are available at eight convenient locations:
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Recovering from a hairline fracture requires careful management and effective physiotherapy to restore strength and prevent further injury. If you are seeking professional physiotherapy services to support your recovery, there are clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These locations offer specialized care and personalized treatment plans to help you heal properly and regain full function.
A knee sprain is an injury of the ligaments; tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect the bones of the upper and lower leg at the knee joint. One of the main forms of knee sprain is in the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ACL and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) bridge the inside of the knee joint, forming an, “X” pattern that stabilizes the knee against front-to-back and back-to-front forces.
There are certain movements in the knee that cause a sprain in the ACL such as:
- a sudden stop;
- a twist,
- pivot, or change in direction at the joint;
- extreme over-straightening (hyperextension);
- or a direct impact to the outside of the knee or lower leg.
These injuries are quite common among athletes in sports such as football, basketball, soccer, rugby, wrestling, gymnastics, and skiing.

It is suggested that when one knee ligament suffers a sprain, there is a good chance that the other parts of the knee may also be injured, most commonly the ACL. Knee sprains are very common. ACL sprains tend to cause more significant symptoms compared to MCL injuries.
The most frequent signs of an ACL sprain are:
- A pop heard or felt inside your knee at the time of injury
- Significant knee swelling within a few hours after injury
- Severe knee pain that prevents you from continued participation in your sport
- Black-and-blue discoloration around the knee
- Knee instability- the feeling that your knee will buckle or give out
Treatment of an ACL Sprain
A physiotherapist will examine both knees, comparing the injured knee to the uninjured one. During this exam, the physiotherapist will check your injured knee for signs of swelling, deformity, tenderness, fluid inside the knee joint, and discoloration. If the patient does not have too much pain and swelling, a physiotherapist will then evaluate the knee’s range of motion and will pull against the ligaments to check their strength. During the exam, the patient will have to bend their knee and the physiotherapist will gently pull forward or push backward on their lower leg where it meets the knee.
Based on the results of the patient’s exam, diagnostic tests may need to be performed to further evaluate the condition of the patient’s knee. These tests may include standard X-rays to check for ligament separation from bone or fracture. Tests may also include an MRI scan or a camera–guided knee surgery (arthroscopy). The expected duration of recovery depends on the severity of the patient’s knee sprain, their rehabilitation program, and what type of sports the patients play. In general, milder sprains heal within 2-4 weeks, whereas other types may take 4-12 months.
There are many ways of preventing ACL knee sprain, to help sports related injuries you can:
- Warm up and stretch before participating in athletic activities
- Do exercises that strengthen the leg muscles around the knee, especially the quadriceps.
- Avoid sudden increases in the intensity of a training program. Do not push too hard or too fast. Gradually increase intensity.
- Wear comfortable, supportive shoes that fit your feet and fit your sport
About 90% of people with ACL injuries can expect a full recovery after proper treatment and a good physical therapy program. As a long-term complication, some patients who suffered from an ACL sprain eventually develop pain from osteoarthritis in the joint where the knee has been injured. This symptom may not become present until 15 to 20 years after the initial knee injury.
Call a professional when:
- Knee becomes very painful or swollen
- Cannot bear weight
- Feels as if it will buckle or give out.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Recovering from an ACL sprain involves targeted physiotherapy to restore knee stability, strength, and mobility. If you need professional physiotherapy services for ACL rehabilitation, consider clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics provide expert care and customized treatment plans to help you recover fully and return to your active lifestyle.
What is ALS?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the most common type of adult-onset motor neuron disease. Neurological disorders are characterized primarily by progressive degeneration and loss of motor neurons. ALS involves upper and lower motor neurons and presents as an idiopathic, progressive degeneration of anterior horn cells and their associated neurons, resulting in progressive muscle weakness, atrophy, and fasciculations.
What are the symptoms of ALS?
ALS is a gradual-onset disease. The first initial symptoms of ALS vary from person to person. One person may have trouble with their grip, such as holding a cup or pen, while another person may experience a change in pitch in their voice while speaking. The rate at which ALS develops also varies from person to person, with the mean survival time ranging from three to five years.
Although there are cases in which people have lived five, and ten or more years. Onset symptoms can begin in the muscles that control speech and swallowing, or in the hands, arms, legs, or feet. Not all people who suffer from ALS experience the same symptoms as others or the same sequences or patterns of progression. Although, universally progressive muscle weakness and paralysis are experienced.
How is ALS diagnosed?
ALS is a somewhat difficult disease to diagnose. There is not one test or procedure to instantly establish the diagnosis of ALS. Through the use of clinical examination, and a series of diagnostic tests, often ruling out other diseases that mimic ALS, that a diagnosis can be established. A comprehensive diagnostic check-list includes most, if not all, of the following procedures:
- Electrodiagnostic tests- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve conduction velocity (NCV)
- Blood & Urine studies
- Spinal tap
- X-rays including MRI
- Myleogram of cervical spine
- Muscle and/or nerve biopsy
- A thorough neurological examination
These tests are done at the discretion of the physician, usually based on the results of other diagnostic tests and the physical examination. There are several diseases that have some of the same symptoms as ALS, and most of these conditions are treatable.
What are the treatments for ALS?
Treatment of ALS can be done with physiotherapy, focusing on stretching and daily range of motion (ROM) exercises. Our physiotherapists at Triangle will focus on the emphasis of energy conservation and teach patients and caregivers methods for performing safe, efficient transfers. They can also provide instruction for strengthening exercise programs.
In one study, individualized, moderate-intensity, endurance-type exercises for the trunk and limbs performed 15 minutes twice daily were shown to significantly reduce spasticity as measured by the Ashworth scale. At Triangle, we may have to recommend wheelchairs to anticipate the patient’s future needs. Initially, a lightweight wheelchair should be rented, with future plans to purchase a heavier chair when the patient is no longer able to ambulate. Modifications will be recommended on the basis of the patient’s condition and tolerance for gadgets.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Physiotherapy is a crucial component in managing ALS, helping to maintain mobility, reduce discomfort, and improve quality of life. For those seeking specialized physiotherapy services to support ALS management, there are clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics offer expert care and personalized treatment plans tailored to the needs of individuals living with ALS.
Are you feeling a bit of a pain in the neck lately? Does your neck feel stiff, painful, tender, or are you not able to turn it and move around as much as you used to? You may be a victim of whiplash.
What is Whiplash?
Whiplash is most associated with traumatic events involving sudden acceleration-deceleration forces mainly on the neck. It can affect a variety of issues pertaining to your muscles, joints, bones, ligaments, discs, and nerves. Whiplash is mostly associated with car accidents, but other causes may include roller-coasters, bungee jumping, or a sports-related condition.

What are the symptoms of Whiplash?
Symptoms and severity of whiplash can vary significantly between people. The most commonly reported symptom is neck pain or stiffness. This can occur anywhere from immediately after the injury to several days after.
Symptoms may include:
- Neck pain or stiffness
- Headache
- Shoulder pain, arm pain, or upper back pain
- Dizziness
- Altered sensation
- Weakness
- Visual disturbances
- Hearing difficulties
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- Difficulty swallowing
How can Whiplash be treated?
Fortunately, most people recover from the pain and stiffness associated with whiplash in a matter of weeks, but some cases require longer recovery time and treatment from a physiotherapist. Healing time varies with the level of tissue damage and promptness of treatment. Most whiplash patients will start to feel better within a few weeks of the injury from physiotherapy treatment. At Triangle Physiotherapy, our physiotherapists will aim to:
- Reduce neck pain, headaches, and inflammation
- Normalise joint range of motion
- Gain strength in your neck
- Strengthen your upper back muscles
- Improve neck posture
- Normalize your muscles lengths and rest muscle tension
- Resolve any deficit in neural tissue extensibility
- Improve neck proprioception, fine motor control, and balance
- Improve your ability to cope with everyday activities
- Minimize your chance of future neck pain or disability
Whiplash injuries can take from a few days to several months to rehabilitate. Just as the symptoms and severity of whiplash can vary from person to person, so can the recovery time. The large majority of whiplash sufferers do recover with actively guided treatment. Depression and trauma-related anxiety may impact the healing process of whiplash. Please consult with a qualified health professional to give yourself the best chance of recovery.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Recovering from whiplash requires a comprehensive physiotherapy approach to restore mobility, reduce pain, and improve strength. If you are looking for professional physiotherapy services to help manage whiplash recovery, consider clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics provide expert care and tailored treatment plans to help you get back to your normal activities safely and effectively.
What is incontinence?
Incontinence can be a fairly sensitive or embarrassing subject to those who suffer from it. Incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine or feces from the bladder and bowel. But know this, incontinence is an ACCIDENT, it is something that is uncontrollable and can happen to any expecting mother.
Urinary incontinence affects around 10-13 million men and women, and it is twice as common in women as in men. Anthony Atala, MD, said, “I would say virtually all pregnant women experience some type of incontinence”. Incontinence should not rule your pregnancy or your life.

What does pregnancy have to do with incontinence?
Pregnancy can interfere with the normal way your urethra relaxes and contracts. You are able to urinate when the muscles around your urethra relax, allowing urine to pass through your bladder and out of your body. After urination, the muscles around your urethra contract, holding off urine flow until your body is ready to urinate again. Hormone changes during pregnancy and the additional pressure on the bladder from your uterus can cause stress incontinence. Mothers who are experiencing stress incontinence may urinate whilst sneezing, walking, coughing, laughing, running, and during exercise. Women who have a family history of incontinence, gain more weight than recommended during pregnancy, and are over the age of 35 are at higher risk of experiencing incontinence.
How do I avoid incontinence during pregnancy?
There are numerous ways to avoid pregnancy incontinence, along with visiting a pelvic health physiotherapist, to avoid leakage.
- Schedule your bathroom breaks. Try to make it to the toilet at least every two hours, as when pregnant, women urinate more frequently.
- If you think your bathroom visits are proper, try practicing kegel exercises. Kegels help strengthen the pelvic floor. Practicing a kegel is the same as stopping the flow of urine within your urethra. Contract your muscles to the count of ten and then release. Repeat exercises ten to twenty times in a row two to three times a day. The average time to see results is four to eight weeks of regular practice.
- Watching your weight while carrying has a significant effect on developing incontinence. Women who gain more weight during pregnancy are more likely to experience incontinence. Combining these factors with your pelvic physiotherapist will lower your risk of developing incontinence during your pregnancy, allowing your experience to be worry-free.
If you are still unsure or worried about the risk of incontinence during your pregnancy, contact a pelvic floor physiotherapist at Triangle Physiotherapy. Triangle Physiotherapy has eight convenient locations: Etobicoke, Oakville, Mississauga, North York, Toronto, and King West. At Triangle Physiotherapy, our team is compromised of professionals who love what they do. Triangle staff will ensure that you will have a safe and comfortable pregnancy while in their care, and will help get your pregnancy back on track and in your hands.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Incontinence during pregnancy can be challenging, but physiotherapy can help manage symptoms and improve pelvic floor strength. If you’re looking for specialized physiotherapy services to support incontinence management, consider clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics offer expert care and personalized treatment plans to help you stay comfortable and healthy throughout your pregnancy journey.
Back pain? You are not alone. Over 80 % of Canadians will experience back pain atleast once in their life. However, about 90% of back pain is not caused by any serious injury or disease. That being said, it doesn’t make it any less painful or debilitating. For a lot of people, traditional physiotherapy and massage therapy works well, but if it doesn’t don’t be discouraged… there is still hope! As a physiotherapist myself that has suffered from back pain, yoga has changed my life! It has helped me increase my flexibility, core strength, improve my posture and overall enhance my life.

Why Yoga?
1. Stretching
The spine is meant to move in lots of different ways. If we don’t move or stretch it gets stiff and rusty. This can start to cause some aches and pains which can get worse over time if it is not addressed. It can also make you more susceptible to becoming that 10% of people that suffer from a more significant injury. “But it hurts to move,” you say… Yes, oftentimes it does cause some discomfort to move especially if you haven’t tried to move in certain directions for a long time but science now tells us that it is far better for your back to move in a controlled and safe way rather than not moving. This is where yoga can help…. Yoga is a very gentle and proven way to help loosen up your back and make sure it moves smoothly within all its normal ranges of motion.
2. Strengthening
All of us have heard that if you have back pain you should strengthen your core, right? Yoga creates a great way of functionally strengthening your core. What that means is instead of isolating certain muscles, the yoga poses (asanas) that you are taken through will help you learn how to use all the muscles of your core together (including your diaphragm and pelvic floor!). If you continue strengthening your core on the ground then your body doesn’t get stronger in the positions it needs for everyday activities. For example, vacuuming your house requires you to be slightly bent over and pushing/pulling. Yoga poses that can simulate will force you to strengthen your core muscles in the positions it is needed so that once you get stronger, vacuuming won’t be painful.
There are many other benefits of yoga that can help with pain from breathing techniques (if it works for women in labour then it can work for your back pain too!) Also, mind-body awareness and connection is developed to help you realize if there are postures or positions that you are doing out of habit that you don’t realize can be harming your body. Yoga can correct imbalances of your musculoskeletal system that you didn’t even know existed.
Click HERE to book an appointment with a physiotherapist at one of our eight locations.
- Physiotherapy Etobicoke – Triangle Physiotherapy Etobicoke
- Oakville Physiotherapy Clinic – Triangle Physiotherapy Oakville
- Physiotherapy North York – Triangle Physiotherapy North York
- Mississauga Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Mississauga
- Downtown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy King West
- Uptown Physiotherapy Clinics – Triangle Physiotherapy Lawrence Park
- Physiotherapy Clinic Downtown Toronto – Triangle Physiotherapy Queens Quay
- Physiotherapy Clinics Mississauga – Triangle Physiotherapy Erin Mills
Yoga can be a powerful tool for improving back health, enhancing flexibility, and reducing pain when combined with physiotherapy. For those seeking professional physiotherapy services to complement their yoga practice, there are clinics in physiotherapy Etobicoke, Oakville, North York, Toronto, Lawrence Park, Queens Quay, Erin Mills, Mississauga, and Liberty Village. These clinics offer expert care and personalized treatment plans to help you maintain a healthy back and overall well-being.